Cheonhado
| Cheonhado | |
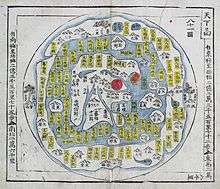 Cheonhado, Korean circular world map. | |
| Korean name | |
|---|---|
| Hangul | 천하도 |
| Hanja | 天下圖 |
| Revised Romanization | Cheonhado |
| McCune–Reischauer | Ch'ŏnhado |
The Cheonhado (hangul:천하도, hanja:天下圖, literally "Map of the world beneath the heavens"), or sometimes Cheonha jeondo (hangul:천하전도, hanja:天下全圖, literally "Complete map of the world beneath the heavens"), is a peculiar type of circular world map developed in Korea during the 17th century. It is based on the Korean term for map, jido, translated roughly as "land picture".[1]
Description
The Cheonhado maps were made in response to the encounter with the geographical knowledge of the West, but based in content on traditional Asian sources and Asian in style. The structure of the maps consists of an internal continent with historical place names, an internal sea with place names connected to descriptions of Taoist immortality, an external continent, and an external sea.[2] Surprisingly, the maps did not reflect the highest levels of geographic knowledge available to Koreans, but this is not likely to be intentional.[3] Some of this was due to the nautical distance between Korea and other Southeast Asian locales affected the mapmakers perceptions of Asia. Similarly, European mapmakers of the day often treated Korea as an island.
Some scholars have attributed the development of Korean circular world maps to Western influence, such as the maps of Matteo Ricci (Kunyu Wanguo Quantu) or the maps of Giulio Aleni (Wanguo Quantu). In this case, the central landmass can be viewed as a combination of Asia, Africa, and Europe, and the external "ring" continent as North America and South America.[4]
Such maps were produced in Korea only, and have not been found in China or Japan.[5]
The Cheonhado remained popular in Korea until the late 19th century.[6]
Gallery
 A coloured Cheonhado.
A coloured Cheonhado. Another Cheonhado map.
Another Cheonhado map. Another Cheonhado.
Another Cheonhado. Cheonhado, a 17th-century Korean circular world map.
Cheonhado, a 17th-century Korean circular world map.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Short, John Rennie. The World Through Maps (Firefly Books, 2003) pg.81
- ↑ Oh Sang-Hak, p.1
- ↑ Suarez, Thomas. Early Mapping Of Southeast Asia (Tuttle Publishing, 1999) pg. 50
- ↑ Oh Sang-Hak, p.16-17
- ↑ "Cheonhado (천하도 天下圖)" (in Korean). Doosan Encyclopedia. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
중국·일본 등에서는 찾아볼 수 없는 한국 고유의 세계지도이다.
- ↑ Suarez pg.50
References
- Oh Sang-Hak Circular World Maps of the Joseon Dynasty, KOREA JOURNAL, Spring 2008 Pdf
- Short, John Rennie (2003). "Map of the Far East". The World Through Maps: A History of Cartography. Firefly Books. pp. 80–81p. ISBN 1-55297-811-7. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
- Gunn, Geoffrey C. (2003). "5. Mapping Eurasia". First Globalization: The Eurasian Exchange, 1500-1800. Rowman & Littlefield. pp. 132–133p. ISBN 0-7425-2662-3. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
- Suarez, Thomas (1999). Early Mapping Of Southeast Asia. Tuttle Publishing. pp. 50 p. ISBN 962-593-470-7. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
- Hyun, Theresa. "Byron Lands in Korea: Translation and Literary/Cultural Changes in Early Twentieth-Century Korea". Canada: York University hosted by erudit. pp. 286 p. Retrieved 2008-07-31. External link in
|publisher=(help) - "Cheonhado (천하도 天下圖)" (in Korean). Empas / EncyKorea. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
- "Cheonhado (천하도 天下圖)" (in Korean). Empas / Britannica. Retrieved 2008-07-31.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cheonhado. |
- Yojido Ch'onhado at memory.loc.gov
- Ch'onhado
- (Korean) 천하도 at Sungshin Women's University