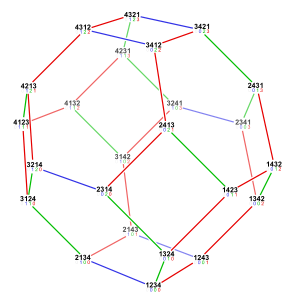
Bitruncated cubic honeycomb
| Bitruncated cubic honeycomb | |
|---|---|
  | |
| Type | Uniform honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbol | 2t{4,3,4} t1,2{4,3,4} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | |
| Cell type | (4.6.6) |
| Face types | square {4} hexagon {6} |
| Edge figure | isosceles triangle {3} |
| Vertex figure | 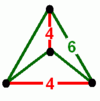 (tetragonal disphenoid) |
| Space group Fibrifold notation Coxeter notation | Im3m (229) 8o:2 [[4,3,4]] |
| Coxeter group | , [4,3,4] |
| Dual | Oblate tetrahedrille Disphenoid tetrahedral honeycomb |
| Properties | isogonal, isotoxal, isochoric |
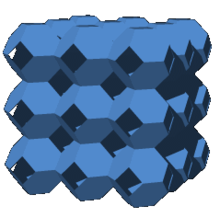
The bitruncated cubic honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space made up of truncated octahedra (or, equivalently, bitruncated cubes). It has 4 truncated octahedra around each vertex. Being composed entirely of truncated octahedra, it is cell-transitive. It is also edge-transitive, with 2 hexagons and one square on each edge, and vertex-transitive. It is one of 28 uniform honeycombs.
John Horton Conway calls this honeycomb a truncated octahedrille in his Architectonic and catoptric tessellation list, with its dual called an oblate tetrahedrille, also called a disphenoid tetrahedral honeycomb. Although a regular tetrahedron can not tessellate space alone, this dual has identical disphenoid tetrahedron cells with isosceles triangle faces.
Geometry
It can be realized as the Voronoi tessellation of the body-centred cubic lattice. Lord Kelvin conjectured that a variant of the bitruncated cubic honeycomb (with curved faces and edges, but the same combinatorial structure) is the optimal soap bubble foam. However, the Weaire–Phelan structure is a less symmetrical, but more efficient, foam of soap bubbles.
The honeycomb represents the permutohedron tessellation for 3-space. The coordinates of the vertices for one octahedron represent a hyperplane of integers in 4-space, specifically permutations of (1,2,3,4). The tessellation is formed by translated copies within the hyperplane.
The tessellation is the highest tessellation of parallelohedrons in 3-space.
Symmetry
The vertex figure for this honeycomb is a disphenoid tetrahedron, and it is also the Goursat tetrahedron (fundamental domain) for the Coxeter group. This honeycomb has four uniform constructions, with the truncated octahedral cells having different Coxeter groups and Wythoff constructions. These uniform symmetries can be represented by coloring differently the cells in each construction.
| Space group | Im3m (229) | Pm3m (221) | Fm3m (225) | F43m (216) | Fd3m (227) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibrifold | 8o:2 | 4−:2 | 2−:2 | 1o:2 | 2+:2 |
| Coxeter group | ×2 [[4,3,4]] =[4[3[4]]] |
[4,3,4] =[2[3[4]]] |
[4,31,1] =<[3[4]]> |
[3[4]] |
×2 [[3[4]]] =[[3[4]]] |
| Coxeter diagram | |||||
| truncated octahedra | 1 |
1:1 |
2:1:1 |
1:1:1:1 |
1:1 |
| Vertex figure |  |
 |
 |
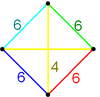 |
 |
| Vertex figure symmetry |
[2+,4] (order 8) |
[2] (order 4) |
[ ] (order 2) |
[ ]+ (order 1) |
[2]+ (order 2) |
| Image Colored by cell |
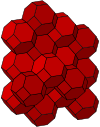 |
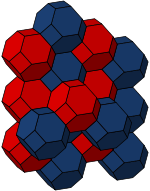 |
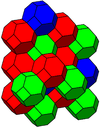 |
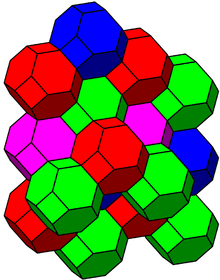 |
 |
Related polyhedra and honeycombs
The [4,3,4], ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , Coxeter group generates 15 permutations of uniform tessellations, 9 with distinct geometry including the alternated cubic honeycomb. The expanded cubic honeycomb (also known as the runcinated tesseractic honeycomb) is geometrically identical to the cubic honeycomb.
, Coxeter group generates 15 permutations of uniform tessellations, 9 with distinct geometry including the alternated cubic honeycomb. The expanded cubic honeycomb (also known as the runcinated tesseractic honeycomb) is geometrically identical to the cubic honeycomb.
| C3 honeycombs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space group |
Fibrifold | Extended symmetry |
Extended diagram |
Order | Honeycombs |
| Pm3m (221) |
4−:2 | [4,3,4] | ×1 | ||
| Fm3m (225) |
2−:2 | [1+,4,3,4] ↔ [4,31,1] |
↔ |
Half | |
| I43m (217) |
4o:2 | [[(4,3,4,2+)]] | Half × 2 | ||
| Fd3m (227) |
2+:2 | [[1+,4,3,4,1+]] ↔ [[3[4]]] |
↔ |
Quarter × 2 | |
| Im3m (229) |
8o:2 | [[4,3,4]] | ×2 | ||
The [4,31,1], ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , Coxeter group generates 9 permutations of uniform tessellations, 4 with distinct geometry including the alternated cubic honeycomb.
