Des Voeux Road
| <span class="nickname" ">德輔道 | |
 Des Voeux Road Central in Central | |
| Location | Hong Kong |
|---|---|
| Construction | |
| Construction start | 1857 |
| Completion | 1904 |
| Des Voeux Road Central | |||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 德輔道中 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 德辅道中 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Des Voeux Road West | |||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 德輔道西 | ||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 德辅道西 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Des Voeux Road Central and Des Voeux Road West are two roads on the north shore of Hong Kong Island, Hong Kong. They were named after the 10th Governor of Hong Kong, Sir William Des Vœux. The name was predominantly spelt with the ligature œ in pre-war documents but is nowadays spelt officially as Des Voeux Road.
History
Beginning in 1857, the northern shore of Hong Kong Island (also known as Victoria City) underwent a series of reclamations under then-Governor Sir John Bowring. The first phase of the Praya Reclamation Scheme had a direct effect on this current street, which used to be known as Praya Central during the Colonial Hong Kong era.[1] Bowring's plans were opposed by British merchants who held lands in the Central area, and in response, the government instead commenced work in land reclamation in the Chinese-populated Western District. By the time the reclamation was extended to Central, the newly reclaimed land in Western had already been settled, and there was a discontinuity between the two roads running along the western and middle portions of the reclaimed shoreline. Upon completion, the roads were named Bowring Praya West and Bowring Praya Central respectively.
Another series of extensive reclamation projects began in 1887 under then-Governor Des Voeux. Upon completion in 1904, Bowring Praya West and Bowring Praya Central (which by then were situated inland from the shoreline) were respectively renamed Des Voeux Road West and Des Voeux Road Central per the orders of then-Colonial Secretary and acting Governor Francis Fleming during the Duke of Connaught's visit to Hong Kong in 1890.
From 1942 to 1945, the road was renamed Shōwa-dori by the Japanese occupation government.
Des Voeux Road Central
Des Voeux Road Central runs from Western to Central. It begins at the intersection with On Tai Street in Western and merges with Queen's Road Central where it becomes Queensway (and, later, Hennessy Road). Landmarks along Des Voeux Road Central include:
- 9 Queen's Road Central
- Alexandra House
- Bank of China Building (#2A), which houses the China Club
- Central Market
- Hang Seng Bank Headquarters Building
- HSBC Main Building, Hong Kong
- Man Yee Building
- Prince's Building
- Standard Chartered Bank Building
- Statue Square
- The Landmark
- Western Market (#323)[2]
- Wing On House (#71)
- World-Wide House
Des Voeux Road West

Des Voeux Road West runs from Western Shek Tong Tsui. It reaches an alignment several blocks down at the junction with Connaught Road West and becomes Kennedy Town Praya in Shek Tong Tsui.
Pedestrianisation proposal

Various groups have long proposed pedestrianising a section of Des Voeux Road Central. The idea was first proposed in 2000 by the Hong Kong Institute of Planners (HKIP) in collaboration with the MTR Corporation and the MVA Asia traffic engineering firm. The proposal was deemed technically feasible but was not implemented by the government.
The plan involves converting a 1.4 km section of Des Voeux Road Central, between Pedder Street and the Western Market, from a thoroughfare for motorised traffic to a pedestrian zone. The tramway would be maintained in situ and the cross-streets would remain open to traffic. Bus routes would be diverted onto Connaught Road. The pedestrian zone would remain open to delivery vehicles and emergency services.[3]
The proposal was updated in 2014 in light of various infrastructure projects that will significantly increase the east-west transport capacity in the area, namely the West Island Line and the Central-Wanchai Bypass. It was resubmitted by HKIP, Civic Exchange, City University of Hong Kong, and MVA. In 2015 a lobby group was formed called Des Voeux Road Central Initiative, comprising a variety of groups including the Clean Air Network, the Conservancy Association, Knight Frank, Friends of the Earth (HK), Designing Hong Kong, the Hong Kong Institute of Landscape Architects, and the Hong Kong Public Space Initiative.
Public transportation
Des Voeux Road Central is shared between motor traffic and the tram line, with tracks and reserved lanes for the trams laid in the middle of the road. A bus lane runs along the road for most of its length. Part of the MTR Island Line also runs underneath Des Voeux Road.
Due to the discontinuity between Des Voeux Roads Central and West, the tram line takes a detour along Connaught Road West and then continues along Des Voeux Road West towards Kennedy Town.
The Central-Mid-Levels escalators link Des Voeux Road Central with Conduit Road in the Mid-levels, passing through narrow streets.
Des Voeux Road, Hunghom
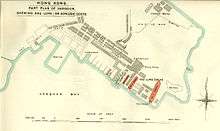
A street called Des Voeux Road existed in Kowloon along Hunghom Bay. The street no longer exists following extensive re-development of the area.
See also
References
- Leung, To (1992). Origins of Hong Kong Street Names. Urban Council.
- ↑ Wordie, Jason (2002). Streets: Exploring Hong Kong Island. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press. ISBN 962-209-563-1.
- ↑ "Declared Monuments in Hong Kong: Western Market". Lcsd.gov.hk. 2013-01-18. Retrieved 2013-01-23.
- ↑ Fung, Fanny (29 April 2014). "Transform Des Voeux Road into pedestrian-tram green zone, Hong Kong planners urge". South China Morning Post.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Des Voeux Road. |
- Hong Kong Place: Hong Kong streets named after colonial governors (Taiwanese Mandarin)
- Des Voeux Road Central Inititative (pedestrianisation proposal)
Coordinates: 22°16′58.62″N 114°9′25.25″E / 22.2829500°N 114.1570139°E