Cimarron River (Arkansas River)
| Cimarron River | |
| River | |
 The Cimarron River, near Forgan, Oklahoma | |
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| States | Colorado, Kansas, New Mexico, Oklahoma |
| Cities | Cushing, Oklahoma, Mannford, Oklahoma |
| Source | Confluence of Dry Cimarron River and Carrizozo Creek |
| - location | Kenton, Cimarron County, Oklahoma |
| - elevation | 4,318 ft (1,316 m) |
| - coordinates | 36°54′24″N 102°59′12″W / 36.90667°N 102.98667°W [1] |
| Mouth | Arkansas River |
| - location | Keystone Lake, at Westport, Pawnee County, Oklahoma |
| - elevation | 722 ft (220 m) |
| - coordinates | 36°10′14″N 96°16′19″W / 36.17056°N 96.27194°WCoordinates: 36°10′14″N 96°16′19″W / 36.17056°N 96.27194°W [1] |
| Length | 698 mi (1,123 km) |
| Basin | 18,950 sq mi (49,080 km2) |
| Discharge | for Guthrie, Oklahoma, 65 miles (105 km) from the mouth |
| - average | 1,163 cu ft/s (33 m3/s) [2] |
| - max | 158,000 cu ft/s (4,474 m3/s) |
| - min | 0.3 cu ft/s (0 m3/s) |
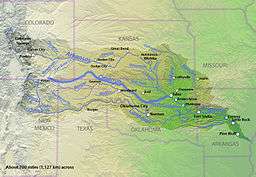 Map of the Arkansas River basin with the Cimarron River highlighted.
| |
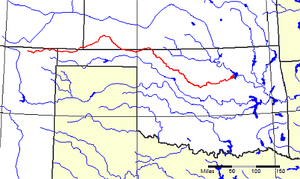
The Cimarron River extends 698 miles (1,123 km) across New Mexico, Oklahoma, Colorado, and Kansas. The headwaters flow from Johnson Mesa west of Folsom in northeastern New Mexico. Much of the river's length lies in Oklahoma, where it either borders or passes through eleven counties. There are no major cities along its route.The river enters the Oklahoma Panhandle near Kenton, crosses the southeastern corner of Colorado into Kansas, re-enters the Oklahoma Panhandle, re-enters Kansas, and finally returns to Oklahoma where it joins the Arkansas River at Keystone Reservoir west of Tulsa, Oklahoma, its only impoundment. The Cimarron drains a basin that encompasses about 18,927 square miles (49,020 km2).[3]
Etymology
The river's present name comes from the early Spanish name, Río de los Carneros Cimarrón, which is usually translated as River of the Wild Sheep. Early American explorers also called it the Red Fork of the Arkansas because of water's red color. Early explorers and map-makers called it by several other names, including Grand Saline, Jefferson (in John Melish's 1820 U.S. map), Red Fork, Salt Fork, and Salt River.[3]
Description

In New Mexico and extreme western Oklahoma the river is known as the Dry Cimarron River. This is by contrast to a wetter Cimarron River located further west and flows only through New Mexico. The Dry Cimarron River is not completely dry but sometimes its water disappears entirely under the sand in the river bed. The Dry Cimarron Scenic Byway follows the river from Folsom to the Oklahoma border. In Oklahoma the river flows along the southern edges of Black Mesa, the highest point in that state. As it first crosses the Kansas border, the river flows through the Cimarron National Grassland.
The quality of Cimarron water is rated as poor because the river flows through natural mineral deposits, salt plains, and saline springs, where it dissolves large amounts of minerals.[3] It also collects quantities of red soil, which it carries to its terminus. Before the Keystone Dam was built, this silt was sufficient to discolor the Arkansas River downstream.
Early explorers
The first Europeans to see the Cimarron River were apparently Spanish conquistadores led by Francisco Vásquez de Coronado in 1541. The Spanish seemed to do little to exploit the area. The Osage tribe claimed most of the territory west of the confluence of the Cimarron and the Arkansas as theirs. In 1819, Thomas Nuttall explored the lower Cimarron and wrote a report describing the flora and fauna that he found there. In 1821, Mexico threw off Spanish rule and William Becknell opened the Santa Fe Trail.[3]
Historical notes of interest
- One branch of the Santa Fe Trail, known variously as the Cimarron Route, the Cimarron Cutoff, and the Middle Crossing (of the Arkansas River), ran through the Cimarron Desert and then along the Cimarron River.[4]:144,148 Lower Cimarron Spring on the bank of the river was an important watering and camping spot.[5]
- In 1831 Comanche Indians killed Jedediah Smith (a famous hunter, trapper, and explorer) on the Santa Fe Trail near the Cimarron River. His body was never recovered.[6]
- In 1834 General Henry Leavenworth established Camp Arbuckle (Fort Arbuckle) at the mouth of the Cimarron River.[3] This fort, later known as Old Fort Arbuckle, was only active for about a year, and its former site is now submerged beneath the Arkansas River. It should not be confused with the later Fort Arbuckle in Garvin County, Oklahoma.
