Adelaide Educational Institution
Adelaide Educational Institution was a privately run non-sectarian academy for boys in Adelaide founded in 1852 by John Lorenzo Young[1][2] "He avoided rote learning, punishment and religious instruction, but taught moral philosophy, physiology, political economy and mechanical drawing ... (and) surveying on field trips".[3] The school closed when he retired in 1880. By this time Prince Alfred College had emerged as a strong alternative for sons of well-to-do Protestants.
History
In 1852 Young opened a school with two, then three pupils (Hubert Giles,[4] Caleb Peacock and John Partridge) in the "Peacock Chapel"[5] lent by Mr Peacock[4] in the rear of the (Congregational) Ebenezer Chapel in Ebenezer Place,[3] off the east end of Rundle Street. The two grew to seventeen at years end.[6] and he was advertising for evening classes in Geometry and Arithmetic, apply between 6 and 7pm at Stephens Place,[7] off the west end of Rundle Street. Fees for day students were 10 guineas (₤10/10/-) per annum, (payable quarterly in advance). Facilities were available for boarding.[8] His residence was also located on Stephens Place.[9] By December 1855 the school had 107 students,[6] perhaps close to 200 in 1857,[4] 130 in 1862,[10] 133 in 1868.
Next venue was the Congregational chapel in Freeman Street (now that section of Gawler Place between Pirie and Flinders Streets).[11]
In 1872 new premises were built at Parkside in Young Street, which had been named after the headmaster.[2]
"Many of Young's pupils later attained positions of public and professional importance in the province and attested the value of the inspiration he had given. Ex-scholars included Caleb Peacock, William Bickford, Walter Samson, (Herschel) Babbage, Elias Solomon, W. P. Auld and Charles Kingston, premier and federationist. An Old Scholars' Association was formed and when the school closed in 1880 on Young's retirement, he was presented with 336 gold sovereigns and many grateful testimonials to his genial, sympathetic counselling."[2]
"He is commemorated by scholarships at the University of Adelaide for research in political economy and for general research."[2]
E.S. Hughes recalled, in a letter to The Advertiser, a tableau of life during his time at the institution. "About that time I was at the late JL Young's - at Young's Lane, as it was then called - Parkside, as a boarder, and with three other strong Churchmen used to attend St Paul's Church, Flinders Street. Dear old Dean Russell, of blessed memory, wished us to be confirmed; and, as our parents agreed, we escaped from lessons two nights a week to attend classes. Consequently we had a good time going home afterwards, on some occasions climbing the posts and 'dousing the glim' as the sailors say, performing other boyish tricks, and arriving very late because of such 'awfully long classes'"[12]
Education in Early South Australia
(Taken from Geoffrey H. Manning's A Colonial Experience)[13]
- From a welter of amateur establishments emerged two institutions, one of which did noble service to two generations, the other the germ of one of the colony's greatest denominational schools today. The first was John Lorenzo Young's Adelaide Educational Institute, which in its peregrinations from a room at the rear of Ebenezer Chapel (now built over by the East End Market), by way of Stephens Place and Gawler Place, to a final home at Young Street, Parkside, educated 1,500 young South Australians many of later distinction – Caleb Peacock, Adelaide's first native-born Mayor, Charles Cameron Kingston, the dominating figure on the colony's political horizon and Joseph Verco, doyen of our medical fraternity. The other institution was the crib in which St Peter's College was created.
John L Young
John Lorenzo Young (1826–1881) was a Londoner, the son of John Tonkin Young, a builder from Veryan, Cornwall.[14][15][16]
He received a non-sectarian education in Europe and England, with emphasis on mathematics and the newly developed sciences of geology, physics and chemistry. He worked in Cornwall on railway and mining construction then left for Adelaide in 1850.[3] on the ship "Panama", arriving on 31 October 1850. He joined the rush to the Victorian goldfields but soon returned.[15]
In 1851 he was appointed second master at the newly opened South Australian High School,[17] under Headmaster Charles Gregory Feinaigle (1817? – 10 March 1880), but the venture failed by the end of the year. The following year Young was persuaded by a group of Congregationalists to open his own school at the rear of the old chapel in Ebenezer Street off Rundle Street East, and soon moved to larger premises in Stephens Place.[15][18] His brother, Oliver Young, held classes for some time,[19] and acted as headmaster in 1860 while J. L. Young was away on recuperation leave.
In 1861 he built the large two-storey "Young House" in Parkside, which was used both as his private residence and as a student boarding house. He then commissioned architects Wright and Hamilton to design and oversee building of a schoolhouse next door. (Edmund Wright had designed many prominent Adelaide buildings including the Town Hall).[20] In 1871 he was able to relinquish the Freeman Street premises.
John retired in 1880 and closed the school, with the intention of joining his wife and large family who were visiting brother Oliver and his father in Veryan, in Cornwall. On his retirement, a testimonial was held 17 December 1880 by his old scholars, and he was presentated with a purse of sovereigns.[21] His 16-room residence, with schoolhouse and various other houses on Young Street,[22] after several auction attempts in February 1881, was eventually purchased by Alfred Allen Simpson (who coincidently had also purchased the Gawler Place school property).[11] The two Parkside buildings, at 61-71 Young Street, were sold by Alfred A., Fred N. and Violet Laura Simpson to Mr. C. O. A. Lapidge in 1922.[20] "Young House" has since been demolished but the heritage-listed schoolhouse still stands.
