Aranc
| Aranc | ||
|---|---|---|
|
The Town Hall | ||
| ||
 Aranc | ||
|
Location within Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region  Aranc | ||
| Coordinates: 46°00′19″N 5°30′36″E / 46.0053°N 5.51°ECoordinates: 46°00′19″N 5°30′36″E / 46.0053°N 5.51°E | ||
| Country | France | |
| Region | Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes | |
| Department | Ain | |
| Arrondissement | Belley | |
| Canton | Hauteville-Lompnes | |
| Intercommunality | Plateau d'Hauteville | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor (2014–2020) | Daniel Mathieu | |
| Area1 | 21.65 km2 (8.36 sq mi) | |
| Population (2009)2 | 297 | |
| • Density | 14/km2 (36/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | |
| INSEE/Postal code | 01012 / 01110 | |
| Elevation |
431–1,011 m (1,414–3,317 ft) (avg. 750 m or 2,460 ft) | |
|
1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km² (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. 2 Population without double counting: residents of multiple communes (e.g., students and military personnel) only counted once. | ||
Aranc is a French commune in the department of Ain in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of eastern France.
The inhabitants of the commune are known as Randaoillards or Randaoillardes[1]
Geography
Location
The commune lies in the Aranc Valley 10 km north-east of Amberieu-en-Bugey and 25 km south-east of Bourg-en-Bresse. It is bordered to the east by the mountains of Ain and Tré Pellay (1016 metres), in the north by the Avocat mountain chain, and in the west by the valley of the Mandorne. The Aranc Valley has an average altitude of 780 metres. A marsh borders the village to the north. The Borrey river has its source in the marsh. The mountains of Aranc (924 metres) creates a natural border to the east. The lowest point of the commune is the hamlet of Moment at 406 metres.
A number of roads can be used to access the commune: the D34 from Saint-Rambert-en-Bugey in the south-west, the D63A from the D63 in the west, the D12 from the north, the D8 from Hauteville-Lompnes in the south-east, and the D102 from Evosges in the south. The D34 and the D102 intersect in the village.[2]
Geology
The Aranc Valley, like the Hauteville plateau is a syncline of modest size. The origin of the soil is from the Mesozoic period, mainly Late Jurassic for the Aranc Valley and Middle Jurassic for the Madorne Valley. Soils consist of mixed material alternating with layers of Oxfordian type limestone in the middle of the Birmensdorf layer. Meticulous research has discovered fossil bivalves, gastropods, and more rarely ammonites along the outcrop. The Aranc Valley and the Hauteville plateau are generally bordered by numerous cliffs where caves, waterfalls, chasms, and indentations were formed by the action of water with small basins formed by rivers.
The quality of the limestone was exploited in quarries that are near Résinand and a manganese mine was reported at the beginning of the 20th century, but poverty and the difficulty of extracting the ore made the mines uneconomic.
Neighbouring communes and villages[2]
 |
Boyeux-Saint-Jerome | Izenave | Corcelles |  |
| Ambronay | |
Champdor | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Amberieu-en-Bugey | Evosges | Hauteville-Lompnes |
History
Heraldry
.svg.png) |
Details Designed by Thierry Faure David-Nillet. Adopted by the municipal council on 15 November 1991.
Blazon: |
Etymology
According to Henry Suter and presented on his website, the name is of Burgundian origin derived originally from Aringos, meaning "place of the Aringi", derived from the proper name Aro which is old High German aro giving the Germanic aran meaning "eagle".[3]
Anne Marie Vurpas in her book Place Names of Ain is a bit more precise: "Ar is the origin of the name Aranc whose territory is watered by the Borrey and Mandorne: the suffix -ancum was a pre-Latin form" and adds "some toponymists prefer to see an unattested latin man's name of Arincus".[4]
Further details have been provided in the collective work Tourist and archaeological Resources of the Canton of Hauteville: Aranc, Corlier, Cormaranche-en-Bugey, Hauteville-Lompnes, Lacoux, Longecombe, Prémillieu, Thézillieu / Department of Ain; authors Guy St-Pierre and Jean Dumarest suggest the Celtic Ar, meaning "near to" and Randa, meaning "limit", then the Latin Arena meaning "sand", then the Indo-European Ar meaning "watering place".[5] The latter meaning may seem plausible given the presence of a swamp and two rivers which have their sources in the Aranc Valley.
