Deslorelin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ovuplant, Suprelorin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | implant / Inhalation |
| ATCvet code | QH01CA93 (WHO) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Excretion | renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
57773-65-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 16133804 |
| ChemSpider |
16736553 |
| UNII |
TKG3I66TVE |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL2365665 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.165.050 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
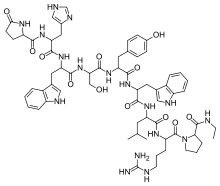
| Formula | C64H83N17O12 |
| Molar mass | 1282.45 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Deslorelin acetate is an injectable gonadotropin releasing hormone super-agonist (GnRH agonist) also known as an LHRH agonist. It stops the production of sex hormones (testosterone and oestrogen).
One commercial form of Deslorelin Acetate is marketed by Peptech with the brand name Ovuplant.[1] Another form is available in the USA, Sucromate Equine,[2] which was FDA-approved for use in horses in November 2010.[3] This is manufactured by Thorne BioScience LLC and was introduced to the USA market following the withdrawal of Ovuplant. The Deslorelin products are currently approved for use in veterinary medicine and to promote ovulation in mares as part of the artificial insemination process. It is also used to stabilize high-risk pregnancies, mainly of livestock. Unlike other GnRH agonists, which are mainly used to inhibit luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone by their ultimate downregulation of the pituitary gland, Deslorelin is primarily used for the initial flare effect upon the pituitary, and its associated surge of LH secretion. Suprelorin is a slowly releasing deslorelin implant used for chemical castration of dogs and ferrets. It is marketed by Virbac. Deslorelin is also used to treat benign prostate hyperplasia in dogs.
Buserelin is a similar GnRH agonist used in humans.
Pharmacokinetics
Deslorelin is a synthetic analogue of a naturally occurring luteinising-hormone releasing hormone (LHRH). Bioavailability is almost complete.
Clinical trials
Deslorelin was successfully trialed in the US and was approved for veterinary use under certain circumstances. In Europe, it was approved for use in equine assisted reproduction.[4]
Ovuplant was withdrawn from the US market following issues with mares which did not become pregnant failing to return to estrus in a timely manner. Techniques were developed where the implant was removed 48 hours after implantation in the mare,[5] however compounded biorelease Deslorelin products were at the time available as well as more commonly used ovulation promoters such as hCG, which did not produce the same failure effect. Upon "Sucromate Equine" receiving FDA-approval, the compounded products were no longer legally available within the USA, however they remain available in Australia and New Zealand where an approved version is marketed.
It is also being trialed in humans to study its efficacy in treatment of breast cancer in women,[6] and in treating precocious puberty and congenital adrenal hyperplasia in male and female children.[7]
As of August 2011 this drug was not approved for general use outside the FDA-licensed functions in the US, other than within approved clinical trials. Orphan drug status has been designated in the US, though approval had not been issued as of 2011.[8]
References
- ↑ Peptech official Ovuplant site
- ↑ Thorne BioScience official Sucromate site
- ↑ FDA Approval Release
- ↑ Deslorelin Acetate - European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products
- ↑ McCue PM, Farquhar VJ, Carnevale EM, Squires EL. 2002. Removal of deslorelin (Ovuplant) implant 48 h after administration results in normal interovulatory intervals in mares. Theriogenology 58(5):865-70
- ↑ Deslorelin Combined With Low-Dose Add-Back Estradiol and Testosterone in Preventing Breast Cancer in Premenopausal Women Who Are at High Risk for This Disease - National Cancer Institute
- ↑ Three Drug Combination Therapy Versus Conventional Treatment of Children With Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia - National Institutes of Health Clinical Center
- ↑ "Results for Orphan Drug Product Designations Search". FDA. Retrieved 3 September 2011.