He embarked on the steamer John Elder in 1881 to visit England (where his father was still living), his family having preceded him, but died on 26 July 1881 while crossing the Red Sea. He was buried at sea.[15] Martha returned to Adelaide, at first living in Kent Town then settled in Glenelg.[23] She died 6 April 1887 aged 57.[24]
Fred W. Sims, formerly Deputy Registrar of Companies in the Supreme Court, wrote in The Advertiser: I could tell you quite a lot about John L. Young's school— 'dear old Johnny', as we used to call him ... Mr. Young possessed, among his other fine qualities, the saving grace of humor. It is recorded that his first two pupils were Caleb Peacock and John Partridge. He remarked at the time that, whether be met with success or not as a schoolmaster, he would anyway die "game".[25]
Classes and Curriculum
In its first stage of the school's history, Junior (or Third) Class consisted of boys from 7 to 10 years, Science being a chief subject with (although a non-sectarian school) a little religious insight. A small but significant number of students were Orthodox Jews (e.g. Solomon family). No homework was set.
In the Second Class, homework was encouraged and after five hours of schoolwork the more industrious students would voluntarily turn in up to four long essays a week.
In Senior or First Class, subjects covered included political economy, history, .[26]
Masters
Other academics at the Institution included:
- Thomas Boutflower Bennett (1808- 14 September 1894), nicknamed "Tiger",[27] helped run the school, taught English and bookkeeping, later at St. Peter's College. His headstone in Moonta cemetery mentions SPC but not AEI.[28] His son J. W. O. Bennett was killed on the Goyder expedition of 1869.
- Thomas Caterer (around 1854) went on to found the notable Norwood Grammar School
- John Howard Clark taught occasionally
- Rev. F. W. Cox drawing 1864, 1866
- Edward Dewhirst
- C. J. Fox taught junior Latin 1870, then all levels
- Henry Greffrath taught French and German from beginning 1852 to mid-1863 then St. Peter's College (overlap?). Left for Jena, Germany in 1864.
- Theodore Hack may have been a teacher
- Wilton Hack succeeded Charles Hill as drawing teacher 1868[29] W. Hack also taught drawing at Norwood Grammar and St. Peters College.
- A teacher named Harrison, called "Cocky" by students (as was Oliver Young); described as young and pimply, was sacked for drunkenness at a June prizegiving, possibly 1856.[30]
- Charles Hill taught drawing[31]
- P. T. Hill taught writing and arithmetic NOT drawing[29]
- G. R. Irwine (d. 7 October 1871)[32] taught Latin, Greek and English.
- Dr Carl Heinrich Loessel (Lössel) taught French, German in 1863, 1864 ([33] is interesting)
- Adolph Emile Marval taught French 1866, also at St Peters College. Mme. Caroline Emma Marval opened a Ladies' College.
- F. H. Needham R.N. taught mathematics, Latin 1861
- G. Needham (1805 – 19 March 1894)[34] (no relation though both taught Latin – [30])
- Hamilton Charles Palmer (died 19 January 1880)
- A lawyer arrived from England ca. 1857, based in Kapunda
- Brother of Charles Edwin Palmer (Glenelg Congregational minister)
- Wrote newspaper articles as "Templar"
- Classics master 1861 [35]
- J. R. P. Parsons
- Rev. Canon Poole (Frederic Slaney Poole) taught advanced Latin 1870
- H. von Schleinitz taught French, German 1865 to 1873 (also at St Peter's College, Norwood Grammar).
- Educated at universities of Leipzig and "Greisewalde" (perhaps Greifswald).[36]
- He arrived in Adelaide on the "Pauline" from Bremen on 9 December 1849.
- In 1851 he founded a German School in Freeman Street.[37] Teachers at his school included Messrs Hansen, Klette and Nootnagel. He left in 1852.[38]
- For several years he was clerk to C. Schilling, landbroker of Gawler Place.[39]
- 1864 he was with St Peter's College and offering private tuition at his North Terrace (east) home.[40]
- 1874 he's replaced by Jung at SPC.[41] Then no mention to 1876 when he's advertising for anything anywhere.
- Rev. Thomas Smellie (pronounced "smiley") Presbyterian minister arrived Adelaide 1861, registered to grant marriage licences 1862, taught Latin at AEI from 1863 to 1866 and at Leslie's school Alberton 1864. Founded Gawler Academy 1868 returned to Britain 1872
- Uren[42]
- Oliver Young (J. L. Young's brother) taught drawing, ran the school in 1860 during his brother's absence. Oliver, whom the students called "Cocky", though not to his face, suffered from a deformed back.[43] He returned to Cornwall in 1866,[44] and never married.[45]
Timeline
- 1852 School opened in Ebenezer Place with two students Caleb Peacock and John Partridge, soon joined by G. T. and T. L. Cottrell, John Waterman and Richard Mahoney.[15]
- 1853 Moved to "Stephens Place" schoolroom at rear of Freeman Street Congregational chapel [46]
- 1860 JL Young in poor health, on leave in England. Oliver Young acting head for the year.[47]
- 1861 J L Young returns, buys 2 acres in Parkside. T. B. Bennett joins staff.
