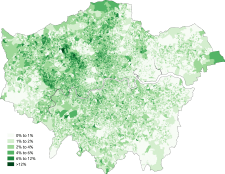
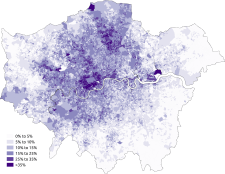
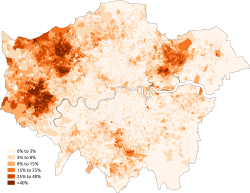
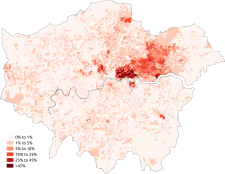
Ethnic groups in London

London is one of the most ethnically diverse cities in the world. In 2007 there were over 300 languages spoken in it and more than 50 non-indigenous communities with a population of more than 10,000.[1]
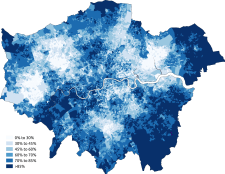
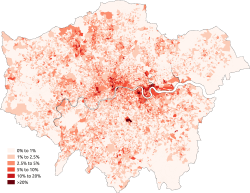
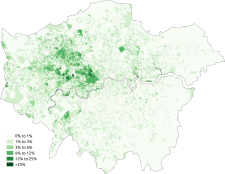
At the 2011 census London had a population of 8,173,941. Of this number, 44.9% were White British. 37% of the population were born outside the UK, including 24.5% born outside of Europe.[2]
Ethnic breakdown
2011 Census
| Number | Percentage of total population[3] | |
| White: English/Welsh/Scottish/Northern Irish/British | 3,669,284 | 44.9 |
| White: Irish | 175,974 | 2.2 |
| White: Gypsy or Irish Traveller | 8,196 | 0.1 |
| White: Other White | 1,033,981 | 12.6 |
| White: Total | 4,887,435 | 59.8 |
| Mixed/multiple ethnic group: White and Black Caribbean | 119,425 | 1.5 |
| Mixed/multiple ethnic group: White and Black African | 65,479 | 0.8 |
| Mixed/multiple ethnic group: White and Asian | 101,500 | 1.2 |
| Mixed/multiple ethnic group: Other Mixed | 118,875 | 1.5 |
| Mixed/multiple ethnic group: Total | 405,279 | 5.0 |
| Asian/Asian British: Indian | 542,857 | 6.6 |
| Asian/Asian British: Pakistani | 223,797 | 2.7 |
| Asian/Asian British: Bangladeshi | 222,127 | 2.7 |
| Asian/Asian British: Chinese | 124,250 | 1.5 |
| Asian/Asian British: Other Asian | 398,515 | 4.9 |
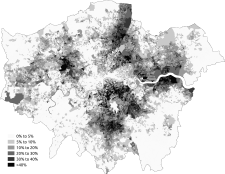
| Asian/Asian British: Total | 1,511,546 | 18.4 |
| Black/African/Caribbean/Black British: African | 573,931 | 7.0 |
| Black/African/Caribbean/Black British: Caribbean | 344,597 | 4.2 |
| Black/African/Caribbean/Black British: Other Black | 170,112 | 2.1 |
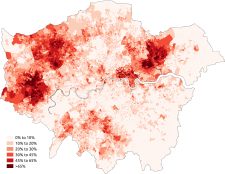
| Black/African/Caribbean/Black British: Total | 1,088,640 | 13.3 |
| Other ethnic group: Arab | 106,020 | 1.3 |
| Other ethnic group: Any other ethnic group | 175,021 | 2.1 |
| Other ethnic group: Total | 281,041 | 3.4 |
| Total | 8,173,941 | 100 |
| Distribution of ethnic groups in Greater London according to the 2011 census. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Black population of London
At the 2011 census, the total Black population of London stood at 1,088,640.[4] This is a rise of 39% from the 2001 census, when the population stood at 781,751.
Inner London and Outer London have a near-equal black population. The 2011 census is the first time that the black population in Outer London has overtaken that of Inner London:
| Black African Population | Black Caribbean Population | Other Black Population | Total Black Population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inner London | 276,513 | 173,959 | 89,709 | 540,181 |
| Outer London | 297,418 | 170,638 | 80,403 | 548,459 |
| London | 573,931 | 344,597 | 170,112 | 1,088,640 |
The black population of London is concentrated across the city. Southwark has the highest Black African population, Croydon has the highest Black Caribbean population and Lambeth has the highest total black population in London. The twenty London boroughs with the highest total Black population (Black African, Black Caribbean and Other Black) are listed below:
| Rank | London Borough | Black African Population | Black Caribbean Population | Other Black Population | Total Black Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lambeth | 35,187 | 28,886 | 14,469 | 78,542 |
| 2 | Southwark | 47,413 | 17,974 | 12,124 | 77,511 |
| 3 | Lewisham | 32,025 | 30,854 | 12,063 | 74,942 |
| 4 | Croydon | 28,981 | 31,320 | 12,955 | 73,256 |
| 5 | Newham | 37,811 | 15,050 | 7,395 | 60,256 |
| 6 | Brent | 24,391 | 23,723 | 10,518 | 58,632 |
| 7 | Hackney | 27,976 | 19,168 | 9,714 | 56,858 |
| 8 | Enfield | 28,222 | 17,334 | 8,131 | 53,687 |
| 9 | Greenwich | 35,164 | 8,051 | 5,440 | 48,655 |
| 10 | Haringey | 23,037 | 18,087 | 6,706 | 47,830 |
| 11 | Waltham Forest | 18,815 | 18,841 | 7,135 | 44,791 |
| 12 | Barking and Dagenham | 28,685 | 5,227 | 3,228 | 37,140 |
| 13 | Ealing | 17,299 | 13,192 | 6,369 | 36,860 |
| 14 | Barnet | 19,392 | 4,468 | 3,571 | 27,431 |
| 15 | Islington | 12,622 | 7,943 | 5,729 | 26,294 |
| 16 | Redbridge | 12,357 | 9,064 | 3,424 | 24,845 |
| 17 | Hammersmith and Fulham | 10,552 | 7,111 | 3,842 | 21,505 |
| 18 | Merton | 10,442 | 8,126 | 2,243 | 20,811 |
| 19 | Hillingdon | 11,275 | 4,615 | 4,192 | 20,082 |
| 20 | Harrow | 8,526 | 6,812 | 4,370 | 19,708 |
Asian population of London
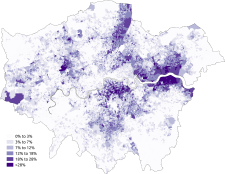
At the 2011 census, the total Asian population of London stood at 1,511,546.[4] This is a rise of 60% from the 2001 census, when the population stood at 947,425.
