Ascosphaera
| Ascosphaera | |
|---|---|
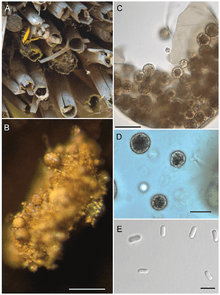 | |
| A) habitat. Phragmites reeds and female Chelostoma florisomne returning with pollen for her brood. B) fecal pellet of C. florisomne larva covered with spore cysts; pale spore balls are visible through the transparent spore cyst wall. C) close-up of spore cyst showing spore balls and smooth, unornamented spore cyst wall. D) spore balls. E) bacilliform ascospores. Scale bars: B = 200 µm, C = 50 µm, C = 10 µm, D = 15 µm, E = 10 µm. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Onygenales |
| Family: | Ascosphaeraceae |
| Genus: | Ascosphaera L.S.Olive & Spiltoir (1955) |
| Type species | |
| Ascosphaera apis (Maasen ex Claussen) L.S.Olive & Spiltoir (1955) | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Pericystis Betts (1912)[1] | |
Ascosphaera is a genus of fungi in the family Ascosphaeraceae. It was described in 1955 by mycologists Charles F. Splitoir and Lindsay S. Olive.[2] Members of the genus are insect pathogens. The type species, A. apis, causes chalkbrood disease in honey bees.[3] The reproductive ascospores of the fungus are produced within a unique structure, the spore cyst, or sporocyst.[4]
Species
- A. acerosa
- A. aggregata
- A. apis
- A. asterophora
- A. atra
- A. callicarpa[5]
- A. celerrima
- A. cinnamomea
- A. duoformis
- A. fimicola
- A. flava
- A. fusiformis
- A. larvis
- A. major
- A. naganensis
- A. osmophila
- A. parasitica
- A. pollenicola
- A. proliperda
- A. scaccaria
- A. solina
- A. subcuticularis
- A. tenax
- A. torchioi
- A. variegata
- A. verrucosa
- A. xerophila
References
- ↑ Betts AD. (1912). "A bee-hive fungus, Pericystis alvei, gen. et sp. nov.". Annals of Botany. 26 (3): 795–800.
- ↑ Spiltoir CF, Olive LS (1955). "A reclassification of the genus Pericystis Betts". Mycologia. 47 (2): 238–44. doi:10.2307/3755414.
- ↑ Capinera JL. (2008). Encyclopedia of Entomology. Springer. p. 304. ISBN 978-1-4020-6242-1.
- ↑ Wynns, A.A.; Jensen, A.B.; Eilenberg, J.; James, R. (2012), "'Ascosphaera subglobosa, a new spore cyst fungus from North America associated with the solitary bee Megachile rotundata", Mycologia, 104 (1): 108–114, doi:10.3852/10-047
- ↑ Wynns AA, Jensen AB, Eilenberg J (2013). "Ascosphaera callicarpa, a new species of bee-loving fungus, with a key to the genus for Europe". PLoS ONE. 8 (9). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073419.

External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.