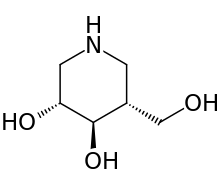
Afegostat
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Plicera |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | Isofagomine; AT-2101, HGT-3410 |
| CAS Number |
169105-89-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 447607 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7410 |
| ChemSpider | 394649 |
| UNII |
G23AP190YS |
| KEGG | D09576 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL206468 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6H13NO3 |
| Molar mass | 147.17 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Afegostat (INN; also known as isofagomine; planned trade name Plicera) was an experimental drug for the treatment of certain forms of Gaucher's disease, that was being developed by Amicus Therapeutics and Shire plc until a failed clinical trial in 2009 led to termination of its development. The substance was used in form of the tartrate.
Mechanism of action
β-Glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme needed for the metabolisation of glucocerebroside, is misfolded in individuals with Gaucher's disease due to various mutations, one of which is called N370S. Afegostat, an iminosugar, binds selectively to N370S glucocerebrosidase and restores its correct conformation and, consequently, enhances its activity about threefold.[1][2]
Invention and development
Afegostat was invented by Mikael Bols and Troels Skrydstrup, and was first prepared by Jespersen and Bols.[3]
Amicus Therapeutics licensed patents related to afegostat from Mt. Sinai School of Medicine, University of Maryland, and Novo Nordisk A/S, and also signed a collaboration agreement with Shire plc related to this drug and others.[4]:13
It was granted orphan drug status by the European Medicines Agency (EMA)[5] and by the US FDA.[4]:10
When afegostat failed a Phase II clinical trial in 2009, Shire terminated the collaboration agreement and Amicus determined it would no longer develop the afegostat.[4]:2,10,11 The first patents in Amicus' patent portfolio on afegostat expire in 2015.[4]:12
See also
- Imiglucerase, a recombinant human β-glucocerebrosidase for enzyme replacement therapy of Gaucher's disease
- Miglustat, another orphan drug for the treatment of Gaucher's disease with a different mechanism of action
- Eliglustat
References
- ↑ Dulsat, C.; Mealy, N. (2009). "Isofagomine tartrate". Drugs of the Future. 34 (1): 23. doi:10.1358/dof.2009.034.01.1323946.
- ↑ Richard A. Steet; Stephen Chung; Brandon Wustman; Allan Powe; Hung Do; Stuart A. Kornfeld (2006). "The iminosugar isofagomine increases the activity of N370S mutant acid β-glucosidase in Gaucher fibroblasts by several mechanisms" (PDF). PNAS. 103 (37): 13813–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.0605928103. PMC 1564243
 . PMID 16945909.
. PMID 16945909. - ↑ Jespersen, T. M.; Dong, W; Skrydstrup, T; Sierks, M.R; Lundt, I; Bols, M. (1994). "Isofagomine, a Potent New Glycosidase Inhibitor". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 33 (17): 1778–1779. doi:10.1002/anie.199417781.
- 1 2 3 4 Amicus Amicus 10-K Annual Report Filed Mar 10, 2010
- ↑ Public summary of positive opinion for orphan designation of isofagomine tartrate for the treatment of Gaucher disease Archived July 18, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.