- Historic sites along the river include the ruins of Camp Nichols, a stone fort built by Kit Carson in 1865 to protect travelers from raids by Plains Indians on the Cimarron Cutoff. It was located near present-day Wheeless, Oklahoma.
- The old Chisholm Trail crossed the river at Red Fork Station near present-day Dover, Oklahoma.
- In the 1890s, the Creek Nation Cave along the Cimarron River near Ingalls in the Oklahoma Territory, was a hideout for the Doolin gang, which included the teenaged bandits, Cattle Annie and Little Britches.[7]
- On September 18, 1906, a bridge across the Cimarron near Dover, Oklahoma Territory, collapsed beneath a Rock Island train bound for Fort Worth, Texas from Chicago. The bridge was a temporary structure unable to withstand the pressure of debris and high water. Replacement with a permanent structure had been delayed by the railroad for financial reasons. Several sources report that over 100 persons were killed,[8][9][10] although this figure is disputed. The true number may be as low as four.[11]
See also
- List of rivers of Colorado
- List of rivers of Kansas
- List of rivers of New Mexico
- List of rivers of Oklahoma
- List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem)
- Cimarron National Grassland
- Maxwell National Wildlife Refuge (NWR)
- Point of Rocks (Kansas)
- Santa Fe Trail
References
- 1 2 "Cimarron River". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. 1979-12-18. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- ↑ "USGS Gage #07160000 on the Cimarron River near Guthrie, OK" (PDF). National Water Information System. U.S. Geological Survey. 1938–2009. Retrieved 2010-11-21.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Larry O'Dell, "Cimarron River," Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture. Accessed March 6, 2015.
- ↑ Stocking, Hobart (1971). The Road to Santa Fe. New York: Hastings House Publishers. ISBN 978-0-8038-6314-9.
- ↑ Whitacre, Christine; Steven De Vore (March 17, 1997). Patty Henry, ed. "LOWER CIMARRON SPRING NATIONAL HISTORIC LANDMARK NOMINATION USDI/NPS" (PDF). National Park Service. p. 36. Retrieved December 13, 2012.
- ↑ "Cimarron Cutoff". Santa Fe Trail Research Site. Retrieved 2013-09-30.
- ↑ "Cattle Annie & Little Britches, taken from Lee Paul [http://www.theoutlaws.com]". ranchdivaoutfitters.com. Archived from the original on January 17, 2012. Retrieved December 27, 2012. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ Kite, Steven (September 20, 2000). "Corporate Greed Leads to Death in Oklahoma Territory". Oklahoma Audio Almanac. Oklahoma State University Library. Archived from the original on June 4, 2010. Retrieved May 18, 2010.
- ↑ "Dover". Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture. Oklahoma Historical Society. Archived from the original on July 28, 2010. Retrieved May 18, 2010.
- ↑ Goins, Charles Robert; Goble, Danney (2006). Historical Atlas of Oklahoma. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 119. ISBN 0-8061-3482-8.
- ↑ Sencicle, Lorraine (January 2008). "Dover Oklahoma". The Daughters of Dover: Dover around the world. Dover, England: The Dover Society. Archived from the original on September 21, 2010. Retrieved May 22, 2010.
Further reading
- Anshutz, Carrie W. Schmoker; M.W. (Doc) Anshutz. Cimarron Chronicles: Saga of the Open Range. Meade, Kansas: Ohnick Enterprises, 2003. ISBN 0-9746222-0-6
- Dary, David. The Santa Fe Trail: Its History, Legends, and Lore. New York: Penguin, 2002 (Reissue). ISBN 0-14-200058-2
- Hanners, Laverne; Ed Lord. The Lords of the Valley: Including the Complete Text of Our Unsheltered Lives. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1996. ISBN 0-8061-2804-6
- Hoig, Stan. Beyond the Frontier: Exploring the Indian Country. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1998. ISBN 0-8061-3052-0
- Schumm, Stanley A. Channel Widening and Flood-Plain Construction along Cimarron River in Southwestern Kansas: Erosion and Sedimentation in a Semiarid Environment. Washington D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1963. ISBN B0007EFJLY
- Schumm, Stanley A. River Variability and Complexity. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2005. ISBN 0-521-84671-4
- Stovall, John Willis. Geology of the Cimarron River Valley in Cimarron County, Oklahoma. Chicago, 1938.
- Woodhouse, S. W. (Eds. John S. Tomer, Michael J. Brodhead). A Naturalist in Indian Territory: The Journals of S.W. Woodhouse, 1849-50 (The American Exploration and Travel Series, Vol 72). Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1996. ISBN 0-8061-2805-4
External links
| Look up cimarrón in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Cimarron River
- Santa Fe Trail Research Site
- Mouth of the Cimarron TopoQuest.
- Headwaters of the Cimarron TopoQuest.
- Cimarron National Grassland USDA Forest Service.
- Dry Cimarron Scenic Byway New Mexico Historic Markers.
- Kansas connections (Eco-History Trails and Tales)
- Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture - Cimarron River
- Oklahoma Digital Maps: Digital Collections of Oklahoma and Indian Territory