- 1865 Old Scholars' Association dinner[48]
- 1866 Oliver Young returns to England
- Old Scholars' Association dinner[49]
- 1867 Congregational Church moves to Stow Hall, AEI takes over Freeman Street chapel.[50]
- 1868 Pupil numbers down to 133.
- 1869 "The Star" first (and last?) issue.[53]
- Old Scholars' dinner[54]
- 1870 Old Scholars dinner[55]
- Old Scholars' annual meeting scheduled for 24 June postponed to following week due to poor attendance.[56]
- 1871 All teaching now at Young Street, Parkside.[20] T. B. Bennett resigns.
- Old Scholars' dinner [57] poor attendance
- 1872 Old Scholars' dinner [57] 12 attendees
- 1880 Presentation to Thomas Bennett [58] >30 attendees
- 1880 School closed
- 1881 JL Young died
- 1887 Mrs Young died[42]
- 1896 funeral of Caleb Peacock[59]
- 1897 Stephens Place buildings demolished [30] (a beaut reminiscence)
- 1912 Reunion[43] It was at this reunion that Peter Wood moved that a JLYoung scholarship be established.
- 1913 Second reunion
- 1914 Third reunion[60]
- 1915 Fourth reunion[61]
- 1916 Fifth reunion[62]
- 1917 Sixth reunion
- 1918 Seventh reunion
- Function for Eden Herschel Babbage 21 May 1918[63]
- 1919 Eighth reunion[64]
- 1920 Ninth reunion[65]
- 1921 Tenth reunion[66]
- 1922
- 1923
- 1924
- 1925 reunion[67][68]
Reunions
Around 1912 a group of old scholars felt it appropriate to establish a memorial for J L Young, and from 1912 held a series of annual reunion dinners to raise funds for the memorial. I need to re-read the reunion news clippings and expand this
Notable students

Robert Brazil, John Cleland & James Fitzgerald, 1875.
A remarkable number of Young's alumni became leading figures in Adelaide's businesses and public service. The following is sourced from Old Scholars reunions and other sources e.g. List of mayors and lord mayors of Adelaide

- George Agars Mildura and Renmark pioneer[69]
- W. P. Auld (Stuart Expedition 1861-1862[70])
- C. W. Babbage lapsed banker and Wanganui civic leader
- E. H. Babbage banker and Roseville, New South Wales civic leader
- Thomas William Babbage (4 October 1859 – 1945) manager of the Glenelg Railway Company, later nurseryman, not closely related
- John Barker (son of A. E. Barker)
- G. T. Bean
- J. W. O. Bennett
- Edwin S. Berry Second in Charge, Gosse's 1873 expedition to Central Australia; probably the first white man to climb Ayers Rock/Uluru.
- Harry Bickford (1843–1927)
- John Pepperell Bickford (1851–1921) cousin of Harry and William
- William Bickford (1841–1916)
- Theodore Bruce (1847–1911) mayor of Adelaide and MLC
- Fred Bullock (Mayor of Adelaide 1891-1892)[71]
- William Burford
- C. J. Carleton – son of Caroline Carleton died in Northern Territory
- W. B. Carr[72]
- John Carruthers (surveyor)[73]
- B. B. Carvosso
- (Frederick) Arthur Chapman (1864–18 September 1925) managing director Lion Brewing and Malting Company[74]
- Edward Cheetham (c. 1838 – 12 May 1866), only son of Rev. Henry Cheetham
- ?? Cherry
- Francis Howard Clark (son of John Howard Clark)
- M. L. Clark
- M(atthew) Symonds Clark (1839?-10 July 1920)[75]
- P. Howard Clark (typo for F(rancis) Howard Clark?)
- John "Jack" Cleland (of SS Gothenburg fame)[76]
- W. Cleland
- C. N. Collison
- J. F. Conigrave (1843–1920), businessman
- W(illiam) Moxon Cook (1857–1917), sports writer "Trumpator" of the Register and "Terlinga" with The Australasian.
- G. Cottrell
- T. Cottrell
- Joseph Coulls
- F. I. Crowder
- Augustus E Davies
- Edward Nicolle Dewhirst (son of Edward Dewhirst)
- George Dodgson, one of the first pioneer births and one of the first pupils. Plumber and painter of Rundle Street. Sounds hardly notable but big news at the time![77][78]
- D(avid) Walter Duffield (died 24 January 1922[79])miller and pastoralist son of Hon. Walter Duffield,[80] father of Kenneth Duffield)
- Ebenezer Finlayson
- Ned Finlayson
- John Harvey Finlayson (editor of The Register)
- Robert Kettle Finlayson
- William Finlayson
- J. T. Fitch[75]
- James Frew, Jr. (Stuart Expedition 1861-1862.[70] Frewville, South Australia named for James Frew Sr)
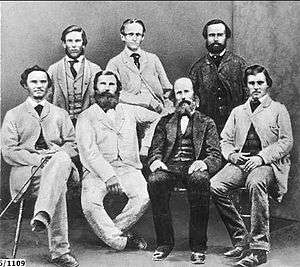 Members of John McDouall Stuart's 1861–1862 Expedition.
Members of John McDouall Stuart's 1861–1862 Expedition.
