Carpinus betulus
| Carpinus betulus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| European Hornbeam in summer | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Betulaceae |
| Genus: | Carpinus |
| Species: | C. betulus |
| Binomial name | |
| Carpinus betulus L. | |
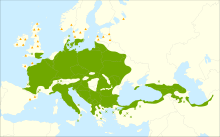 | |
| Distribution map | |
Carpinus betulus, commonly known as the European or common hornbeam, is a hornbeam native to Western Asia and central, eastern, and southern Europe, including southern England.[1] It requires a warm climate for good growth, and occurs only at elevations up to 600 metres (1,969 ft). It grows in mixed stands with oak, and in some areas beech, and is also a common tree in scree forests. Hornbeam was also known as 'Yoke Elm'.[2]
Description
It is a deciduous small to medium-size tree reaching heights of 15–25 metres (49–82 ft), rarely 30 m (98 ft), and often has a fluted and crooked trunk. The bark is smooth and greenish-grey, even in old trees. The buds, unlike those of the beech, are 10 mm (0.39 in) long at the most, and pressed close to the twig. The leaves are alternate, 4–9 cm (1.6–3.5 in) long, with prominent veins giving a distinctive corrugated texture, and a serrated margin. It is monoecious, and the wind-pollinated male and female catkins appear in early summer after the leaves. The fruit is a small 7–8 mm (0.28–0.31 in) long nut, partially surrounded by a three-pointed leafy involucre 3–4 cm (1.2–1.6 in) long; it matures in autumn. The seeds often do not germinate till the spring of the second year after sowing. The hornbeam is a prolific seeder and is marked by vigorous natural regeneration.
Carpinus betulus is a shade-loving tree, which prefers moderate soil fertility and moisture. It has a shallow, wide-spreading root system and is marked by the production of stump sprouts when cut back. Because it stands up well to cutting back and has dense foliage, it has been much used in landscape gardening, mainly as tall hedges and for topiary. The wood is heavy and hard, and is used for tools and building constructions. It also burns hot and slowly, making it a very suitable firewood.[3] This was the reason for lopping and hence indirectly the saving of Epping Forest, where the hornbeam was a favoured pollarding tree.
The leaves provide food for some animals, including Lepidoptera such as the case-bearer moth Coleophora anatipennella.
There are a number of notable forests where C. betulus is a dominant tree species, among which are:
- Epping Forest, Essex/London, UK
- Halltorp Nature Reserve, Öland, Sweden
Cultivation
Carpinus betulus is cultivated as an ornamental tree, for planting in gardens and parks. There are several cultivars, notably C. betulus 'Fastigiata' or 'Pyramidalis', a very fastigiate tree when young, which has become a popular urban street tree in the United Kingdom.
Both the species[4] and the cultivar C. betulus 'Fastigiata'[5] have gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Carpinus betulus. |
Gallery

 European Hornbeam in winter
European Hornbeam in winter Veteran tree
Veteran tree Hornbeamtree-covered walk (573m)
Hornbeamtree-covered walk (573m) Carpinus betulus - MHNT
Carpinus betulus - MHNT bud
bud
References
- ↑ http://www.nhm.ac.uk/fff-pcp/glob.pl?report=pcfllist&group=&sort=&inpos=nr6
- ↑ Brown, John (1816). Encyclopaedia Perthensis. 23. p. 364.
- ↑ http://www.gardeningcentral.org/hornbeam_tree/hornbeam_tree.html Tree Profile for Hornbeam
- ↑ "RHS Plant Selector - Carpinus betulus". Retrieved 25 June 2013.
- ↑ "RHS Plant Selector - Carpinus betulus 'Fastigiata'". Retrieved 25 June 2013.
External links
- Den virtuella floran: Carpinus betulus distribution
- EUFORGEN species page: Carpinus betulus Information and related resources
