Mepivacaine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a603026 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| ATC code | N01BB03 (WHO) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
96-88-8 |
| PubChem (CID) | 4062 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 7224 |
| DrugBank |
DB00961 |
| ChemSpider |
3922 |
| UNII |
B6E06QE59J |
| KEGG |
D08181 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:6759 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1087 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.313 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H22N2O |
| Molar mass | 246.348 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
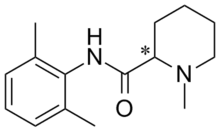
Mepivacaine /mɛˈpɪvəkeɪn/ is a local anesthetic[1] of the amide type. Mepivacaine has a reasonably rapid onset (more rapid than that of procaine) and medium duration of action (shorter than that of procaine) and is marketed under various trade names including Carbocaine and Polocaine.
Mepivacaine became available in the United States in the 1960s.
Mepivacaine is used in any infiltration and regional anesthesia.
It is supplied as the hydrochloride salt of the racemate, [2] which consists of R(-)-mepivacaine and S(+)-mepivacaine in equal proportions. These two enantiomers have markedly different pharmacokinetic properties. [3]
References
- ↑ Porto GG, Vasconcelos BC, Gomes AC, Albert D (January 2007). "Evaluation of lidocaine and mepivacaine for inferior third molar surgery" (PDF). Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 12 (1): E60–4. PMID 17195831.
- ↑ Burm AG, Cohen IM, van Kleef JW, Vletter AA, Olieman W, Groen K (January 1997). "Pharmacokinetics of the enantiomers of mepivacaine after intravenous administration of the racemate in volunteers". Anesth. Analg. 84 (1): 85–9. doi:10.1097/00000539-199701000-00016. PMID 8989005.
- ↑ http://journals.lww.com/anesthesia-analgesia/Fulltext/1997/01000/Pharmacokinetics_of_the_Enantiomers_of_Mepivacaine.16.aspx
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/25/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.