Xylidine
Xylidine can refer to any of the six isomers of xylene amine, or any mixture of them. All isomers are toxic.
The chemical formula of xylidines is C8H11N, or (CH3)2C6H3NH2. They are stable and combustible and react with strong oxidizing agents. They may be light sensitive. The CAS number for the isomer mixture is
Xylidines are produced as byproducts of fractional distillation of coal tar.
Their risk and safety phrases are R20 R22 R36 R37 R38.
Xylidines are chiefly used in production of pigments and dyestuffs, and also various antioxidants, agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and many other organic chemicals.
Xylidines are also used as a component of the Tonka rocket fuel.
2,3-xylidine
2,3-xylidine, also called o-xylidine, 2,3-dimethylaniline, 2,3-xylylamine, or 2,3-dimethylphenylamine, is a liquid with melting point 2.5 °C and boiling point 222 °C, and flash point at 96 °C. Its CAS number is
2,4-xylidine
2,4-xylidine, also called 2-methyl-p-toluidine, 2,4-dimethylaniline, 2,4-xylylamine, or 2,4-dimethylphenylamine, is a liquid with melting point 16 °C, boiling point 217 °C, and flash point at 90 °C. Its CAS number is
2,5-xylidine
2,5-xylidine, also called p-xylidine, 2,5-dimethylaniline, 2,5-xylylamine, or 2,5-dimethylphenylamine, is a liquid with melting point 11.5 °C and boiling point 215 °C. Its CAS number is
2,6-xylidine
2,6-Xylidine, also called 2,6-dimethylaniline, 2,6-xylylamine, or 2,6-dimethylphenylamine, is a liquid with melting point 8.4 °C and boiling point 216 °C. Its CAS number is
3,4-xylidine
3,4-xylidine, also called 3,4-dimethylaniline, 3,4-xylylamine, or 3,4-dimethylphenylamine, is a crystalline solid with melting point 51 °C and boiling point 226 °C. Its CAS number is
3,5-xylidine
3,5-xylidine, also called 3,5-dimethylaniline, 3,5-xylylamine, or 3,5-dimethylphenylamine, is a liquid with melting point 9.8 °C and boiling point 220–221 °C. Its CAS number is
Safety
People can be exposed to xylidines in the workplace by breathing them in, skin absorption, swallowing them, and eye contact. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the legal limit (Permissible exposure limit) for xylidine exposure in the workplace as 5 ppm (25 mg/m3) skin exposure over an 8-hour workday. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a Recommended exposure limit (REL) of 2 ppm (10 mg/m3) skin exposure over an 8-hour workday. At levels of 50 ppm, xylidine is immediately dangerous to life and health.[1]
-
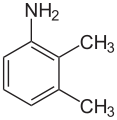
2,3-xylidine
-
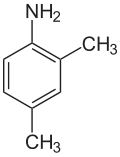
2,4-xylidine
-
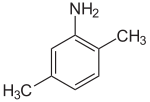
2,5-xylidine
-
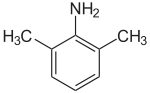
2,6-xylidine
-
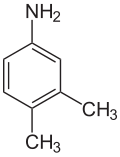
3,4-xylidine
-
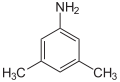
3,5-xylidine
External links
References
- ↑ "CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards - Xylidine". www.cdc.gov. Retrieved 2015-11-28.