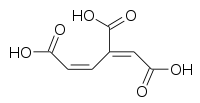
3-Carboxy-cis,cis-muconic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1E,3Z)-Buta-1,3-diene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1116-26-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| 3DMet | B00251 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:15749 |
| ChemSpider | 4444085 |
| KEGG | C01163 |
| PubChem | 5280404 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H6O6 | |
| Molar mass | 186.12 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.25 g cm−3 |
| 0.40 D | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Carboxy-cis,cis-muconic acid is a metabolite of the catechin degradation by Bradyrhizobium japonicum.[2]
The enzyme 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate cycloisomerase uses 2-carboxy-2,5-dihydro-5-oxofuran-2-acetate to produce 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate.
The enzyme carboxy-cis,cis-muconate cyclase uses 3-carboxy-2,5-dihydro-5-oxofuran-2-acetate to produce 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate.
The enzyme protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase uses 3,4-dihydroxybenzoate and O2 to produce 3-carboxy-cis,cis-muconate.
References
- ↑ "(1E,3Z)-buta-1,3-diene-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ↑ Waheeta Hopper and A. Mahadevan (1997). "Degradation of catechin by Bradyrhizobium japonicum". Biodegradation. 8 (3): 159–165. doi:10.1023/A:1008254812074.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/24/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.