Acedapsone
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names |
Rodilone Hansolar |
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
77-46-3 |
| PubChem (CID) | 6477 |
| ChemSpider |
6232 |
| UNII |
0GZ72U84TN |
| KEGG |
D02751 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL154166 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
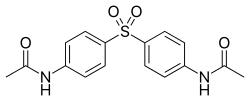
| Formula | C16H16N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 332.374 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Melting point | 290 °C (554 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Acedapsone (INN) is an antimicrobial drug, which also has antimalarial activity.
Acedapsone, or 1399 F, is a diacetyl compound, derived from dapsone. It was synthesized and developed in 1937 by Ernest Fourneau and his team in the pharmaceutical chemistry laboratory of Pasteur Institute,[1] and it was marketed as Rodilone by the Rhône-Poulenc company.[2]
It is a long-acting prodrug of dapsone. It is used for treating leprosy.[3]
It crystallises as pale yellow needles from diethyl ether, and as leaflets from dilute ethanol. It is slightly soluble in water.
Synthesis
Acedapsone is conveniently prepared by acetylation of dapsone.
References
- ↑ (French) E. Fourneau, J. et Th. Tréfouël, F. Nitti, D. Bovet, « Chimiothérapie de l'infection pneumococcique par la di-(p-acétylaminophényl)-sulfone (1399 F) », C. r. Acad. sci., vol. 205, 1937, pp. 299-300.
- ↑ (French) Marcel Delépine, Ernest Fourneau (1872–1949) : Sa vie et son œuvre, extrait du Bulletin de la Société chimique de France, Masson et Cie, 1950, pp. 64-67.
- ↑ Shaw IN, Christian M, Jesudasan K, Kurian N, Rao GS (June 2003). "Effectiveness of multidrug therapy in multibacillary leprosy: a long-term follow-up of 34 multibacillary leprosy patients treated with multidrug regimens till skin smear negativity". Lepr Rev. 74 (2): 141–7. PMID 12862255.
- ↑ Elslager, Edward F.; Gavrilis, Zoe B.; Phillips, Annette A.; Worth, Donald F. (1969). "Repository drugs. IV. 4',4 ' ' ' -Sulfonylbisacetanilide (acedapsone, DADDS) and related sulfanilylanilides with prolonged antimalarial and antileprotic action". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 12 (3): 357. doi:10.1021/jm00303a003. PMID 4892242.
- ↑ Raiziss, G. W.; Clemence, L. W.; Severac, M.; Moetsch, J. C. (1939). "Chemistry and Chemotherapy of 4,4′-Diaminodiphenylsulfone, 4-Amino-4′-hydroxy-diphenylsulfone and Related Compounds". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 61 (10): 2763. doi:10.1021/ja01265a060.
- ↑ Fromm, E.; Wittmann, J. (1908). "Derivate desp-Nitrothiophenols". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 41 (2): 2264. doi:10.1002/cber.190804102131.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/5/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