Back Row: W.P. Auld, J.W. Billiatt and F.W. Thring
Front Row: J. Frew, W.D. Kekwick, F.G. Waterhouse and S. King.
http://johnmcdouallstuart.org.au/companions - John Frew was his twin brother [30]
- E. Gall
- Gavin F(orrest) Gardner (a founder of Adelaide Stock Exchange) died 20 March 1919 [81] Gardners were sons of Rev. John Gardner [82]
- Alfred Leslie Giles (son of Henry Giles) (died 5 October 1902) cricketer, bank manager, partner in Giles and Smith
- Acland Giles (son of William Giles)
- Alfred Giles, explorer involved with Overland Telegraph Line, Dr. W. J. Browne's stations Springvale, Delamere, Newcastle Waters
- Clement Giles (son of William Giles)
- Louis Giles (son of William Giles)
- Mortimer Giles (son of William Giles), Registrar-General of Deeds at the Lands Titles Office[75]
- S. Goldsack
- W. Gollin (head of the firm of Gollin & Co., Sydney)[75]
- William Edward Goode, husband of Mrs. A. K. Goode
- D. Gordon
- William "Willie" Gosse[76]
- Dr. Charles Gosse
- H. D. Gouge [83]
- Harry Robin Guerin[84]
- John Gurr
- Charles Hack son of John Barton Hack
- Dr. R. E. Harrold[75]
- J. H. M. Hawkes (manager Fowler's "Lion" factory)
- James Symons Hawkes "Geometry Hawkes" civil engineer [85]
- A. H. Henning
- A. H. Hill
- J. Hodgson
- J. H. Horwood founder of Horwood Bagshaw Ltd.
- E. S. Hughes[75]
- F. B. Hughes
- W. A. Hughes
- H(erbert) P(arbury) Ive (1866–1942), inspector of stock at Gepps Cross abattoirs
- Samuel Joshua Jacobs
- A. Johnson
- Frank Johnson
- J. Johnson
- William Johnstone, S.M. (1843–1897)
- J. H. B. Jones
- James W. Jones (secretary to the Commissioner of Public Works)
- Robert Kelly
- S. Kidd
- Stephen King jr (Stuart Expedition 1861-1862[70]) "Kingsford"
- Charles Kingston "Charlie" later the Right Hon. C. C. Kingston[75]
- Strickland Gough "Pat" Kingston 1848-3 October 1897 (suicide) [86]
- C. J. Langley
- G. G. Legoe
- R. Lewis
- Isaac Little (manager Austral Downs station)
- Sylvanus James Magarey politician
- A. W. Marshall[75]
- H. M. Martin
- Mortimer Menpes artist[87]
- J. M. Moorhouse
- Beaumont Arnold Moulden[75]
- George Murray (later His Honour Sir George Murray, Chief Justice, Supreme Court of South Australia)[75]
- George Needham
- Alfred Odgers
- J. S. O'Halloran
- Edward Andrew Devonshire Opie associate of George Witherage Cotton and his son
- I. W. Partridge (John Partridge? perhaps b. 13 October 1841 [88])
- Caleb Peacock JL Young's first student, commencing August 1852[75]
- Henry Furneaux Peacock (25 October 1850 – 6 February 1935) Under-Treasurer of S.A. son of Wiles Peacock, winegrower
- W. Herbert Phillipps (later Sir Herbert Phillipps)
- J. R. Reid
- Samuel Reynolds
- Thomas Reynolds
- James P. Roberts (land agent)[75]
- Robert Robertson (owner Chowilla Station) [89]
- William Robertson brother of Robert
- Rev. James de Quetteville Robin
- Roland B. Robin[75]
- E. Sabine
- W. Sandover, Jnr (Perth, W.A.)[75] son of William Sandover
- Francis George Scammell (1861–1927) "In 1891/92, Mr F.G. Scammell, a solicitor ... "[90]
- Luther Robert Scammell (1858–1940) of F. H. Faulding & Co)[91]
- R. H. Scholl
- L. H. Sholl (Under-Secretary)[75]
- A Schramm
- E. Sims
- F. W. Sims[75]
- G. H. Sims
- Spencer J. Skipper wrote and drew as "Hugh Kalyptus"
- H. W. Smith?[75] H. M. Smith? [92]
- J. N. T. Smith
- R. W. Smith (Commissioner of Taxes)
- Quinton Stow Smith[93]
- Benjamin Solomon (1844–1922)
- Elias Solomon MLA, MHR (1839–1909)
- Emanuel Solomon (1855–1938)
- Judah Moss Solomon (1846–1911)
- Samuel Solomon (1848 – )
- Saul Solomon (1848–1909), the businessman not the photographer/MP
- Vaiben Louis Solomon MLA, MHR (1853-1908)
- A. Somerville
- H. Somerville
- R. K. Thomas
- James Townsend
- Charles Tucker (mayor) & M.P.[94][95]
- John Verco
- Joseph Cooke Verco (Dr. J. C. Verco, later Sir Joseph Verco)
- W. H. Wadey
- Arthur Wellington Ware (1861 – 29 January 1927) mayor of Adelaide
- Dr. Edward Willis Way[96] brother of Sir Samuel Way
- Alfred K. Whitby "Dot" [30]
- Frank Whitby of Mt. Remarkable [30]
- H. White (son of George White owner of Assembly rooms) with brother R. B. White (leader of Philharmonic Society) drowned in Gulf St Vincent boating accident July 1872 [97]
- Albert Onslow Whitington secretary of SAJC
- George Falkland Whitington (1842–1883), solicitor, brother of A. O. Whitington[98]
- Peter Whitington (1845 – ), another brother and noted public servant
- William Oswald Whitridge (son of W. W. R. Whitridge) a noted cricketer.[99]
- Alfred Edgar Wigg (second son of Edgar S Wigg)[100]
- Edward Neale Wigg (oldest son of E. S. Wigg)
- H. H. Wigg
- Sidney Wilcox (of Wilcox Mofflin & Co.[101]) – Possibly Sidney George Wilcox (b. 25 Aug 1866)?[102]
- C. Williams
- Peter Wood[75]
- D. Woodforde
- C. W. Wren (General Manager, E.S.& A. Bank)
- G. S. Wright (Inspector General of the State Bank)
- Thomas Young jun. mayor of Port Augusta, son of Thomas Young MHA (not related to J. L. Young)
"and hundreds of others scattered throughout the land".
