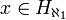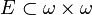Code (set theory)
In set theory, a code for a hereditarily countable set
is a set
such that there is an isomorphism between (ω,E) and (X,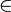 ) where X is the transitive closure of {x}. If X is finite (with cardinality n), then use n×n instead of ω×ω and (n,E) instead of (ω,E).
) where X is the transitive closure of {x}. If X is finite (with cardinality n), then use n×n instead of ω×ω and (n,E) instead of (ω,E).
According to the axiom of extensionality, the identity of a set is determined by its elements. And since those elements are also sets, their identities are determined by their elements, etc.. So if one knows the element relation restricted to X, then one knows what x is. (We use the transitive closure of {x} rather than of x itself to avoid confusing the elements of x with elements of its elements or whatever.) A code includes that information identifying x and also information about the particular injection from X into ω which was used to create E. The extra information about the injection is non-essential, so there are many codes for the same set which are equally useful.
So codes are a way of mapping 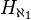 into the powerset of ω×ω. Using a pairing function on ω (such as (n,k) goes to (n2+2·n·k+k2+n+3·k)/2), we can map the powerset of ω×ω into the powerset of ω. And we can map the powerset of ω into the Cantor set, a subset of the real numbers. So statements about
into the powerset of ω×ω. Using a pairing function on ω (such as (n,k) goes to (n2+2·n·k+k2+n+3·k)/2), we can map the powerset of ω×ω into the powerset of ω. And we can map the powerset of ω into the Cantor set, a subset of the real numbers. So statements about 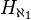 can be converted into statements about the reals. Consequently,
can be converted into statements about the reals. Consequently, 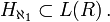
Codes are useful in constructing mice.
See also
References
- William J. Mitchell,"The Complexity of the Core Model","Journal of Symbolic Logic",Vol.63,No.4,December 1998,page 1393.