Outer London has a greater Asian population than Inner London:
| Indian Population | Pakistani Population | Bangladeshi Population | Chinese Population | Other Asian Population | Total Asian Population | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inner London | 109,933 | 59,890 | 163,838 | 65,983 | 115,549 | 515,193 |
| Outer London | 432,924 | 163,907 | 58,289 | 58,267 | 282,966 | 996,353 |
| London | 542,857 | 223,797 | 222,127 | 124,250 | 398,515 | 1,511,546 |
The Asian population of London is noticeably concentrated in East and West London. Harrow has the highest Indian population, Redbridge has the highest Pakistani population and Tower Hamlets has the highest Bangladeshi and Chinese population. Newham has the highest total Asian population in London. The twenty London boroughs with the highest total Asian population (Indian, Pakistani, Bangladeshi, Chinese and Other Asian) are listed below.
| Rank | London Borough | Indian Population | Pakistani Population | Bangladeshi Population | Chinese Population | Other Asian Population | Total Asian Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Newham | 42,484 | 30,307 | 37,262 | 3,930 | 19,912 | 133,895 |
| 2 | Redbridge | 45,660 | 31,051 | 16,011 | 3,000 | 20,781 | 116,503 |
| 3 | Brent | 58,017 | 14,381 | 1,749 | 3,250 | 28,589 | 105,986 |
| 4 | Tower Hamlets | 6,787 | 2,442 | 81,377 | 8,109 | 5,786 | 104,501 |
| 5 | Harrow | 63,051 | 7,797 | 1,378 | 2,629 | 26,953 | 101,808 |
| 6 | Ealing | 48,240 | 14,711 | 1,786 | 4,132 | 31,570 | 100,439 |
| 7 | Hounslow | 48,161 | 13,676 | 2,189 | 2,405 | 20,826 | 87,257 |
| 8 | Hillingdon | 36,795 | 9,200 | 2,639 | 2,889 | 17,730 | 69,253 |
| 9 | Haringey | 36,795 | 9,200 | 2,639 | 2,889 | 17,730 | 69,253 |
| 10 | Barnet | 27,920 | 5,344 | 2,215 | 8,259 | 22,180 | 65,918 |
| 11 | Croydon | 24,660 | 10,865 | 2,570 | 3,925 | 17,607 | 59,627 |
| 12 | Waltham Forest | 9,134 | 26,347 | 4,632 | 2,579 | 11,697 | 54,389 |
| 13 | Merton | 8,106 | 7,337 | 2,216 | 2,618 | 15,866 | 36,143 |
| 14 | Camden | 6,083 | 1,489 | 12,503 | 6,493 | 8,878 | 35,446 |
| 15 | Enfield | 11,648 | 2,594 | 5,599 | 2,588 | 12,464 | 34,893 |
| 16 | Wandsworth | 8,642 | 9,718 | 1,493 | 3,715 | 9,770 | 33,338 |
| 17 | Westminster | 7,213 | 2,328 | 6,299 | 5,917 | 10,105 | 31,862 |
| 18 | Greenwich | 7,836 | 2,594 | 1,645 | 5,061 | 12,758 | 29,894 |
| 19 | Barking and Dagenham | 7,436 | 8,007 | 7,701 | 1,315 | 5,135 | 29,594 |
| 20 | Southwark | 5,819 | 1,623 | 3,912 | 8,074 | 7,764 | 27,192 |
Foreign-born population
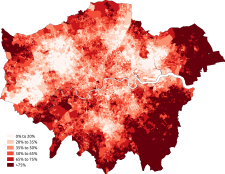
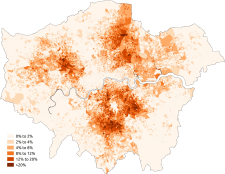
At the 2011 census, 36.7% of London's population was foreign born (including 24.5% born outside of Europe).[5] With 3,082,000 residents born abroad in 2014.[6] London has the largest population number (not percentage) of foreign-born.[6]
| Population born in the UK | Population Foreign-Born | |
|---|---|---|
| Inner London | 2,012,000 | 1,325,000 |
| Outer London | 3,348,000 | 1,757,000 |
| London | 5,359,000 | 3,082,000 |
| % born in the UK | % Foreign-Born | |
|---|---|---|
| Inner London | 57.8 | 42.2 |
| Outer London | 66.9 | 33.1 |
| London | 63.3 | 36.7 |
Significant ethnic minority communities
Arabs
Significant migration from Arab countries to the UK began in the 1940s, mostly by Egyptians. Other waves followed, such as Lebanese fleeing the civil war. The centre of London has a thriving Arab community, centered around Edgware Road.[7]
Bangladeshis
A major wave of immigration began in the 1970s, as people from the Sylhet region arrived in London, fleeing poverty and the Bangladesh Liberation War. Many settled around Brick Lane, where they entered the textile trade. This trade has declined causing unemployment, but the community has moved into other businesses, including restaurants and banking. The level of immigration peaked in 1986 and has since entered a decline with the introduction of harsher immigration laws.
The community remains concentrated around Bethnal Green and Whitechapel and has spread into other east London boroughs. London as a city is home to the single largest number of people of Bangladeshi origin outside of Bangladesh, with close to 200,000 individuals being of full Bangladeshi origin in 2007.
Chinese
Chinese people constitute the fourth largest Asian group in London (behind the Indians, Pakistanis and Bangladeshis respectively); numbering 114,800 in 2007, they are spread more or less across the entire city and have become successful in British life, especially when it comes to cuisine. The history of the Chinese in London is long and complex, with the first Chinese people arriving in the city in the 19th century as sailors.
Germans

