Boyland–Sims oxidation
The Boyland–Sims oxidation is the chemical reaction of anilines with alkaline potassium persulfate, which after hydrolysis forms ortho-hydroxyl anilines.[1][2][3]
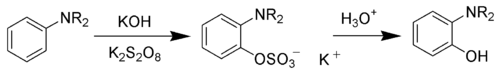
The ortho-isomer is formed predominantly. However, the para-sulfate is formed in small amounts with certain anilines.[4]
Reaction mechanism
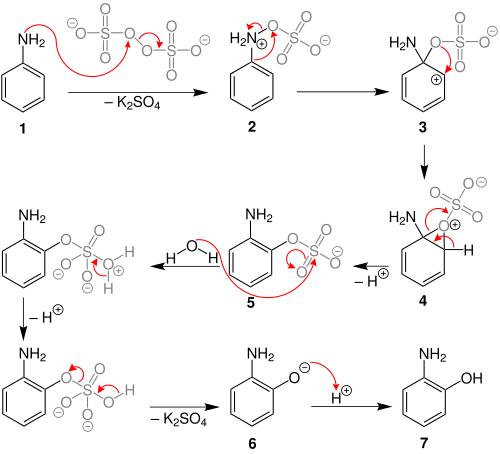
Behrman has shown that the first intermediate in the Boyland–Sims oxidation is the formation of an arylhydroxylamine-O-sulfate (2).[5] Rearrangement of this zwitterionic intermediate forms the ortho- sulfate (5), which then hydrolyses to form the ortho-hydroxyl aniline.
Further reading
- Behrman, Edward J. (2014). "On the Mechanism of the Boyland-Sims Oxidation". Progress in Reaction Kinetics and Mechanism. Science Reviews 2000 Ltd. 39 (3): 308–310. doi:10.3184/146867814X14062204626705.
See also
References
- ↑ Boyland, E.; Manson, D.; Sims, Peter (1953). "729. The preparation of o-aminophenyl sulphates". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 3623. doi:10.1039/jr9530003623.
- ↑ Boyland, E.; Sims, Peter (1954). "The oxidation of some aromatic amines with persulphate". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 980. doi:10.1039/jr9540000980.
- ↑ Behrman, E. J. (1988). "The Persulfate Oxidation of Phenols and Arylamines (The Elbs and the Boyland-Sims Oxidations)". Org. React. 35: 421–511. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or035.02. ISBN 0471264180.
- ↑ Boyland, E.; Sims, P.; Williams, D. C. (1956). "The oxidation of tryptophan and some related compounds with persulphate". Biochem. J. 62 (4): 546–50. PMC 1215958
 . PMID 13315210.
. PMID 13315210. - ↑ Behrman, E. J. (1992). "The ortho-para ratio and the intermediate in the persulfate oxidation of aromatic amines (the Boyland-Sims oxidation)". J. Org. Chem. 57 (8): 2266. doi:10.1021/jo00034a016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.