- Etymological evolution
- 1284: Arena
- 1359: Arens
- 1492: Arenc
- 1495: De Arenco
- 1650: Aran
- 1665: Haranc
- 1670: Aranc en Bugey.[5]
Prehistory
A piece of protohistoric vase was discovered in the commune and studied by a Mr. Pichon. "The morphological and technological characteristics" date this fragment "between 1700 and 1200 BC".
Middle Ages
From 1144, the lords of Rogemont ruled the Aranc Valley. According to the authors this feudal lordship was one of the oldest in the Bugey. The pasturage agreements with the Chartreuse de Meyriat (an ancient Carthusian monastery) in 1116 show that the lordship already existed. Most of village life at that time was governed by the lords of Rogemont and the castle. The Rougemont dynasty spanned five centuries.
16th and 17th centuries
- 1530: the disappearance of the lordship of Rougemont and purchase of the castle by the Grenaud family
- 1696: Marquisate of the Grenaud family
18th century
- 1791 Aranc becomes a canton dependent on the district of Saint-Rambert-en-Bugey and including in the canton the villages and hamlets of: Corlier, Montgriffon, Lacoux, and Chaley
19th century
- 1802: Aranc is attached to the Canton of Hauteville
Second World War

The passive resistance of the village of Aranc was well-known because it was a rallying point for the Maquis of Ain. The hamlet of Gorges was an important rallying point for the resistance. They had to find a rallying point for the young rebels but also a place that could unite all the factions in the region of Aranc and Corlier. It was during the year 1943 that Colonel Henri Romans-Petit set up his headquarters in the tiny hamlet enclosed by mountains and difficult to access (hence the interest). The senior guerrillas arrived in March 1943. During 1944 German troops entered the village of Aranc and made reprisals against the actions of the resistance, capturing, deporting, and shooting the resistance fighters.
Administration
List of Successive Mayors of Aranc[6]
| From | To | Name | Party | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1988 | 1995 | Denise Oraison | ||
| 1995 | 2014 | Jean-François Julliard | ||
| 2014 | 2020 | Daniel Mathieu |
(Not all data is known)
Hamlets

There are four hamlets in the commune of Aranc:
- Salagnat in the north
- Rougemont, in the east
- Résinand
- Pézières in the west
Rougemont
Rougemont is located behind the Aranc Mountains. It is the most populous of the four hamlets in the commune. It is in this village that the ruins of Rougemont Castle are located.
- Etymological evolution
- 1144: Rubro Monte
- 1206: Rubeismontis
- 1213: Rogimonte
- 1284: Monterubes
- 1286: Rubesmonte
- 1301: Rogemont
- 1536: Rougemont
- Buildings
The access difficulties between Aranc and Rougemont led to the creation of a clandestine school. In 1868 a formal decision was reached for the establishment of a school. There is also a public laundry near the old cheese factory. The cheese factory was probably built in 1860 - this is where the clandestine school was organised on the first floor. In 1903 the factory recorded a production of 600 Hectolitres of milk but it is not inoperation today.
Résinand
This hamlet is enclosed in a depression slightly oriented North South.
- Etymological evolution
- 1670: Tizenan
- 1746: Résinand
Another etymology: Résimond or Léatit[7]
- Buildings
- Public Laundry: A public laundry exists but is no longer operational
- Cobbler: next to the laundry
- Bread oven
- School: A school was built in 1865 at "Crétêt" and "Chêne". Currently this house has the date 1890 over the door
- Cheese factory: The first records date back to 1875. 2000 hectolitres of milk were collected in 1903. The cooperative rules were revised in 1924 when 27 members were recorded and 37 in 1918. There remained four dairy farmers in 1990 but today the building is closed.