Fiona Moore, author of "The German School in London, UK: Fostering the Next Generation of National Cosmopolitans?", wrote that the London German community "relies on subtle network connections rather than the displaying of obvious membership traits", since London Germans attended the same churches, joined the same clubs, and sent their children to the same schools.[8] According to Moore this aspect was likely influenced by the outcomes of World War I and World War II, resulting in encouragement for UK-based Germans "to try to blend in to a greater degree than elsewhere."[8]
The German business and expatriate community is centred on the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, which houses the German School London (DSL) and most German expatriates residing in London. Moore wrote that the borough "does not immediately show signs of hosting a German community" due to a lack of obvious German businesses and storefronts,[8] but that most residents know of the location of the DSL and that there are "more subtle signs of German presence."[9]
German expatriates are located throughout London. Some of them do not go to the Borough of Richmond upon Thames even though the centre of the German community is located there.[8]
Ghanaians
Besides Nigerians, Ghanaians are one of the largest Black African groups in London, with the majority living in the boroughs of Southwark, Lambeth, Newham, Hackney, Haringey, Lewisham, Merton, Croydon, Enfield and Brent.[10]
Greeks
According to the "History of London's Greek community" by Jonathan Harris,[11] the Greek population of London numbered several thousand by 1870 AD whereas in 1850 AD it was just a few hundred. The 2001 Census recorded 12,360 Greek-born people living in London, with particular concentrations in the Hyde Park, Regent's Park, Chelsea and Kensington Census tracts.[12]
The Census tracts with the highest number of Cypriot-born people in 2001 were Palmers Green, Upper Edmonton, Cockfosters, Lower Edmonton, Tottenham North and Tottenham South.[13] Many Greek-Cypriots reside in Wood Green, Harringay and Palmers Green, the latter harbouring the largest community of Greek-Cypriots outside Cyprus, resulting in these areas bearing local nicknames whereby the Green is replaced by Greek – as in Greek Lanes and Palmers Greek.[14][15][16]
According to a City of London Corporation sponsored report,[17] there are between 280,600 and 310,000 Greek speakers in Greater London.
The Greek Primary School of London and the Greek Secondary School of London both serve the community.
Indians
British Indians have long been one of London's largest ethnic minority groups and in 2007 over 500,000 Indians were residing in London (this excludes people of half or less Indian origin). Around 7% of London's population is of Indian origin. Indians have been in the British capital for generations and come from all walks of life.
Irish
Irish migration to Great Britain has a lengthy history due to the close proximity of, and complex relationship between, the islands of Ireland and Great Britain and the various political entities that have ruled them. Today, millions of residents of Great Britain are either from the island of Ireland or have Irish ancestry. Around six million Britons have an Irish grandfather or grandmother (approximately 10% of the UK population).[18] 900,000 ethnic Irish people live in the capital (12% of the city's population); despite this, some sources put the population of people of Irish descent in London at 77% (some five and a half million people), although the White British and White Irish populations combined are less than this.[19][20]
Jamaicans
There are records that show Black people, predominantly from Jamaica, living in London during the 17th and 18th centuries; but it was not until the arrival of the Empire Windrush, on 22 June 1948, that significant numbers of Caribbeans, in particular Jamaicans, arrived in the capital. This has since become an important landmark in the history of modern multicultural Britain. During the post World War II era, the presence of these immigrants was requested to help reconstruct the British economy. Employers such as British Rail, the NHS and London transport recruited almost exclusively from Jamaica. Some 250,000 Londoners are of Jamaican origin.[21]
Japanese
Junko Sakai, author of Japanese Bankers in the City of London: Language, Culture and Identity in the Japanese Diaspora, stated that there is no particular location for the Japanese community in London, but that the families of Japanese "company men" have a tendency of living in North London and West London. Japanese restaurants and shops are located around these groups of Japanese people.[22]
Koreans

