Araucaria moist forests
| Araucaria moist forests | |
|---|---|
|
Araucaria moist forest in Aparados da Serra National Park, Brazil. | |
|
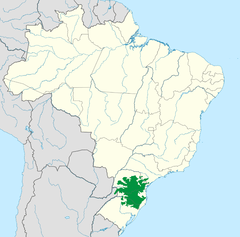
Araucaria moist forests ecoregion as defined by WWF. | |
| Ecology | |
| Biome | Atlantic Forest |
| Borders | Alto Paraná Atlantic forests, Cerrado, Pampas and Serra do Mar coastal forests |
| Bird species | 440[1] |
| Mammal species | 141[1] |
| Geography | |
| Area | 216,100 km2 (83,400 sq mi) |
| Countries |
|
| States | São Paulo (state), Paraná, Santa Catarina, Rio Grande do Sul and Misiones Province |
| Conservation | |
| Habitat loss | 87.0%[2] |
| Protected | 0.62%[3] |
The Araucaria moist forests are a coniferous forest ecoregion of the Atlantic Forest Biome. The forest ecosystem is located in southern Brazil and northeastern Argentina.
Setting
The moist forests cover an area of 216,100 square kilometres (83,400 sq mi), encompassing a region of mountains and plateaus in the Brazilian states of São Paulo, Paraná, Santa Catarina, and Rio Grande do Sul, and extending into Misiones Province of Argentina.
The ecoregion lies above 500 metres (1,600 ft), rising to 1,600 metres (5,200 ft) elevation on the high slopes of the Serra da Mantiqueira.
The ecoregion is bounded by the Paraná-Paraíba interior forests to the north, west, and south, the Cerrado savannas and shrublands to the northeast, The Serra do Mar coastal forests to the east, and the Uruguayan savanna to the southwest.
Climate
The Araucaria moist forests have an oceanic temperate climate (Cfb), with frequent frosts during the winter months and considerable snowfalls (generally light) in the highest areas. Annual precipitation is high, ranging from 1,300 to 3,000 millimetres (51 to 118 in), without a dry season.
Flora
The ecoregion mostly consists of evergreen subtropical moist forests, with a canopy made up of Ocotea pretiosa and O. catharinense (Lauraceae), Campomanesia xanthocarpa (Myrtaceae), and Parapiptadenia rigida (Leguminosae). Brazilian araucaria (Araucaria angustifolia) forms an emergent layer, growing up to 45 metres (148 ft) in height. The forests are significant from an evolutionary perspective, as a relict of mixed coniferous and broad-leafed forests that were once much more widespread, and are home to many taxa characteristic of the Antarctic flora.
Fauna
The ecoregion is home to several threatened species endemic to the Atlantic forests, including the brown howler monkey (Alouatta guariba) and the red-spectacled parrot (Amazona pretrei). The Araucaria moist forests is recognized as an important endemic bird area.
Conservation and threats
The Araucaria moist forests are within the Atlantic Forest Biome (Mata Atlântica), which is recognized as a biodiversity hotspot by Conservation International, and as a Global 200 ecoregion by the World Wildlife Fund.
References
- 1 2 Hoekstra, J. M.; Molnar, J. L.; Jennings, M.; Revenga, C.; Spalding, M. D.; Boucher, T. M.; Robertson, J. C.; Heibel, T. J.; Ellison, K. (2010). The Atlas of Global Conservation: Changes, Challenges, and Opportunities to Make a Difference. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-26256-0.
- ↑ SOS MATA ATLÂNTICA. 1998. Atlas da evolução dos remanescentes florestais e ecossistemas associados no domínio da Mata Atlântica no período 1990-1995. Fundação SOS Mata Atlântica, Instituto Socioambiental e Instituto de Pesquisas Espaciais, São Paulo.
- ↑ SILVA, J.M.C. & DINNOUTI, A. 1999. Análise de representatividade das unidades de conservação federais de uso indireto na Floresta Atlântica e Campos Sulinos. In: Conservation International (ed.). Workshop Avaliação e Ações Prioritárias para Conservação dos Biomas Floresta Atlântica e Campos Sulinos, São Paulo. http://www.conservation.org.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Atlantic Forest. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mata Atlântica. |
- "Araucaria moist forests". Terrestrial Ecoregions. World Wildlife Fund.