Black rosy finch
| Black rosy finch | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Fringillidae |
| Genus: | Leucosticte |
| Species: | L. atrata |
| Binomial name | |
| Leucosticte atrata Ridgway, 1874 | |
 | |
The black rosy finch, or black rosy-finch, (Leucosticte atrata) is a species of passerine bird in the family Fringillidae native to alpine areas above treeline, of the western United States.
Taxonomy
The black rosy finch was first classified by American ornithologist Robert Ridgway in 1874.[1] This bird has been thought to form a superspecies with the three other rosy finches: gray-crowned rosy finch (L. tephrocotis) and the brown-capped rosy finch (L. australis), all of which were classified as the same species as the Asian rosy finch (L. arctoa) from 1983-1993.[2][3][4] Recent mitochondrial DNA evidence shows the rosy finches are all indeed very closely related and can be easily confused with one another.[3][5] Along with four Asian rosy finches, the three North American rosy finches form the mountain finch genus Leucosticte. There are no recognized subspecies of the black rosy finch.[4] Alternative common names include: roselin (in French), Rußschneegimpel (in German), and pinzón montano negro (in Spanish).[6]
Description
Adults are black on the head, back and breast with pink on the belly, rump and wings. There is a patch of grey at the back of the head. They have short black legs and a long forked tail.[7][8] The gray-crowned rosy finch has a brown body instead of black and the brown-capped rosy finch and lacks the gray patch on the back of the head.[8]
Distribution and habitat
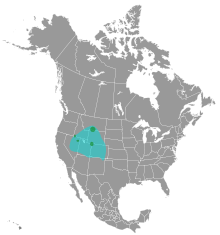
The black rosy finch's breeding habitat is mountain areas above the tree-line, amongst alpine rocks and cliffs. Because of this it is one of the least studied birds in North America.[3] Its distribution range is between that of the gray-crowned rosy finch (L. tephrocotis), which is located to north and west, and the brown-capped rosy finch (L. australis), which is located to the south and east.[3]
Behavior
The black rosy finch builds a cup nest in a cavity on a cliff. Most birds migrate short distances to lower elevations and further south and return to the alpine areas in April.[3] These birds forage on the ground, may fly to catch insects in flight. They mainly eat seeds from weeds and grasses and insects,[2] often in areas where snow is melting, uncovering food items and new plant shoots are growing.[3] They often feed in small flocks, sometimes mixing with gray-crowned rosy finches.[7] A male will defend its female's territory during breeding season, not just the nest but where ever she goes. This behavior is common with the rosy finches.[2][9] When breeding both males and females develop throat pouches, known as gular pouches or gular skin, to carry food to their chicks,[10][11] a trait seen in only one other North American genus, Pinicola.[3] Due to their inaccessibility, actual black rosy finch nests had been reached by only three researchers as of 2002.[5] The nests are made of grass and stems and lined with fine grass, hair, and feathers. They are known to use protected areas such as openings in cliffs, mine shafts, caves, and rafters. They eat seeds and insects, usually foraged from the ground, including snowfields.[2] Their call is a buzz-sounding "chew".[12]
References
- 1 2 BirdLife International (2012). "Leucosticte atrata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 "Black Rosy-Finch". All About Birds (life), The Cornell Lab of Ornithology. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Black Rosy-Finch". Birds of North America, The Cornell Lab of Ornithology. doi:10.2173/bna.678. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
- 1 2 Wright, Rick. "Notes on Rosy-Finch Taxonomy, Distribution, and Identification". Arizona Field Ornithologists. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
- 1 2 "Black Rosy-Finch - Leucosticte atrata". Montana Field Guide. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Black Rosy-finch (Leucosticte atrata)". Internet Bird Collection. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
- 1 2 Ottaviani, Michel (2008). Monographie des Fringilles, Volume 1: Fringillinés - Carduélinés: Histoire Naturelle et Photographies (in French). France: Editions Prin. ISBN 978-2-909136-20-2.
- 1 2 "Black Rosy-Finch". All About Birds (identification), The Cornell Lab of Ornithology. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Gray-crowned Rosy-Finch - Leucosticte tephrocotis". Montana Field Guide. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Gray-crowned Rosy-Finch". Bird Web. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Gray-crowned Rosy-Finch". Bird-Friend. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Black Rosy-Finch". All About Birds (sounds), The Cornell Lab of Ornithology. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
Further reading
Book
- Johnson, R. E. 2002. Black Rosy-Finch (Leucosticte atrata). In The Birds of North America, No. 678 (A. Poole and F. Gill, eds.). The Birds of North America, Inc., Philadelphia, PA.
Articles
- Behle WH. (1973). Further Notes on Rosy Finches Wintering in Utah. Wilson Bulletin. vol 85, no 3. pp. 344–346.
- Bjorklund CF. (1991). Black Rosy Finch Sighting on Big Muddy Cbc. Blue Jay. vol 49, no 3.
- Bull EL & Wales BC. (2001). Effects of disturbance on birds of conservation concern in eastern Oregon and Washington. Northwest Sci. vol 75, pp. 166–173.
- Hendricks P. (1978). Notes on the Courtship Behavior of Brown-Capped Rosy Finches. Wilson Bulletin. vol 90, no 2. pp. 285–287.
- Johnson RE. (1975). New Breeding Localities for Leucosticte in the Contiguous Western USA. Auk. vol 92, no 3. pp. 586–589.
- Johnson RE. (1977). Seasonal Variation in the Genus Leucosticte in North America. Condor. vol 79, no 1. pp. 76–86.
- Lichtwardt, Eric (2000). Rare, local, little-known and declining North American breeders, a closer look: Black Rosy-finch Birding 32(5): 402-408
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Leucosticte atrata. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Leucosticte atrata |
- "Black Rosy-finch Leucosticte atrata". BirdLife International. Retrieved July 4, 2011.