As of 2014 there were about 10,000 ethnic Koreans in New Malden proper,[23] and as of the same year the Korean population in the area around New Malden is around 20,000, including about 600 originating from North Korea, giving it the largest group of North Koreans in Europe.[24] Many of the Koreans living in New Malden work for Korean companies, and they are either permanently settled and formerly expatriate, or they are still expatriates.[25] In 2015 Paul Fischer of The Independent wrote that the North Koreans were insular, and that there were tensions between the South Korean majority and the North Koreans in New Malden.[23]
The New Malden area has Korean-language churches and nursery schools as well as restaurants and shops with Korean clientele.[26] The area has Korean supermarkets, about 20 Korean restaurants and cafes,[23] including those serving bulgogi.[23] It also has a noraebang (Karaoke bar).[24] The Korean language is visible on several shop signs. The original Embassy of South Korea to the United Kingdom is in Malden.[23]
Some factors cited in The Telegraph as reasons why the Korean community formed in New Malden included a 1950s joint venture partnership between a chaebol and Racal Avionics (formerly Dacca), Lord Chancellor's Walk in Coombe Lane West previously serving as the residence of the Ambassador of South Korea to the United Kingdom, and Samsung Electronics having its UK offices in New Malden until they moved to their current location in Chertsey, Surrey in 2005. Many Koreans settled the New Malden in the 1970s due to the ambassador's location.[24]
There is a newspaper published in New Malden, Free NK, which is opposed to the government of North Korea.[24]
Nigerians
London (in particular the southern boroughs) is home to the largest Nigerian community in the UK, and possibly the largest overseas Nigerian community in the world. The first Nigerians in London were those caught up in the slave trade over 200 years ago.
In the mid-20th century a wave of Nigerian immigrants came to London after hearing of the need for more skilled workers. Civil and political unrest in the country contributed to numerous refugees arriving in England.[27] The vast majority of famous and notable British people of Nigerian origin were either born in or now live in London.
Peckham (also known as Little Lagos and Yorubatown) is home to one of the largest overseas Nigerian communities in the world; many of the local establishments are Yoruba-owned. Nigerian churches and mosques can be found in the area. As immigrants become assimilated, English is becoming the predominant language of the local Nigerian British population. The Yoruba language is declining in use in the Peckham area despite the increasing Nigerian population.[28] In 2001, about 7% of Peckham's population was born in Nigeria.[29] A much larger proportion of the ward's 60% Black population is of Nigerian descent, as 40% are of other African descent.[30]
Pakistanis
Pakistanis in London form the largest concentrated community of British Pakistanis; immigration from regions which now form Pakistan predate Pakistan's independence.[7] The main concentrations of Pakistani settlement in London are found in Outer London with the boroughs of Redbridge, Newham and Waltham Forest accounting for nearly a third of Londoners of Pakistani Descent.
Turkish
Gallery
-

