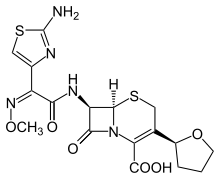
Cefovecin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | dorsoscapular subcutaneous injection |
| ATCvet code | QJ01DD91 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | Dogs: 98.5%, Cats: 99.8% |
| Metabolism | none |
| Biological half-life | Dogs: 133 hours, Cats: 166 hours |
| Excretion | unchanged in urine/bile |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
234096-34-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 9578573 |
| ChemSpider |
7851662 |
| UNII |
0D1OL46ZIE |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL2104475 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H19N5O6S2 |
| Molar mass | 453.49 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Cefovecin (INN) is an antibiotic of the cephalosporin class, licensed for the treatment of skin infections in cats and dogs. It is marketed by Zoetis under the trade name Convenia. It is the first single-dose injectable antibiotic for dogs and cats that assures owner compliance with dosing for the animal. It is used for the treatment of skin infections caused by Pasturella multocida in cats, and Staphylococcus intermedius/S. canis in dogs. The advantage of using injectable antibiotics is not missing a dose that can allow partially resistant microbes to recover during missed doses. The disadvantage is the durable presence of subtherapeutic concentrations in the weeks after the resolution of infections. This is associated with the development of resistance in microbes. It is effective, but should not be used in pregnant or lactating animals or in animals with a history of allergies to penicillin or cephalosporin drugs.[1]
Approval and usage
Cefovecin was first authorized for use in the European Union in June 2006,[2] and was approved for use in the United States in June 2008.[3]
It is approved as a broad-spectrum, third-generation cephalosporin for subcutaneous injection lasting 14 days for treating skin and soft tissue infections.[4]
Precautions
Contraindications include known allergies to cefovecin or antibiotics containing β-lactam rings such as penicillin or cephalosporins. Adverse reactions can include anaphylaxis. It is not for use in humans and should be kept out of reach of children. Individuals with similar known allergies should avoid dermal contact when handling the drugs.
Adverse reactions in dogs can include lethargy, decreased appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, blood in feces, and flatulence. Adverse reactions in cats can include vomiting, diarrhea, decreased appetite, lethargy, odd hyperactive behavior, and inappropriate urination. Mildly increased serum ALT and gamma glutamyl transferase have been noted.[5]
The following adverse events were reported voluntarily during post-approval use of the product in dogs and cats: death, tremors/ataxia, seizures, anaphylaxis, acute pulmonary edema, facial edema, injection site reactions (alopecia, scabs, necrosis, and erythema), hemolytic anemia, salivation, pruritus, lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea, and inappetance..[6]
Effectiveness
Cefovecin functions by interfering with cell wall synthesis. The chemical covalently binds to the so-called penicillin-binding proteins. Due to the high protein-binding of the chemical, it is not effective against Pseudomonas spp., or enterococci.
In drug studies, cefovecin administered to dogs was 92.4% effective against skin infections (secondary superficial pyoderma, abscesses, and infected wounds). In cats, it was 96.8% effective against skin infections.[7]
References
- ↑ Pfizer Animal Health. "Pfizer Convenia" (PDF). Pfizer. Retrieved 29 January 2013.
- ↑ "European Public Assessment Report for Convenia (from the EMEA website)". Retrieved 2008-07-11.
- ↑ "FDA Approves First and Only Single-dose Antibiotic for Dogs and Cats" (Press release). Pfizer Inc. 2008-06-30. Retrieved 2008-07-11.
- ↑ Pfizer Animal Health. "Convenia". Pfizer. Retrieved 29 January 2013.
- ↑ Pfizer Animal Health. "Pfizer Convenia" (PDF). Pfizer. Retrieved 29 January 2013.
- ↑ Convenia Prescribing Information. "Convenia Prescribing Information" (PDF). Pfizer. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ↑ Pfizer Animal Health. "Pfizer Convenia" (PDF). Pfizer. Retrieved 29 January 2013.
External links
- CID 23670874 from PubChem - Cefovecin sodium
- Official website by Pfizer