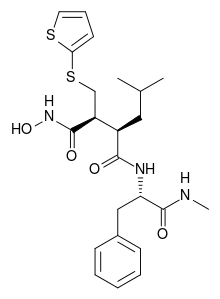
Batimastat
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Injection into pleural space or abdomen |
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 130370-60-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5362422 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 5145 |
| DrugBank | DB03880 |
| ChemSpider | 4515033 |
| KEGG | D03061 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL279786 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H31N3O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 477.64 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Batimastat (INN/USAN, codenamed BB-94) is an anticancer drug that belongs to the family of drugs called angiogenesis inhibitors. It acts as a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (MMPI) by mimicking natural MMPI peptides.
Batimastat was the first MMPI that went into clinical trials. First results of a Phase I trial appeared in 1994. The drug reached Phase III but was never marketed; mainly because it couldn't be administered orally (as opposed to the newer and chemically similar MMPI marimastat), and injection into the peritoneum caused peritonitis.[1]
References
- ↑ Rothenberg, M. L.; Nelson, A. R.; Hande, K. R. (1999). "New Drugs on the Horizon: Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors". Stem Cells. 17 (4): 237–240. doi:10.1002/stem.170237. PMID 10437989.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the U.S. National Cancer Institute document "Dictionary of Cancer Terms".
This article incorporates public domain material from the U.S. National Cancer Institute document "Dictionary of Cancer Terms".
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/27/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.