(Somewhere it says he educated 1,500 young men – in 28 years, that's about 100 per annum (estimated mean 2 years per student), @ 10 guineas per annum.)
Old Scholars Association
(First A.G.M.)[103] held 15 Dec 1863 at Mr. J. L. Young's school room, Stephens-place; Mr. E. Cheetham occupied the chair. Satisfactory reports were received with reference to the success of the association. Annual prize awarded to Edward Neale Wigg. Elected: C. Peacock, President; M. L. Clark, Treasurer; Joseph Coulls, Secretary; and E. Cheetham, Walter Samson, Wm. Bickford, A. K. Whitby, and G. Cottrell.
Prizegivings and Examinations
J. L. Young held twice-yearly public demonstrations, mostly held in White's Rooms, which showcased the boys' accomplishments to parents and the public. A report was published as news in the newspapers immediately after, and always in glowing terms, the copy being provided by the school. Any flaws in the operation of the school and the training of eager young minds were only hinted at in retrospect – by pronouncements on the great strides made in the current year.
There were so many other schools that copied his example that the newspapers soon recognised these reports for what they were – advertisements – and charged by the column-inch. No longer were the speeches by the headmaster and the visiting dignitary quoted verbatim and, sadly for the historian, the only students named were the recipients of prizes.
Sports
The school fielded a (soccer) football team and two cricket teams.
The first school Sports Day was held in November 1874. Prizes included silver pencil cases and gold shirt studs.[104]
Other Adelaide private schools of the period
This list is by no means exhaustive. Many schools changed location, identity and management. And there were many women of culture and attainment, particularly widows (such as Caroline Carleton), who subsisted on their earnings as tutors.
- Adelaide Collegiate School in North Adelaide, run by Thomas Field. Incorporated into Queen's School 1892.
- Adelaide Model School (Alexander Clark) not strictly private school, run by Council of Education
- Albert House Academy – see Haire's Academy
- Alix House Academy, 100 South Terrace run by Eliza Hill (died October 1918), wife of Charles Hill, artist (died September 1915)
- Mrs. Bell's school[31]
- Billiatt's Grammar School at St. Leonards, Glenelg[105]
- Bowden Day Schools (Methodist?) (Mr & Mrs Lawton)
- Brougham School, Gilles Street ca. 1869 (Thomas Stevens Burgan, died 3 July 1858, succeeded by son Thomas Burgan,[106] also at Fellenberg Commercial School)
- School run by W. A. Cawthorne on what was later Page Street, Adelaide,[5] became Victoria Square Academy.
- Church of England Collegiate School see St. Peter's Collegiate School
- Collegiate and Commercial Institute, Victoria Square 1860 see Haire's academy
- Commercial School, Port Adelaide (Henry Nootnagel)[107] later language master St Peter's College, later Prince Alfred College.
- Mr Dollison's school, Port Adelaide.
- Fellenberg Commercial School, Hindmarsh Square run by John Martin (c. 1814 – 9 July 1876) schoolmaster previously at Pulteney Street
- German School, Freeman St (von Schleinitz, then Hansen) 1851-52
- German School, Wakefield Street, run by Theodor Niehuus[108] and Adolph Leschen.
- Glenelg Educational Institution (M. Mitchell)
- Glenelg Grammar (1868) Frederick Isaac Caterer (c. 1840 – c. 24 August 1892)
- Gouger Street Academy, James Hosking (c. 1822–1888)
- Grote Street Model School (coeducational – many female students prominent in Adelaide University examinations 1878)[109]
- Haire's Academy, Albert House, Victoria Square then Collegiate Institute, Whitmore House, Whitmore Square between Gilbert Street and South Terrace.[5] (Francis Haire, died insolvent? ca. 1875)
- Hill House School (E. W. Wickes, later G. W. Moore)
- School run by Miss Hillier (later Mrs Taylor) North Terrace.[5]
- Mr Howard's Academy
- James Jolly (died 3 November 1881)'s school in Waymouth Street (he later ran the Board of Education school at Encounter Bay then Port Elliot)
- Mr King's Academy, Port Adelaide
- St Leonards Grammar, Glenelg (W. K. Smart)
- Mr Leslie's School
- Mr McLaughlin's Public School, Port Adelaide
- Martin's Grammar School, Port Adelaide, conducted by Allen Martin (12 August 1844 – 13 July 1924) 1870–1876 then as a State school 1877–1900.[110]
- Miss Martin's School. Founded by Annie Montgomerie Martin. Second headmistress was Caroline Clark
- North Adelaide Educational Institution (aka Nesbit & Drews')(1869- ) http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article41394776
- North Adelaide Grammar (John Whinham) (1804?-13 March 1886) and son Robert (died 24 October 1884) later called Whinham College.