Les Pézières

A hamlet bordering Résinand and generally included with Résinand. This hamlet appeared under the name of Pessières (spruce forests) in 1873. The road passing through gives access to farms at Gorges and the former hamlets of Colognat and Malaval. The same road continues higher up to the village of Montgriffon.
- Buildings
- Public Laundry: Powered by three fountains, the system still works.
- Bread oven
- Church of Pézières: Built in 1830 by Father Miller, the pastor of Oncieu. In 1871 the church had its own parish priest and a location for the cemetery was allocated near the church. In 1874 a parsonage was built. Work was undertaken in 1882 to restore the building. In 1895 the bell tower was built. The parish was active until 1971 when it was joined with the parish of Aranc. The church consists of a nave of three bays and a choir covered with a barrel vault. There are two chapels: one dedicated to St Joseph and the other to the Virgin.
Salagnat

This hamlet is located in the extreme east of the Aranc Valley not far from the Avocat chain. The houses of Salagnat border the highway in the direction of Hauteville-Lompnes. A stream rises in the hamlet before flowing into the Jarine.
- Etymological evolution
- 1492: Siliniaco
- 1538: Saligniaco
The etymology of this name is not certain but, among other explanations, the name may refer to a person: Sallinius or Silinius as in chartreuse de Sélignac (Simandre-sur-Suran: Siliniacus in 854), the name of a Carthusian monastery occupied from 1202 to the Revolution.
Demography
In 2010 the commune had 302 inhabitants. The evolution of the number of inhabitants is known through the population censuses conducted in the town since 1793. From the 21st century, a census of municipalities with fewer than 10,000 inhabitants is held every five years, unlike larger towns that have a sample survey every year.[Note 1]
| 1793 | 1800 | 1806 | 1821 | 1831 | 1836 | 1841 | 1846 | 1851 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 839 | 917 | 981 | 1,191 | 1,232 | 973 | 1,111 | 1,116 | 1,104 |
| 1856 | 1861 | 1866 | 1872 | 1876 | 1881 | 1886 | 1891 | 1896 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,139 | 1,017 | 1,008 | 899 | 872 | 828 | 849 | 766 | 737 |
| 1901 | 1906 | 1911 | 1921 | 1926 | 1931 | 1936 | 1946 | 1954 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 718 | 657 | 650 | 577 | 519 | 491 | 480 | 422 | 393 |
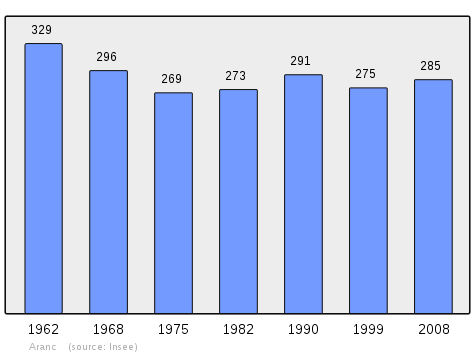
| 1962 | 1968 | 1975 | 1982 | 1990 | 1999 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 329 | 296 | 269 | 273 | 291 | 275 | 285 | 286 | 285 |
| 2009 | 2010 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 297 | 302 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Sources : Ldh/EHESS/Cassini until 1962, INSEE database from 1968 (population without double counting and municipal population from 2006)
Education
Aranc has a peri-scholastic daycare centre. A class of Middle Path (CM) and maternity jpintly with Évosges; a Preparatory Course (CP) and an Elementary Course (EC) at Aranc (2 classes).
Associations
Some associations exist in the commune with one for the elderly called The Friends of the Mandorne which is headquartered in the town hall in Aranc. The commune also has a choir called The polyphones of the plateau.
