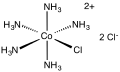
Chloropentamminecobalt chloride
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pentaamminechlorocobalt(III) chloride | |||
| Other names
Pentaamminechlorocobalt(III) chloride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 13859-51-3 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.163 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 | |||
| Molar mass | 250.4 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | red-violet rhomb-shaped crystal | ||
| Density | 1.783 g/mL | ||
| Boiling point | N/A | ||
| 0.4 g/100 mL | |||
| Vapor pressure | 5990 mm Hg | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−1.0376E+06 Jmol−1; Molar Gibbs energy of formation = −606480 J/mol | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Chloropentamminecobalt chloride is a cobalt coordination compound. It is a red-violet, diamagnetic, water-soluble salt with the formula [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2. The compound has been of academic and historical interest.
Synthesis and reactions
The complex is prepared with a two-step process starting with oxidizing a solution of cobalt chloride and ammonia.[1]
- 2 CoCl2,6H2O + 8 NH3 + 2 NH4Cl + H2O2 → 2 [Co(NH3)5(OH2)]Cl3 + 12 H2O
This intermediate is then heated to induce coordination of one of the outer sphere chloride ligands:
- [Co(NH3)5(OH2)]Cl3 → [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 + H2O
The complex is a dication with idealized C4v symmetry.[2]
In an aqueous solution, chloropentaamminecobalt(III) chloride reforms aquopentammine complex. With concentrated sulfuric acid, chloropentaamminecobalt(III) chloride forms the hydrogen sulfate complex.
History
Cobalt complexes have been of long interest because they are numerous, easily prepared, and colorful. It was partly on the basis of his study of cobalt coordination chemistry that Alfred Werner was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Prior to Werner, the models of amine complexes postulated chains of pentavalent nitrogen centers. This Jørgensen–Bloomstrand model was ovethrown by Werner who introduced the idea that coordination complexes feature metal atoms of octahedral and tetrahedral shapes, with ammonia and other ligands attached individually to the metal. Werner's model accounted for the inner sphere ligands being less reactive.[3] In [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2, two chlorides are outer sphere and one is bound to the Co(III) center.
References
- ↑ Gert G. Schlessinger (1967). "Chloropentaamminecobalt(III) Chloride". Inorganic Syntheses. 9: 160. doi:10.1002/9780470132401.ch43.
- ↑ G. G. Messmer; E. L. Amma (1968). "Redetermination of the crystal structure of chloropentaamminecobalt(III) dichloride". Acta Crystallogr. B. 24: 417–422. doi:10.1107/S0567740868002475.
- ↑ Template:Cjournal