- Norwood Grammar School (Thomas Caterer) 1861 became South Australian Commercial College 1881
- Port Adelaide Grammar (A. Martin)
- Mr Potter's School
- Prince Alfred College (J. A. Hartley)
- Princes street School (T. Cater?) (founded by James Cater, taken over by Department the following year)[111]
- Pulteney Street School (1848)[112] (W. Moore) became Pulteney Grammar
- Pulteney Street Central Schools (coeducational) 1847[113] (same as above?)
- Queen's School, North Adelaide (1892) was founded by J.H. Lindon and E.L. Heinemann, both ex-St. Peter's College, taking over the building (and the bulk of the students) of Thomas Field's Adelaide Collegiate School.
- Queenstown Commercial School
- Miss Roland's school on Tavistock Street[31]
- Rundle Street Grammar (R.C. Mitton and W.J. Anderson) in Stephens Place from 1866 to 1872
- St. Peter's Collegiate School (previously Church of England Collegiate School)
- Semaphore Collegiate School
- Stepney College
- Tranmere School, run by David Wylie[114] brother-in-law of William Scott MHR
- Union College (religious training)[115]
- Victoria Square Academy – W. A. Cawthorne's school on west of the Square.
- Way College – a Bible Christian college on Park Terrace, North Unley, named for Rev. James Way. W. G. Torr principal
- Whinham College – see North Adelaide College
- Wickes and Titherington opened a school at Jeffcott Street 1847[116]
- Mrs. Woodcocks Christ Church school room[31]
Further reading
- Chessell, Diana Adelaide's Dissenting Headmaster — John Lorenzo Young and his Premier Private School 2014; Wakefield Press, Kent Town, South Australia. ISBN 978 1 74305 240 2
References
- ↑ Adelaide Educational Institution, 6 January 1853, South Australian Register, p.2
- 1 2 3 4 B. K. Hyams, 'Young, John Lorenzo (1826–1881)', Australian Dictionary of Biography, Volume 6, Melbourne University Press, 1976, pp 457-458.
- 1 2 3 Cumming, D.A. and Moxham, G. They Built South Australia published by the authors February 1986 ISBN 0 9589111 0 X
- 1 2 3 Adelaide Educational Institution South Australian Register 16 June 1857 p.3 accessed 28 April 2011
- 1 2 3 4 Old Schools The Register 18 August 1926 p.19 accessed 3 July 2011
- 1 2 Adelaide Educational Institution South Australian Register 15 December 1855 p.3 accessed 26 April 2011
- ↑ Evening Classes, 2 November 1852, South Australian Register (Adelaide, SA), p.4
- ↑ Adelaide Educational Institution, 25 March 1853, South Australian Register, p.2
- ↑ Philosophical Society, 10 January 1853, South Australian Register (Adelaide, SA), p.3
- ↑ Adelaide Educational Institution South Australian Register 15 December 1862 p.3 accessed 3 May 2011
also contains reference to growth of Philosophical Society - 1 2 In and Out of the City. By Autolycus., 22 October 1928, The Register (Adelaide, SA), p.10
- ↑ "13 Jun 1913 - The Advertiser - p1". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ Geoffrey H. Manning Education in Early South Australia, in A Colonial Experience
- ↑ "07 Jun 1882 - Family Notices". nla.gov.au.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Young's School Diamond Jubilee Today South Australian Register Friday 11 October 1912 p.8 accessed 20 May 2011
- ↑ Life Summary, Young, John Lorenzo (1826–1881), Australian Dictionary of Biography
- ↑ South Australian High School, 19 July 1951, South Australian Register, pg.1
- ↑ "22 Oct 1914 - THE JOHN L. YOUNG SCHOOL.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "25 Jun 1860 - Classified Advertising". nla.gov.au.
- 1 2 3 Payne, G.B. (1972) History of Unley, 1871-1971, ISBN 0 959917403 pp. 93-94, 173-174.
- ↑ "22 Dec 1880 - SOUTH AUSTRALIA. ADELAIDE, December 16.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "06 Dec 1880 - Advertising". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "09 Apr 1887 - THE CRIMINAL SESSIONS.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "07 Apr 1887 - Family Notices". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ Out among the People Advertiser and Register 13 July 1931 p.8 accessed 12 February 2011
- ↑ "16 Jun 1857 - Adelaide Educational Institution". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "The "Old Boys"". Daily Herald (Adelaide, SA : 1910 - 1924). Adelaide, SA: National Library of Australia. 12 October 1912. p. 5. Retrieved 25 December 2015.
- ↑ "The Grave on Fort Hill". ancestry.com.
- 1 2 "04 Aug 1888 - MR. MORTIMER MENPES, THE ARTIST. TO THE EDITOR.". nla.gov.au.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "04 Jan 1897 - OLD STEPHENS-PLACE.". nla.gov.au.
