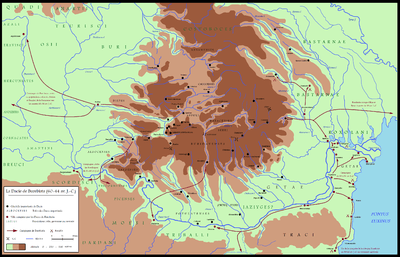
Dava (Dacian)
Dava (Latin alphabet plural davae) is a Geto-Dacian name for a city, town or fortress. Generally, the name indicated a tribal center or an important settlement, usually fortified. Some of the Dacian settlements and the fortresses employed the Murus Dacicus traditional construction technique.
Many city names of the Dacians were composed of an initial lexical element (often the tribe name) affixed to -dava, -daua, -deva, -deba, -daba or -dova (<PIE *dʰeh₁-, "to set, place").[1]
Most of these towns are attested by Ptolemy, and therefore date from the 1st century CE.
Therefore, dava 'town' derived from the reconstructed proto-Indo-European *dhewa 'settlement',[2] cognate with Zazaki dewe, meaning "village".
The "dava" towns can be found as south as Sandanski and Plovdiv. Strabo specified that the Daci are the Getae. The Dacians, Getae and their kings were always considered as Thracians by the ancients (Dio Cassius, Trogus Pompeius, Appian, Strabo, Herodotus and Pliny the Elder), and were both said to speak the same Thracian language.
List of davae
Below is a list of Dacian towns which include various forms of dava in their name:

- Acidava[3] (Acidaua), a fortress town close to the Danube. Located in today's Enoşeşti, Olt County, Romania
- Aedava[4] (Aedeva, Aedabe, Aedeba or Aedadeba), placed by Procopius on the Danubian road between Augustae and Variana,[1] in Moesia (the present Northern Bulgaria)
- Aiadava[1] (Aiadaba or Aeadaba, Greek: Αἰάδαβα[5]), was a locality in the Remesiana region, present Bela Palanka, Serbia.[6]
- Argedava[7] (Argedauon, Sargedava, Sargedauon, Zargedava, Zargedauon, Ancient Greek: Αργεδαυον, Σαργεδαυον), mentioned in the Decree of Dionysopolis, potentially the dava discovered at Popeşti, a district in the town of Mihăilești, Giurgiu County, Romania and maybe Burebista's court/capital
- Argidava (Argidaua, Arcidava, Arcidaua, Argedava, Argedauon, Sargedava, Sargedauon, Zargedava, Zargedauon, Ancient Greek: Ἀργίδαυα, Αργεδαυον, Σαργεδαυον), potentially Burebista's court/capital, located in today's Vărădia, Caraş-Severin County, Romania
- Bregedaba
- Buricodava[3]
- Buridava[8] or Burridava, today's Ocnele Mari, Romania
- Buteridava[3]
- Capidava[3] or Kapidaua, a fortress town on the southern side of the lower Danube
- Carsidava or Karsidaua
- Cumidava,[3] Comidava or Komidaua, ancient Râşnov, Romania
- Dausdava, Dausadava or Dausdavua,[3] "The shrine of wolves", a fortress town close to the Danube
- Desudaba
- Deva nowadays Romanian city near to Sarmisegetuza
- Docidava or Dokidaua
- Gildova[9] or Gildoba, located alongside the Vistula river
- Giridava[9]
- Itadeba[9] or Itadava, in north eastern Republic of Macedonia
- Jidava,[3] near Câmpulung Muscel, Romania
- Jidova[3]
- Klepidaua
- Kuimedaba
- Marcodava or Markodaua
- Murideba
- Nentinava[8] or Netindaua, ancient Slobozia, Romania
- Nentivava,[3] ancient Oltenița, Romania
- Patridava or Patridaua
- Pelendava[3] or Pelendova, ancient Craiova, Romania
- Perburidava
- Petrodava[8] or Petrodaua located in Piatra Neamţ
- Piroboridava or Piroboridaua
- Pulpudeva, originally named Eumolpias by the Dacians. Philip II of Macedon conquered the area in 342-341 BC and renamed the city Philippoupolis (Greek: Φιλιππούπολις), of which the later Dacian name for the city, Pulpu-deva, is a reconstructed translation. Today's city of Plovdiv in Bulgaria.