Sport
Aranc has many mountain bike trails including one of the paths used by the resistance of the Maquis of Ain.
Economy
Employment
Today, the village lives mainly on logging and also a little farming. There are still some cultivated fields in the Aranc Valley but this activity is currently experiencing a strong decline. The village is economically dependent on Hauteville-Lompnes and its watershed. However, there are actions to promote tourism, with the presence of an Aranc escape website that offers hiking and tries to promote the natural heritage of the Aranc Valley.
Business
During the 18th and 19th centuries there was cultivation of hemp and hemp combers in the Hauteville Valley. There was also stone and wood work. At the entrance of the marsh was a pigsty which is still present today but not used. At the beginning of the century there were still farmers who sent milk daily to the cheese factories at Aranc, Rougemont, and Résinand. Today, the activity of the village is mainly timber with some farmers.
Commerce
Aranc has a hotel-restaurant called Aranc-évasion as well as an Australian restaurant based on the village of Résinand.
Heritage[8]
Sights
N.B.: Most of the sights listed below no longer exist.
- Footbridge to the vicarage
A small footbridge over the Jarine over the swamp on the Corlier road. It is mentioned on the Napoleonic cadastral maps available at the Ain archives. It obviously no longer exists and has been replaced with the Corlier road.[9]
The location of this tumulus is not reported on maps. This was a circular mound 50 metres in diameter and 5 to 8 metres high. It was between the stream and the Jarine the path leading to the ruins of the Moulin de Merlet.
- Coal
There were many places for the manufacture of charcoal, especially at a place called Montreal on the road to Montgriffon.
- Lime Kiln
Also at Montreal was a lime kiln. Materials for the manufacture of lime were extracted here. In 1920 the ruins of two platforms with the remains of stones and ashes could still be seen. Today, taking the road through Montgriffon passing by Colognat it is possible to clearly discern the place where this industry was practiced.
Saint Paul's Church

The precise dating of the building is made difficult by the variety of its components. In fact, they are from different eras. The oldest part is probably the nave.
- The Choir
This is based on huge rectangular pillars on the side of the nave and two side columns beside the apse. The rosette of the keystone is composed of four concentric leafy decorations. The choir was crowned by a tower for which the wall reached a height of 4 metres. The remains of the wall are still visible in the attic.
- The Apse
The three stained glass windows composing the apse are decorated with tracery probably dating from the 1500s. The central window is in three forms: two transoms for the centre mullion and one transom for the sides. The apse probably dates from 1508.
- The Nave
This part of the church underwent major renovations during the work undertaken between 1655 and 1700. Vaults have replaced the wooden ceiling and the roof and steeple were renovated.
- Chapels
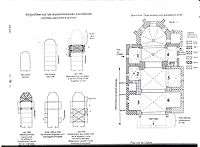
Four chapels were built at the same time as the choir. Two chapels are ribbed crosses and both consist of corbels supporting sculptures of a medieval character. Two chapels were added between 1655 and 1700. In the 16th century, a chapel was added at the request of the Lords of Rougemont.
- Chapel 1: once dedicated to Saint Peter, it was later dedicated to Saint Catherine and finally transformed into a sacristy
- Chapel 2: formerly dedicated to Saint Michael, is now dedicated to Saint Anthony
- Chapel 3: dedicated to Saint Claude, now dedicated to Saint Paul
- Chapel 4: dedicated to Saint Madeleine, it is now named Rougemont chapel because it has a side door on the edge of the hamlet
- Chapel 5: called the Rosary, it has a commemorative plaque for the Moyne family
- Chapel 6: dedicated to Saint Anthony, is currently dedicated to Saint Philomena
- Furniture
- Statue of Saint Anthony: a wooden statue dating back to the 18th century. Probably once gilded.
