Bulbocapnine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
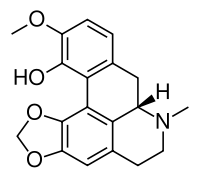
| IUPAC name
(S)-6,7,7a,8-tetrahydro-11-methoxy-7-methyl-5H-
benzo[g]-1,3-benzodioxolo-[6,5,4-de]quinolin-2-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
| 298-45-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:3211 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL157912 |
| ChemSpider | 11934 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.511 |
| PubChem | 12441 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H19NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 325.36 g/mol |
| Melting point | 201 to 203 °C (394 to 397 °F; 474 to 476 K) racemate 213-214 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Bulbocapnine is an alkaloid found in Corydalis (Papaveraceae) and Dicentra, plants in the family Fumariaceae that can cause fatal poisoning in sheep and cattle. It has been shown to act as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor,[1] and inhibits biosynthesis of dopamine via inhibition of the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase.[2][3]
According to the Dorlands Medical Dictionary, it "inhibits the reflex and motor activities of striated muscle. It has been used in the treatment of muscular tremors and vestibular nystagmus".[4] The psychiatrist Robert Heath carried out experiments on prisoners at the Louisiana State Penitentiary using bulbocapnine to induce stupor.[5]
In popular culture
In literature
- The author William S. Burroughs references the drug in his book Naked Lunch (1959), in which the fictional Dr. Benway uses it to induce obedience in torture victims.
In television
- The drug's use to treat Mayor Kane's father-in-law and predecessor is a plot point in season 2 of the TV series Boss, e.g., in episodes s2.e8 ("Consequences"; October 5, 2012) and s2.e9 ("Church"; October 12, 2012).
See also
References
- ↑ Adsersen, A.; Kjølbye, A.; Dall, O.; Jäger, A. K. (Aug 2007). "Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitory Compounds from Corydalis cava Schweigg. & Kort.". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 113 (1): 179–182. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2007.05.006. PMID 17574358.
- ↑ Zhang, Y. H.; Shin, J. S.; Lee, S. S.; Kim, S. H.; Lee, M. K. (Aug 1997). "Inhibition of Tyrosine Hydroxylase by Bulbocapnine". Planta Medica. 63 (4): 362–363. doi:10.1055/s-2006-957702. PMID 9270381.
- ↑ Shin, J. S.; Kim, K. T.; Lee, M. K. (Mar 1998). "Inhibitory Effects of Bulbocapnine on Dopamine Biosynthesis in PC12 Cells". Neuroscience Letters. 244 (3): 161–164. doi:10.1016/s0304-3940(98)00148-7. PMID 9593514.
- ↑ "Dorlands Medical Dictionary at Merck".
- ↑ Scheflin, A. W.; Opton, E. M. (1978). The Mind Manipulators: A non-fiction Account. New York: Paddington Press. pp. 314–315. ISBN 0-448-22977-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/3/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.