, Coxeter group generates 9 permutations of uniform tessellations, 4 with distinct geometry including the alternated cubic honeycomb.
| B3 honeycombs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space group |
Fibrifold | Extended symmetry |
Extended diagram |
Order | Honeycombs |
| Fm3m (225) |
2−:2 | [4,31,1] ↔ [4,3,4,1+] |
↔ |
×1 | |
| Fm3m (225) |
2−:2 | <[1+,4,31,1]> ↔ <[3[4]]> |
↔ |
×2 | |
| Pm3m (221) |
4−:2 | <[4,31,1]> | ×2 | ||
This honeycomb is one of five distinct uniform honeycombs[1] constructed by the Coxeter group. The symmetry can be multiplied by the symmetry of rings in the Coxeter–Dynkin diagrams:
| A3 honeycombs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space group |
Fibrifold | Square symmetry |
Extended symmetry |
Extended diagram |
Extended group |
Honeycomb diagrams |
| F43m (216) |
1o:2 | a1 |
[3[4]] | (None) | ||
| Fm3m (225) |
2−:2 | d2 |
<[3[4]]> ↔ [4,31,1] |
↔ |
×21 ↔ |
|
| Fd3m (227) |
2+:2 | g2 |
[[3[4]]] or [2+[3[4]]] |
↔ |
×22 | |
| Pm3m (221) |
4−:2 | d4 |
<2[3[4]]> ↔ [4,3,4] |
↔ |
×41 ↔ |
|
| I3 (204) |
8−o | r8 |
[4[3[4]]]+ ↔ [[4,3<sup>+</sup>,4]] |
↔ |
½×8 ↔ ½×2 |
|
| Im3m (229) |
8o:2 | [4[3[4]]] ↔ 4,3,4 |
×8 ↔ ×2 |
|||
Projection by folding
The bitruncated cubic honeycomb can be orthogonally projected into the planar truncated square tiling by a geometric folding operation that maps two pairs of mirrors into each other. The projection of the bitruncated cubic honeycomb creating two offset copies of the truncated square tiling vertex arrangement of the plane:
| Coxeter group |
||
|---|---|---|
| Coxeter diagram |
||
| Graph | 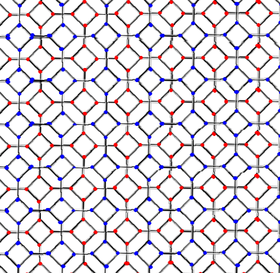 Bitruncated cubic honeycomb |
 Truncated square tiling |
Alternated form

This honeycomb can be alternated, creating regular icosahedron from the truncated octahedra with irregular tetrahedral cells created in the gaps. There are three constructions from three related Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() ,
, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , and
, and ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . These have symmetry [4,3+,4], [4,(31,1)+] and [3[4]]+ respectively. The first and last symmetry can be doubled as [[4,3+,4]] and [[3[4]]]+.
. These have symmetry [4,3+,4], [4,(31,1)+] and [3[4]]+ respectively. The first and last symmetry can be doubled as [[4,3+,4]] and [[3[4]]]+.
This honeycomb is represented in the boron atoms of the α-rhombihedral crystal. The centers of the icosahedra are located at the fcc positions of the lattice.[2]
| Space group | I3 (204) | Pm3 (200) | Fm3 (202) | Fd3 (203) | F23 (196) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibrifold | 8−o | 4− | 2− | 2o+ | 1o |
| Coxeter group | [[4,3+,4]] | [4,3+,4] | [4,(31,1)+] | [[3[4]]]+ | [3[4]]+ |
| Coxeter diagram | |||||
| Order | double | full | half | quarter double |
quarter |
| Image colored by cells |
 |
 |
 |
 |
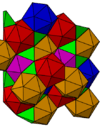 |
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bitruncated cubic honeycomb. |
Notes
References
- John H. Conway, Heidi Burgiel, Chaim Goodman-Strauss, (2008) The Symmetries of Things, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5 (Chapter 21, Naming the Archimedean and Catalan polyhedra and tilings, Architectonic and Catoptric tessellations, p 292-298, includes all the nonprismatic forms)
- George Olshevsky, Uniform Panoploid Tetracombs, Manuscript (2006) (Complete list of 11 convex uniform tilings, 28 convex uniform honeycombs, and 143 convex uniform tetracombs)
- Branko Grünbaum, Uniform tilings of 3-space. Geombinatorics 4(1994), 49 - 56.
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, edited by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6
- (Paper 22) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I, [Math. Zeit. 46 (1940) 380-407, MR 2,10] (1.9 Uniform space-fillings)
- A. Andreini, Sulle reti di poliedri regolari e semiregolari e sulle corrispondenti reti correlative (On the regular and semiregular nets of polyhedra and on the corresponding correlative nets), Mem. Società Italiana della Scienze, Ser.3, 14 (1905) 75–129.
- Klitzing, Richard. "3D Euclidean Honeycombs o4x3x4o - batch - O16".
- Uniform Honeycombs in 3-Space: 05-Batch
- Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-23729-X.