- Statue of Saint Philomena: a wooden statue from the 19th century
- Christ on the cross: dating from the 18th or the 17th century
- Font: in stone, it probably dates from 1876
- Baptismal Font: also stone probably from 1876
- Extensions
In 1858 the church obtained a quote for the construction of a bell tower and an expansion. Approved in 1862, work began five years later. The architect Belley added two low naves in the initial project which focused only on the extension of the central nave.
Open Air Crosses
The Calvary of Three Crosses are open-air crosses located on a hill called the Mont au levet overlooking the village. Two legends are associated with these crosses. The first relates to the death of abandoned children and the other made the connection with the cemetery of lepers. The Michel Antoine cross is located at the southern end of the village although it was formerly located near the bread oven. The Denis cross is on the road to Corlier.
- Cross of Collombet: On the ridge between Mount Aranc and the Pétozan Valley
- Cross of Verbon: a procession is triggered by the priest during droughts. There is only the base at ground level.
- Cross of Salagnat: an old cross in the cemetery
- Cross of Salandru: there is only the base consisting of a single block of stone roughly worked. Probably a very ancient cult site.
- Cross of Rosoiriat: Implanted by the Priest Jolivet on 28 May 1893
- Cross of Crétêt: a metal cross on stone base
- Cross of Colognat: a cross from Argis or Tenay cemetery. Affixed to a base whose inscriptions are almost illegible.
- Our Lady of Mount Aranc: no visible date. The building can probably dates to the 19th century.
- Virgin of Molard: at Résinand, a remembrance of the first mission in 1883.
Administrative buildings
- Town hall
Buildings whose construction is not dated but there is quote dated 28 August 1889 to restore the school-town hall. The work ended in 1890. The architect was Mr. Moncorger. Today, it still houses the school.
- School
The construction of a building for the school was proposed in 1833, then abandoned due to lack of resources then recovered in 1845 and completed in 1848. The boys' school no longer exists (probably on the site of the local fire station), the girls' school was certified in 1876 by the nuns of Belley. It stood at the current site of the post office.
Other buildings
- The cheese factory
In 1820, the Bugey region saw the development of new techniques for making Comté cheese. A cheese factory was installed at Aranc collecting milk from farms around the village. It dates from 1876 and collected 4,000 hectoliters of milk in 1900. In 1930 there were 52 farmer members who sent their milk to the cheese factory. With the decline in farming, the cheese factory closed its doors in 1985. At the initiative of Joel Pelletier, a native of Aranc, the premises have been rehabilitated and new fruit farm opened in September 2011.[10]
Farms and Barns
_Ain.jpg)
- Le Marchat is a barn that hosted the World War II resistance group the Maquis of Ain. It was in ruins until its reconstruction in the 2000s. It is located in a secluded location on the road to Résinand. This farm with Termant was a landmark for the Maquis de l'Ain. It is on the route of the "path of memory".
- Malaval is a farm located in the upper valley of the Mandorne. A path leads to the farm from Colognat. According to the Napoleonic cadastral map, several buildings were at Malaval. There now remains only one building.
- Le Moulin de Colognat refers to a group of farms below the hamlet of Pézières on the road to Montgriffon. A cross indicates the path towards Malaval.
- Etymology
According to Henry Suter the name originates from the Gallo-Roman Coloniacum derived with the suffix -acum from the people's name Colonius from the Latin colonus meaning "peasant, farmer, field, settler", or inhabitant of a colony". Two mills still exist today but only one is still working. It is powered by the Mandorne. The water-wheel has a diameter of 5 metres and is 1 metre wide.
- The Gorges barn was, with the Marchat barn, another place frequented by the Maquis of Ain. Located in the valley of the Mandorne this barn is hidden in a small gorge. Accessible from the road to Montgriffon, a memorial stone was placed at the intersection between the path to the barn and the road.
- The hamlet "Moment" is on the road to Oncieu. It is a small hamlet located in the gorges of the Mandorne.
- The Goyet barn is close to Rougemont.
