Digallic acid
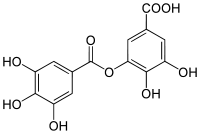 meta-depside bond digalloyl ester | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,4-Dihydroxy-5-[(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy]benzoic acid | |
| Other names
Digallate 3,4-dihydroxy-5-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyloxy)benzoate m-digallic acid Digalloyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| 536-08-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL366356 |
| ChemSpider | 334 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.842 |
| PubChem | 341 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H10O9 | |
| Molar mass | 322.22 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Digallic acid is a polyphenolic compound found in Pistacia lentiscus.[1] Digallic acid is also present in the molecule of tannic acid.[2] Digalloyl esters involve either -meta or -para depside bonds.[3]
Tannase is an enzyme that uses digallate to produce gallic acid. This enzyme can also be used to produce digallic acid from gallotannins.[4]
References
- ↑ Bhouri, W.; Derbel, S.; Skandrani, I.; Boubaker, J.; Bouhlel, I.; Sghaier, M. B.; Kilani, S.; Mariotte, A. M.; Dijoux-Franca, M. G.; Ghedira, K.; Chekir-Ghedira, L. (2010). "Study of genotoxic, antigenotoxic and antioxidant activities of the digallic acid isolated from Pistacia lentiscus fruits". Toxicology in Vitro. 24 (2): 509–515. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2009.06.024. PMID 19563883.
- ↑ Delahaye, P.; Verzele, M. (1983). "Analysis of gallic, digallic and trigallic acids in tannic acids by high-performance liquid chromatography". Journal of Chromatography A. 265: 363–367. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(01)96734-2.
- ↑ Tannin chemistry, by Ann E. Hagerman
- ↑ Nierenstein, M. (1932). "A biological synthesis of m-digallic acid". The Biochemical Journal. 26 (4): 1093–1094. doi:10.1042/bj0261093. PMC 1261008
 . PMID 16744910.
. PMID 16744910.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/5/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.