Tsuga caroliniana
| Carolina hemlock | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Habit, Arboretum in Rogów, Poland | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Pinophyta |
| Class: | Pinopsida |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Pinaceae |
| Genus: | Tsuga |
| Species: | T. caroliniana |
| Binomial name | |
| Tsuga caroliniana Engelm. | |
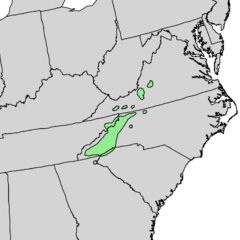 | |
Tsuga caroliniana, the Carolina hemlock,[2] is a species of Tsuga, native to the Appalachian Mountains in southwest Virginia, western North Carolina, extreme northeast Georgia, northwest South Carolina, and eastern Tennessee.[3] Its habitat is on rocky mountain slopes at elevations of 700–1,200 metres (2,300–3,900 ft). The optimal growing condition is a partly shady area with moist but well-drained soil in a cool climate.[4]
It is an evergreen coniferous tree growing up to 30 m (exceptionally 34 m) tall and 110 cm in trunk diameter under forest conditions. The crown is compact and pyramidal, growing up to 8 m wide. The bark is thick, reddish-brown and becomes fissured between scaly ridges. The branches are stout and usually horizontal, but often slightly drooping. The shoots are red-brown to orange-brown, and finely hairy. The leaves are 5–20 mm long and 1.8–2 millimetres (0.071–0.079 in) broad, flattened, not tapering toward their ends, with a rounded or slightly notched apex; they radiate outward in all directions from the twigs, and smell of tangerine if crushed. They are glossy dark green above and paler on the underside, with two white stomatal bands. The cones are 2–4 centimetres (0.79–1.57 in) long, green, maturing light to mid-brown 6–7 months after pollination. When fully open, their scales are positioned at a right angle or reflexed to the central axis.[4][5][6]
The hemlock woolly adelgid Adelges tsugae, an adelgid introduced to the United States from Asia in 1924, threatens Carolina hemlock, which is as susceptible as the related eastern hemlock.[5]
Carolina hemlock is used more often as an ornamental tree than for timber production, due to its overall rarity.[6] In landscaping, it is similar in appearance to eastern hemlock, but the Carolina hemlock has a deep taproot, compared with the shallow, aggressive roots of eastern hemlock. This means shrubs and other plants can be grown more easily under Carolina hemlock.[7]
References
- ↑ Conifer Specialist Group (1998). "Tsuga caroliniana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2006. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 06 May 2006. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - ↑ "Tsuga caroliniana". Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS Database. USDA. Retrieved 12 December 2015.
- ↑ Geographic Distribution Map: Tsuga caroliniana (Carolina Hemlock)
- 1 2 Farjon, A. (1990). Pinaceae. Drawings and Descriptions of the Genera. Koeltz Scientific Books. ISBN 3-87429-298-3.
- 1 2 Gymnosperm Database: Tsuga caroliniana
- 1 2 Flora of North America: Tsuga Caroliniana
- ↑ Richard E. Bir (1992). Growing and Propagating Showy Native Woody Plants. University of North Carolina Press. p. 62. ISBN 0-8078-4366-0.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tsuga caroliniana. |