Houses[8]
- Moyne House: without doubt the oldest house in the village, it probably dates to 1774. The interest in this house is the typical architecture of the houses of Bugey: gabled walls and "dreffia".[11]
- Besson House: a very old building
- Givaudan House: a house with a large stable and a carved stone monolith over 5 metres in height. The barn door has this inscription: "Apingon, Year 6 of the R 1798 VS"
- House of the District Judge: A building in the Mâcon style, it has an exterior staircase that allows entry by a landing. On this level there are two entries with a curved arc from a support on a central pillar. It is in this house that the representative of the law lived from 1791
- Parsonage: a former presbytery converted into a rural cottage. It has windows carved in stone in the Gothic style
- Summer Camp: An old inn called Le Mastroquet - it was still active in 1947
- Reydellet House: the interest of this house is in the forecourt. There is a millstone from Merlet
- Gerard Bozon House: dated from 1764
- Givaudan House: dated from 1806.
- Bettollo House: an inscription over the door reads: "Jean François Savey 1839"
Legends and oral traditions
An oral tradition refers to a cemetery of lepers in the commune of Aranc. Work carried out in 1920 at a place called Le Mollard (repairs to the water tank) unearthed bones. Around 1933 the legend of "La Segnegoga" was recounted. The story unfolded around the Marchat barn and the three crosses pass. "The segnegogues" were lovers at twilight. sometimes it walked, sometimes it flew. They formed, dancing, a large circle around a fire. They tendered to one another a beverage contained in a horse's hoof. "The segnegogues" could also take the form of candles being placed above the head of late bystanders. This legend is found in Evosges but also throughout Bugey and Dombes.[8]
Springs, fountains, streams and rivers
- The waters of the Aranc Valley gather near Corlier to form the Borrey which later flows into the Oignin.
- The Cascade of Tines in the Bois de Lignières
- The Doye Fountain: Located in the centre of the village and built in 1870. It is adjacent to the cheese factory.
See also
External links
- Aranc official website (French)
- Community of communes of the Plateau of Hauteville-Lompnès website (French)
- Aranc on Lion1906
- Aranc on Google Maps
- Aranc on Géoportail, National Geographic Institute (IGN) website (French)
- Aranc on the 1750 Cassini Map
- Aranc on the INSEE website (French)
- INSEE (French)
Notes and references
Notes
- ↑ At the beginning of the 21st century, the methods of identification have been modified by law No. 2002-276 of 27 February 2002 , the so-called "law of local democracy" and in particular Title V "census operations" which allow, after a transitional period running from 2004 to 2008, the annual publication of the legal population of the different French administrative districts. For municipalities with a population greater than 10,000 inhabitants, a sample survey is conducted annually, the entire territory of these municipalities is taken into account at the end of the period of five years. The first "legal population" after 1999 under this new law came into force on 1 January 2009 and was based on the census of 2006.
References
- ↑ Inhabitants of Ain (French)
- 1 2 Google Maps
- ↑ Names of Places in French-speaking Switzerland, Savoy, and surrounding areas (French)
- ↑ Anne-Marie Vurpas, Place Names of Ain, 1999 (French)
- 1 2 Guy Saint-Pierre and Jean Dumarest, Tourist and archaeological Resources of the Canton of Hauteville, Association le Dreffia, 1992, 253 pages, ISBN 2-907656-22-8, consulted on 12 November 2010 (French)
- ↑ List of Mayors of France (French)
- ↑ France by cantons and communes: Department of Ain, Théodore Ogier, p.161
- 1 2 3 Guy Saint-Pierre et Jean Dumarest, Tourist and Archeological riches of the Canton of Hauteville, Association le Dreffia, 1992, 253 p. (ISBN 2-907656-22-8)
- ↑ Thierry Faure David-Nillet, Lords and Lordships of the Plateau of Hauteville-Lompnes, 2009, 264 pages, ISBN 978-2-7466-1256-3, consulted on 17 August 2010 (French)
- ↑ Aranc Fruit Farm
- ↑ Dreffia is the local name for wood
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Aranc. |