- 1 2 3 4 "An Old Art Master". The Register. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 12 October 1912. p. 17. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ↑ Obituary South Australian Register Tuesday 10 October 1871 supplement p.7 accessed 10 March 2011
- ↑ "26 Sep 1867 - LAW AND CRIMINAL COURTS. SUPREME COURT.—CIVIL SI...". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ The Late Mr. G. Needham The Advertiser 22 March 1894 p.7 accessed 10 March 2011
- ↑ http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article43111659/4001218
- ↑ "12 Jul 1865 - Advertising". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ German School Examination South Australian Register 18 July 1851 p.2 accessed 28 September 2011
- ↑ http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article66449310/6280511
- ↑ Employment Wanted South Australian Register Monday 11 May 1863 p.1 accessed 28 September 2011
- ↑ Tuition South Australian Register 4 July 1864 p.1 accessed 29 September 2011
- ↑ "02 Jan 1874 - V.—EDUCATIONAL. SCHOOL EXAMINATIONS.". nla.gov.au.
- 1 2 Obituary for Mrs Young South Australian Register 18 April 1887 supplement p.2 accessed 19 March 2011
- 1 2 (First) Old Scholars Reunion (1912) The Advertiser 12 October 1912 p.20 accessed 10 March 2011
- ↑ Death of Mr. Oliver Young, Adelaide Observer, 12 March 1898, p. 29, col. e
- ↑ The Late Mr Oliver Young, 8 March 1898, South Australian Register (Adelaide, SA), p.5
- ↑ "22 Aug 1853 - UNCLAIMED LETTERS.—July 31, 1853.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ Public Examination of Mr J L Young's Pupils South Australian Advertiser 20 December 1859 p.4 accessed 19 March 2011
- ↑ Old Scholars' Association South Australian Register 16 September 1865 p.3 accessed 26 May 2011
- ↑ Old Scholars Association South Australian Register 15 September 1866 accessed 6 June 2011
- ↑ Adelaide Educational Institution South Australian Register 29 April 1867 p.2 accessed 7 May 2011
- ↑ (First) Old Scholars Association Dinner (1867) South Australian Register 28 September 1867 p.7 accessed 10 March 2011
- ↑ Miscellaneous South Australian Advertiser 29 July 1867 p.6 accessed 15 May 2011
- ↑ "06 May 1869 - OFFICIAL STATISTICS AND THEIR COMPILERS.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ Old Scholars Association Dinner (1869) South Australian Register 25 September 1869 p.2 accessed 2 April 2011
- ↑ Old Scholars Association Dinner (1870) South Australian Register 24 September 1870 p.3 accessed 3 April 2011
- ↑ "25 Jun 1870 - AUSTRAL-AMERICAN RECIPROCITY.". nla.gov.au.
- 1 2 "27 Jul 1872 - THE COPPER MARKET AT HOME.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "24 Jan 1880 - COMPLIMENTARY. PRESENTATION TO MR. T. CATERER, B.A.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "18 Feb 1896 - Family Notices". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ Third Old Scholars' Reunion (1914) The Advertiser 22 October 1914 p.11 accessed 17 February 2011
- ↑ Fourth Old Scholars' Reunion (1915) The Advertiser 19 October 1915 p.9 accessed 17 February 2011
- ↑ Fifth Old Scholars' Reunion (1916) The Advertiser 24 October 1916 p.5 accessed 17 February 2011
- ↑ "22 May 1918 - WELCOME TO AN OLD ADELAIDEAN". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ Eighth Old Scholars' Reunion (1919 The Advertiser 21 October 1919 p.8 accessed 17 February 2011
- ↑ Young's School (9th reunion, 1920) The Register 19 October 1920 p.4 accessed 10 March 2011
- ↑ A Much-Loved Schoolmaster (10th reunion, 1921) The Advertiser 18 October 1921 p.8 accessed 10 March 2011
- ↑ John L. Young's Old Scholars Association (Reunion 1925) The Register 12 May 1925 p.8 accessed 10 March 2011
- ↑ Old Scholars Reunion (1925) The Advertiser 12 May 1925 p.15
- ↑ "Obituaary". Murray Pioneer. Renmark, SA: National Library of Australia. 17 June 1943. p. 4. Retrieved 19 July 2013.
- 1 2 3 Companions of John McDouall Stuart on his sixth expedition (1861-1862)
- ↑ Out among the People Advertiser and Register p.8 many more names in this reminiscence
- ↑ "Search results for 'w. b. carr' - Digitised newspapers and more - Trove". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ Old Time Surveyor The Register 3 August 1928 p.12 accessed 17 February 2011
- ↑ Sudden Death of Mr. F.A. Chapman, The Advertiser 19 September 1925 p.17
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 The Diamond Jubilee The Advertiser 11 October 1912 p.11 accessed 19 March 2011
- 1 2 "Alfred Giles – Enjoying Life at 80.". The Mail. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 22 September 1928. p. 3. Retrieved 30 January 2013. This reference cites nicknames "Jack" Cleland and "Willie" Gosse
- ↑ http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article31969908/2277653
- ↑ "16 Jun 1876 - The Advertiser FRIDAY, JUNE 16, 1876.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "27 Jan 1922 - CONCERNING PEOPLE.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "06 Nov 1882 - DEATH OF MR. WALTER DUFFIELD.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "21 Mar 1919 - CONCERNING PEOPLE.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "11 May 1899 - THE LATE REV. JOHN GARDNER". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "13 Oct 1913 - CONCERNING PEOPLE.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ Municipal nominations 1917, 26 November 1917, The Advertiser (Adelaide, SA), p.5
Elected Auditor for St Peters: H.R. Guerin, accontant, East Adelaide.
