Deshbhushan
| Acharya Shri Deshbhushan Ji Maharaj | |
|---|---|
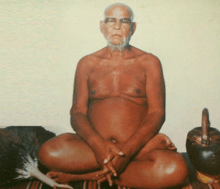 Acharya Shri Deshbhushan ji | |
| Religion | Jainism |
| Sect | Digambara |
| Personal | |
| Born |
Balagauda 1905 Kothali, Karnataka |
| Died |
28 May 1987 (aged 81) Kothali, Karnataka |
| Parents |
|
| Senior posting | |
| Successor | Acharya Vidyananda |
| Religious career | |
| Ascetics initiated | Acharya Vidyananda |
| Initiation |
1936 Kunthalgiri, Maharashtra by Acharya Jaikirti ji |
| Part of a series on |
| Jainism |
|---|
 |
|
Jain prayers |
|
Ethics |
|
Major figures |
|
Major sects |
|
Festivals |
|
Pilgrimages |
|
|
Acharya Deshbhushan (Hindi: आचार्य देशभूषण ) was a Digambara Jain Acharya of 20th century who composed and translated many kannad scriptures to Hindi. He initiated Acharya Vidyananda. He is renowned for his remarkable translations of Kannada scriptures to sanskrit and Hindi. He is the first Digambara Acharya to visit and address the Indian Parliament in the year 1974 along with the Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
Early life
Born on Mārgaśirṣa Śukla Pakṣa Pratipat of the year 1905 in Kothli district of Belgam, Karnataka at a wealthy Kshatriya family of Sh. Satya Gauda and Akka Devi Patil (Parents), Sh. Bala Gauda Patil (Balappa) completed his primary and secondary education in Hindi, English, Marathi and Kannada medium at Sadalga and Secondary Education at Gilginchi Artal High School, Belgaum with his best friend Dr. A.N. Upadhye. Both went on to receive their Bachelor of Arts with Honours from Bombay University in Sanskrit and Prakrit languages and later moved to Pune for Post-Graduation and joined Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute. At this point while Sh. A.N. Upadhye decided to join as Lecturer of Prakrit at Rajaram College, Kolhapur to meet up the social and financial obligations. Bala Gauda decided to continue his further research with the help of original references which were kept intact in the custody of Jain Temples where he came in contact with Acharya Jayakirti ji and got deeply influenced by his lectures.
Initiation as Ailak
Influenced by Acharya Jayakirti ji, Bala Gauda requested him to join his group or Jain Sangha. Looking at his young age and family background Acharya ji explained him about the traditional way of learning along with the Pratima's or the vow's which every student have to practice and follow in order to get associated with them. Observing his determination and zeal towards his quest for the right knowledge as per Jain philosophy Acharya Jayakirti ji initiated him as Ailak or individual researcher to be known as Ailak Deshbhushan in the early 1930s and kept him under observation to be elevated as Jain Muni.
Initiation as Muni
Ultimately, after six years of strict observations under his Jain Sangha. Acharya Jayakirti elevated him as Muni Deshbhushan on 8 March 1936 at the famous Kunthalgiri Jain temple in Maharashtra to further research and explore his ultimate quest for the right wisdom.
Accession & Eminence
Samayaktva Chudamani Acharya Ratna Deshbhushan 1981
Entire Jain community unanimously entitled him as Samayaktva Chudamani Acharya Ratna Shri Deshbhushan ji Muni Maharaja on the event of successfully organizing and conducting the Mahamastakabhisheka at Shravanabelagola in the year 1981.
Acharya Ratna Deshbhushan 1961
Entire Jain community around Delhi organized a huge event under the banner of Delhi Jain Samaj and entitled him as Acharya Ratna Deshbhushan ji Muni Maharaja in the year 1961.
Acharya Deshbhushan 1948
He was entitled as Acharya Shri Deshbhushan ji Muni Maharaja by Acharya Shri PaayaSagar ji Muni Maharaja under the guidance of Chatuh Sangha in the year 1948 during a huge event organised at Surat in Gujarat.
Muni Deshbhushan 1936
He was initiated as Shri Deshbhushan ji Muni Maharaja by Acahrya Shri JayaKirti ji Muniraj on 8 March 1936 at Shri Digambra Jain Siddha Kshetra located at Kunthalgiri, Maharashtra.
Initiation & Elevation
He had initiated and elevated some of the most prominent of Jain monks and Nuns:
- Acaharya Vidyananda
- Ganini Pramukha Aryika Shri Gyanmati Mataji
Chaturmas
- Mangur, Karnataka 1936
- Mangur, Karnataka 1937
- Shravanabelagola 1938
- Nagpur 1939
- Kolhapur 1940
- Shamanewadi 1941
- Bhoj, Madhya Pradesh 1942
- Borgaon Manju 1943
- Pattankudi 1944
- Stavanidhi, Nipani 1945
- Galatga 1946
- Varanasi 1947
- Surat 1948
- Arrah 1949
- Arrah 1950
- Lucknow 1951
- Barabanki 1952
- Tikait Nagar 1953
- Jaipur 1954
- Delhi 1955
- Delhi 1956
- Delhi 1957
- Kolkata 1958
- Kolhapur 1959
- Maan gaon, Pune 1960
- Maan gaon, Pune 1961
- Abdul Lat, Maharashtra 1962
- Delhi 1963
- Jaipur 1964
- Delhi 1965
- Jaipur 1966
- Stavanidhi, Nipani 1967
- Belgaum 1968
- Kolhapur 1969
- Bhoj, Madhya Pradesh 1970
- Jaipur 1971
- Delhi 1972
- Delhi 1973
- Delhi 1974
- Kothli, Maharashtra 1975
- Kothli, Maharashtra 1976
- Kothli, Maharashtra 1977
- Bhoj, Madhya Pradesh 1978
- Shamanewadi 1979
- Kothli, Maharashtra 1980
- Kothli, Maharashtra 1981
- Jaipur 1982
- Kothli, Maharashtra 1983
- Kothli, Maharashtra 1984
- Kothli, Maharashtra 1985
- Sadalga 1986
Achievements
- Acharya Deshbhushan urged for the establishment of Chulagiri in 1953.[1]
- Acharya Deshbhushan Ayurvedic Medical College, Shamanewadi, Karnataka on 13 June 1951 [2][3]
Gallery
 Acharya Deshbhusan Parshvakirti
Acharya Deshbhusan Parshvakirti Acharya Deshbhusan (right) with Indira Gandhi (left) at Indian parliament in 1974
Acharya Deshbhusan (right) with Indira Gandhi (left) at Indian parliament in 1974 Acharya Deshbhushan (left) and Prime Minister Lal Bahadur Shastri (right)
Acharya Deshbhushan (left) and Prime Minister Lal Bahadur Shastri (right)
Notes
References
- Cort, John (2010) [1953], Framing the Jina: Narratives of Icons and Idols in Jain History, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-538502-1
- Aacharya Shri 108 Deshbhushan Ji Maharaj
- Passions of Nation & Community Bahubali Affair