2-Oleoylglycerol
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
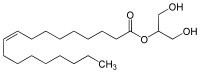
| IUPAC name
1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-yl (Z)-octadec-9-enoate | |
| Other names
2-Monoolein | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3443-84-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 4478086 |
| 5112 | |
| PubChem | 5319879 |
| UNII | 9A2389K694 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H40O4 | |
| Molar mass | 356.55 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.958 g/cm3 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | >113.0 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Oleoylglycerol (2OG) is a monoacylglycerol that is found in biologic tissues. Its synthesis is derived from diacylglycerol precursors. It is metabolized to oleic acid and glycerol primarily by the enzyme monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL).[1] In 2011, 2OG was found to be an endogenous ligand to GPR119.[2] 2OG has been shown to increase glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) levels following administration to the small intestine.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Dinh, T. P.; Carpenter, D.; Leslie, F. M.; Freund, T. F.; Katona, I.; Sensi, S. L.; Kathuria, S.; Piomelli, D. (2002). "Brain monoglyceride lipase participating in endocannabinoid inactivation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 99 (16): 10819–10824. doi:10.1073/pnas.152334899. PMC 125056
 . PMID 12136125.
. PMID 12136125. - 1 2 Hansen, K. B.; Rosenkilde, M. M.; Knop, F. K.; Wellner, N.; Diep, T. A.; Rehfeld, J. F.; Andersen, U. B.; Holst, J. J.; Hansen, H. S. (2011). "2-Oleoyl Glycerol is a GPR119 Agonist and Signals GLP-1 Release in Humans". Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 96 (9): E1409–E1417. doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0647. PMID 21778222.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/2/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.