Municipal nominations 1913, 1 December 1913, The Advertiser (Adelaide, SA), p.17
Elected Auditor for St Peters: Harry Robin Guerin, accontant, East Adelaide.
Public Companies, 12 February 1915, The Advertiser (Adelaide, SA), p.5
Adelaide Co-Operative Society Limited, General Storekeepers, Angas and Nelson Streets, Adelaide. Auditor-Mr. Harry Robin Guerin, F.S.A.S.A., Accountant, St. Peters.
Adelaide Co-Operative Society Limited, 15 September 1917, The Advertiser (Adelaide, SA), p.15
For Auditor.-Mr. Harry Robin Guerin, F.S.A.S.A., Accountant, Pirie-street, Adelaide (unopposed). - ↑ "19 Jul 1919 - PERSONAL.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "05 Oct 1897 - BREAKING THE NEWS.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ Concerning People, The Register, 12 October 1912, pg.15
- ↑ "16 Oct 1841 - Family Notices". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "19 Dec 1928 - CHOWILLA PIONEER. Death of Mr. R. Robertson. REN...". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ Glen Osmond, Self-guided walk, pg.5, www.burnside.sa.gov.au
- ↑ Healey, John (editor) SA's Greats – The men and women of the North Terrace plaques Historical Society of South Australia 2003 ISBN 0957943008
- ↑ "11 Oct 1912 - YOUNG'S SCHOOL. A FAMOUS OLD INSTITUTION. DIAMON...". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ His life has been filled with good deeds, "Out Among the People" by Vox, 11 May 1953, The Advertiser (Adelaide, SA), p.4
- ↑ Vivien Stewart, 'Tucker, Charles (1857–1928)', Australian Dictionary of Biography, Volume 12, Melbourne University Press, 1990, pp 274-275.
- ↑ "On 12 February 1907, as customs agent for John Martin & Co. Ltd, Tucker was found guilty of having defrauded the Customs Department during the 1890s of duties payable on goods imported by the firm. His brother and nephew were also implicated. The amount involved approached £33,000 of which Tucker's share had been about £2,000 a year for more than a decade. Tucker was sentenced to two years imprisonment with hard labour; the Observer cautioned against 'the pretensions of smooth-tongued and clever individuals of gentlemanly address and suitably captivating manners'. It had been South Australia's longest criminal trial: there were 97 witnesses and some 8,000 exhibits, and the case ran for 31 days." – Bio – Vivien Stewart, 'Tucker, Charles (1857–1928)', Australian Dictionary of Biography, Volume 12, Melbourne University Press, 1990, pp 274-275.
- ↑ "DEATH OF DR. E. W. WAY.". The Register. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 30 September 1901. p. 5. Retrieved 17 September 2014.
- ↑ "15 Jul 1872 - Loss of a Pleasure Party in St. Vincent's Gulf". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "Out among the People". The Advertiser (Adelaide, SA : 1931 - 1954). Adelaide, SA: National Library of Australia. 5 April 1932. p. 10. Retrieved 6 November 2015.
- ↑ "Full text of "Notable South Australians; Or, Colonists, Past and Present"". archive.org.
- ↑ A South Australian Student in England, 15 August 1878, SA Register, pg.5, col.2
- ↑ Sidney Wilcox's Retirement, 1 July 1927, The Register, pg.10
Death Of Mr. Sidney Wilcox, 2 February 1942, The Advertiser, pg.8
On Torrens just downstream from Bean Brothers, similar business. And Glen Legoe partner poss. father of 1879 AEI student W. Legoe. - ↑ Wilcox, George and Annie, City of Adelaide: The Splendid Clipper Ship, cityofadelaide.org.au
- ↑ "16 Dec 1863 - TOPICS OF THE DAY.". nla.gov.au.
- ↑ "School Athletics". South Australian Register. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 16 November 1874. p. 5. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
- ↑ Personal, 11 April 1919, The Advertiser, pg.7
- ↑ "Concerning People". The Register. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 21 April 1920. p. 7. Retrieved 1 June 2013.
- ↑ "Advertising". South Australian Register. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 17 January 1876. p. 3. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- ↑ "Obituary". The Chronicle. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 1 June 1912. p. 43. Retrieved 24 September 2014.
- ↑ "Adelaide University Examinations". South Australian Register. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 13 December 1878. p. 6. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- ↑ "A Pioneer Schoolmaster". Port Adelaide News. 11, (49). South Australia. 18 July 1924. p. 2. Retrieved 14 August 2016 – via National Library of Australia.
- ↑ "Personal". The Advertiser. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 11 October 1912. p. 9. Retrieved 1 June 2013.
- ↑ "Local Intelligence". South Australian Register. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 28 June 1848. p. 3. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- ↑ "Pulteney-Street Central Schools". South Australian Register. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 21 June 1856. p. 3. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- ↑ "Tranmere Transformed". The News. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 14 July 1926. p. 8 Edition: Home Edition. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- ↑ "The Union College". South Australian Register. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 17 June 1872. p. 5 Supplement: Supplement to the South Australian Register. Retrieved 30 August 2014.
- ↑ "Advertising". South Australian Register. Adelaide: National Library of Australia. 24 February 1847. p. 1. Retrieved 30 August 2014.