B-flat major
 | |
| Relative key | G minor |
|---|---|
| Parallel key | B♭ minor |
| Dominant key | F major |
| Subdominant | E♭ major |
| Component pitches | |
| B♭, C, D, E♭, F, G, A, B♭ | |
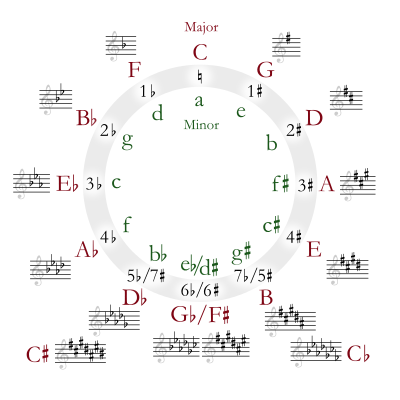
In music theory, B♭ (B-flat) major is a major scale based on B♭. The pitches B♭, C, D, E♭, F, G, and A are all part of the B♭ major scale. Its key signature has two flats.
B♭ major's relative minor is G minor, and its parallel minor is B♭ minor.
Many transposing instruments are pitched in B-flat major, including the clarinet, trumpet, tenor saxophone, and soprano saxophone. As a result, B-flat major is a popular key for concert band compositions.
In Nordic, Baltic, Western and Southern Slavic (except Bulgarian) languages, Hungarian, German and most Central and Northern European languages, the pitch B is called "H" while B♭ is called "B".
History
Joseph Haydn's Symphony No. 98 is credited as the first symphony he (or anyone else) wrote in that key in which he included trumpet and timpani parts. Actually, his brother Michael Haydn had written one such symphony earlier, No. 36, though Joseph Haydn still gets credit for writing the timpani part at actual pitch with an F major key signature (instead of transposing with a C major key signature), a procedure that made sense since he limited that instrument to the tonic and dominant pitches.[1] Many editions of the work, however, use no key signature and specify the instrument as "Timpani in B-flat–F".
Five of Mozart's piano concertos are in B-flat major.
Notable classical compositions
- Brandenburg Concerto No. 6 (Bach)
- Piano Concerto No. 15 (Mozart)
- Piano Concerto No. 27 (Mozart)
- Piano Concerto No. 2 (Beethoven)
- Symphony No. 4 (Beethoven)
- String Quartet No. 6 (Beethoven)
- String Quartet No. 13 (Beethoven)
- Große Fuge (Beethoven)
- Piano Sonata No. 11 (Beethoven)
- Piano Sonata No. 29 (Beethoven)
- Mass No. 3 (Schubert)
- Piano Sonata No. 21 (Schubert)
- Symphony No. 1 "Frühling", Op. 38 (Schumann)
- Humoreske for piano Op. 20 (Schumann)
- Symphony No. 2 "Lobgesang" (Mendelssohn)
- Piano Concerto No. 2 (Brahms)
- String Quartet No. 3 (Brahms)
- String Sextet No. 1 (Brahms)
- Variations and Fugue on a Theme by Handel, for piano (Brahms)
- Symphony No. 5 (Bruckner)
- Symphony No. 5 (Prokofiev)
- Piano Concerto No. 4 (Prokofiev)
- Prelude in B-flat major (Rachmaninoff)
- String Quartet No. 5 (Shostakovich)
- Pines of Rome by Ottorino Respighi
- Les Barricades Mystérieuses
References
- ↑ H. C. Robbins Landon, Haydn Symphonies, London: British Broadcasting Corporation (1966): 57
External links
![]() Media related to B-flat major at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to B-flat major at Wikimedia Commons
| Diatonic scales and keys | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The table indicates the number of sharps or flats in each scale. Minor scales are written in lower case. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||