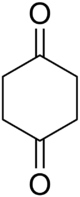
1,4-Cyclohexanedione
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,4-Cyclohexanedione | |
| Identifiers | |
| 637-88-7 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28286 |
| ChemSpider | 11995 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.279 |
| EC Number | 211-306-0 |
| KEGG | C08063 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 112.127 g/mol |
| Melting point | 77 to 78.5 °C (170.6 to 173.3 °F; 350.1 to 351.6 K) |
| Boiling point | 130 to 133 °C (266 to 271 °F; 403 to 406 K) (20 mm.) |
| Hazards | |
| S-phrases | S22,S23,S24,S25 |
| Flash point | 132 °C (270 °F; 405 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
1,4-Cyclohexanedione is an organic compound. This tan or yellow crystalline solid is one of the three isomeric cyclohexanediones. This particular diketone is used as a building block in the synthesis of more complex molecules.
Preparation
1,4-Cyclohexanedione is prepared in two steps from diesters of succinic acid. For example under basic conditions, the diethyl ester condenses to give 2,5-dicarbethoxy-1,4-cyclohexanedione. This intermediate can be hydrolysed and decarboxylated to afford the desired dione.[2]
References
- ↑ MSDS for 1,4-Cyclohexanedione
- ↑ Arnold T. Nielsen and Wayne R. Carpenter (1973). "1,4-Cyclohexanedione". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol., 5, p. 288
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/10/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.