Calyculin
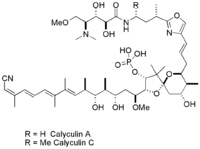 Calyculins A and C | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL384277 |
| ChemSpider | 9084513 (Calyculin A) |
| PubChem | 10909255 (Calyculin A) |
| |
| Properties | |
| C51H83N4O15P (Calyculin C) | |
| Molar mass | 1023.2 g/mol (Calyculin C) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Calyculins are natural products originally isolated from the marine sponge Discodermia calyx.[1] Calyculins have proven to be strong serine/threonine protein phosphatase inhibitors and based on this property, calyculins might be potential anticancer agents.
References
- ↑ Suganuma M, Fujiki H, Furuya-Suguri H, Yoshizawa S, Yasumoto S, Kato Y, Fusetani N, Sugimura T (1990). "Calyculin A, an inhibitor of protein phosphatases, a potent tumor promoter on CD-1 mouse skin". Cancer Res. 50 (12): 3521–3525.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.