AGM-84H/K SLAM-ER
| AGM-84 SLAM-ER (Standoff Land Attack Missile - Expanded Response) | |
|---|---|
|
An F/A-18 Hornet carrying one SLAM-ER missile (top) and two AN/AWW-13 datalink pods (bottom) | |
| Type | Long-range, air-launched, precision cruise missile |
| Place of origin | United States of America |
| Service history | |
| In service | 2000–present[1] |
| Used by | United States and its allies |
| Wars | |
| Production history | |
| Manufacturer | Boeing Company[1] |
| Unit cost | $500,000[1] |
| Variants |
AGM-84H (2000–2002)[2] AGM-84K (2002–present) |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 674.5 kg (1,487 lb)[1] |
| Length | 4.37 m (14.3 ft)[1] |
| Diameter | 34.3 cm (13.5 in)[1] |
|
| |
| Engine |
Teledyne Turbojet > 600 lbs thrust |
| Wingspan | 2.2 m (7.2 ft)[1] |
Operational range | 270 kilometres (170 mi)[3] |
| Speed | 855 km/h (531 mph, 0.698 mach)[3] |
Guidance system |
inertial navigation system supplemented by the Global Positioning System (GPS)[1] infrared homing terminal guidance[1] command guidance data link to controlling aircraft[1] DSMAC Automatic Target Acquisition (ATA)[2] |
Launch platform |
F/A-18C/D Hornet[1] F/A-18E/F Super Hornet[1] F-15E Strike Eagle P-3C Orion[1] P-8 Poseidon [1] and allied air forces, including the South Korean Air Force and the Turkish Air Force |
The AGM-84H/K SLAM-ER (Standoff Land Attack Missile-Expanded Response) is a precision-guided, air-launched cruise missile produced by Boeing Defense, Space & Security for the United States Armed Forces and their allies. Developed from the AGM-84E SLAM (Standoff Land Attack Missile) (itself developed by Boeing Integrated Defense Systems from the McDonnell Douglas Harpoon antiship missile), the SLAM-ER is capable of attacking land and sea targets at medium-to-long-ranges (155 nautical miles/250 km maximum). The SLAM-ER relies on the Global Positioning System (GPS) and infrared imaging for its navigation and control, and it can strike both moving and stationary targets.
The SLAM-ER, can be remotely controlled while in flight, and it can be redirected to another target after launch if the original target has already been destroyed, or is no longer considered to be dangerous (command guidance).[1][4] The SLAM-ER is a very accurate weapon; as of 2009 it had the best circular error probable (CEP) of any missile used by the U.S. Navy.[5]
History
The SLAM-ER obtained initial operating capability in June 2000. A total of three SLAM-ER missiles were fired by the U.S. Navy during the Iraq War,[6] and the missile was also used during Operation Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan.
The General Electric Company provides an Automatic Target Recognition Unit (ATRU) for the SLAM-ER[7] that processes prelaunch and postlaunch targeting data, allows high speed video comparison (DSMAC), and enables the SLAM-ER to be used in a true "fire and forget" manner. It also includes a "man-in-the-loop" mode, where the pilot or weapons system officer can designate the point of impact precisely, even if the target has no distinguishing infrared signature.[4] It can be launched and controlled by a variety of aircraft including the F/A-18 Hornet, F/A-18 Super Hornet, and P-3C Orion, as well as by the U.S. Air Force's F-15E Strike Eagle. Before the retirement of the S-3B Viking, it was also able to launch and control the SLAM-ER, and it is anticipated that the U.S. Navy's new land-based patrol plane, the Boeing P-8 Poseidon will carry the SLAM-ER as well.[4] The South Korean air force's version of the F-15E Strike Eagle, the F-15K Slam Eagle, has been capable of launching and controlling the SLAM-ER since 2006 in test exercises.[8]
Operators
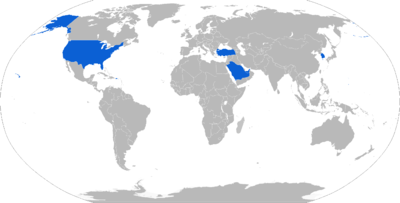
Current operators
References
- 1 2 Parsch, Andreas. "AGM/RGM/UGM-84." Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles. 2008. Web. 22 July 2013.
- 1 2 "AGM-84 Harpoon / SLAM [Stand-Off Land Attack Missile]." Military Analysis Network. Federation of American Scientists, 22 July 2013. Web. 22 July 2013.
- 1 2 3 Boeing SLAM-ER Home: Overview
- ↑ The US Navy - Fact File: SLAM-ER Missile
- ↑ Cordesman, Anthony H. The Iraq War: Strategy, Tactics, and Military Lessons. (Washington: CSIS Press, 2003) 296.
- ↑ GE - Automatic Target Recognition Unit (ATRU)
- ↑ Boeing: "F-15K Makes History with SLAM-ER Release". St. Louis: 27 Mar 2006. Web. Accessed 15 Jan 2013.
- 1 2 "Washington Beef up the Gulf States with 10,000 Strike Weapons Worth US$10 Billion". Defense Update. 17 October 2013. Retrieved 21 October 2013.
- ↑ "Republic of Korea Chooses Boeing SLAM-ER Missile". Boeing.
- ↑ "SLAM-ER and Harpoon Foreign Military Sales".
External links
- Boeing (McDonnell-Douglas) AGM/RGM/UGM-84 Harpoon, Designation Systems
- SLAM-ER, Boeing