- Quemedava, mentioned by Procopius in Dardania [10]
- Ramidava or Rhamidaua
- Recidava
- Rusidava[3] or Rusidava
- Sacidava or Sacidaba
- Sagadava
- Sandava
- Sangidaua
- Scaidava or Skedeba
- Setidava[3] or Setidaua, mentioned by Ptolemy as a thriving settlement
- Singidava or Singidaua
- Sucidava,[3] Suvidava or Sukidaua located in Corabia, Olt County, Romania
- Susudava,[3] mentioned by Ptolemy as a thriving settlement
- Sykidaba
- Tamasidava or Tamasidaua
- Thermidaua or Germidava,[11] a town in Dalmatia, probably found by immigrants from Dacia and mentioned by Ptolemy,[12] near Scodra [10]
- Utidava or Utidaua
- Zargidava or Zargidaua
- Ziridava or Ziridaua
- Zisnedeva,[3] Zisnudeva or Zisnudeba, located in Dacian Moesia
- Zucidaua
- Zisnudeba
- Zusidava
See also
Notes
- 1 2 3 Olteanu.
- ↑ Polome 1982, p. 886.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Grumeza 2009, p. 13.
- ↑ Velkov 1977, p. 92.
- ↑
- Procopii Caesariensis opera omnia. Edited by J. Haury; revised by G. Wirth. 3 vols. Leipzig: Teubner, 1976-64. Greek text.
- ↑ TSR9, Proc. 123. 26
- ↑ Grumeza 2009, p. 88.
- 1 2 3 Grumeza 2009, p. 12.
- 1 2 3 Grumeza 2009, p. 14.
- 1 2 Ethnic continuity in the Carpatho-Danubian area by Elemér Illyés,1988,ISBN 0-88033-146-1,page 223
- ↑ Five Roman emperors: Vespasian, Titus, Domitian, Nerva, Trajan, A.D. 69-117 - by Bernard William Henderson - 1969, page 278,"At Thermidava he was warmly greeted by folk quite obviously Dacians"
- ↑ The Geography by Ptolemy, Edward Luther Stevenson,1991,page 36
References
- Grumeza, Ion (2009). Dacia: Land of Transylvania, Cornerstone of Ancient Eastern Europe. Hamilton Books. ISBN 0-7618-4465-1.
- Velkov, Velizar Iv (1977). The cities in Thrace and Dacia in late antiquity: (studies and materials). Hakkert. ISBN 90-256-0723-3.
- Olteanu, Sorin. "Linguae Thraco-Daco-Moesorum - Toponyms Section". Linguae Thraco-Daco-Moesorum (in Romanian and English). Retrieved 8 December 2010.
- Polome, E. C. (1982). "20e". In Boardman, John. The Cambridge ancient history. London: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-22496-3.
- Tomaschek, Wilhelm (1883). "Les Restes de la langue dace" in "Le Muséon, Volume 2". Belgium: "Société des lettres et des sciences" Louvain, Belgium.
- Joseph, Van Den Gheyn (1885). Les populations Danubiennes'. Belgium: "Revue des questions scientifiques, Volumes 17-18" by "Société scientifique de Bruxelles".
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dacian and Dacians. |
- Dacian Davae in Enciclopedia Dacica (Romanian)
- Dacian materials and construction techniques in Enciclopedia Dacica (Romanian)
- Sorin Olteanu's Project: Linguae Thraco-Daco-Moesorum - Toponyms Section (Romanian, partially English)
- Lists of Dacian fortresses, towns and citadels