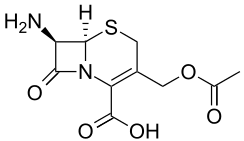
7-ACA
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-(Acetyloxymethyl)-7-amino-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
7-Aminocephalosporinic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 957-68-6 | |
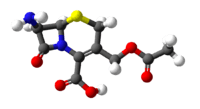
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| 3DMet | B02139 |
| Abbreviations | 7-ACA |
| 622637, 8919572 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:2255 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1161449 |
| ChemSpider | 390087 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.259 |
| EC Number | 213-485-0 |
| KEGG | C07756 |
| MeSH | 7-Aminocephalosporanic+acid |
| PubChem | 483168 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12N2O5S | |
| Molar mass | 272.27 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K)[1] |
| log P | -1.87 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.59 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 11.41 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | Danger |
| H317, H334 | |
| P261, P280, P342+311 | |
| EU classification (DSD) |
|
| R-phrases | R42/43[1] |
| S-phrases | S22 S36/37[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
7-ACA (7-aminocephalosporanic acid) is the core chemical structure for the synthesis of cephalosporin antibiotics and intermediates. It can be obtained by chemoenzymatic hydrolysis of cephalosporin C.[2][3]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 7-ACA at Chemblink
- ↑ Tan, Qiang; Zhang, Yewang; Song, Qingxun; Wei, Dongzhi (2010). "Single-pot conversion of cephalosporin C to 7-aminocephalosporanic acid in the absence of hydrogen peroxide". World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology. 26 (1): 145–152. doi:10.1007/s11274-009-0153-9.
- ↑ Tan, Qiang; Song, Qingxun; Wei, Dongzhi (2006). "Single-pot conversion of cephalosporin C to 7-aminocephalosporanic acid using cell-bound and support-bound enzymes". Enzyme and Microbial Technology. 39 (5): 1166–1172. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.02.028.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/4/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.