London's Irish community celebrating Saint Patrick's Day.
-

Chinatown, London during Chinese new year.
-

London Turks protesting.
-

Kittitian and Nevisian street dancers at the Notting Hill Carnival.
-

London Iraqis celebrating 2007 AFC Asian Cup victory for Iraq.
-

Large numbers of Colombians live in London.
See also
References
- Moore, Fiona. "The German School in London, UK: Fostering the Next Generation of National Cosmopolitans?" (Chapter 4). In: Coles, Anne and Anne-Meike Fechter. Gender and Family Among Transnational Professionals (Routledge International Studies of Women and Place). Routledge, 6 August 2012. ISBN 1134156200, 9781134156207.
Reference notes
- ↑ Benedictus, Leo (2005-01-21). "Almost every race, colour, nation and religion on earth". London: Guardian. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- ↑ http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/4bd95562-4379-11e2-a48c-00144feabdc0.html#axzz2EmHkrZcr
- ↑ "2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. 11 December 2012. Retrieved 27 April 2015.
- 1 2 "Ethnic Groups in London". Census Update. Office for National Statistics. 2011: 1. 11 December 2012. Retrieved 12 December 2011.
- ↑ "A summary of countries of birth in London". Census Update. Office for National Statistics. 2011: 1. 11 December 2012. Retrieved 12 December 2011.
- 1 2 "Population of the United Kingdom by Country of Birth and Nationality".
- 1 2 "Arabic London". BBC. 2008-04-30. Retrieved 24 May 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Moore, Google Books PT89 (actual page number unstated).
- ↑ Moore, Google Books PT90 (actual page number unstated).
- ↑ Ghanaian London. Books.google.co.uk. 2008. ISBN 978-0-7546-4841-3. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- ↑
- ↑ "Born abroad: Greece". BBC. 2005-09-07. Retrieved 2008-12-07.
- ↑ "Born abroad: Cyprus". BBC. 2005-09-07. Retrieved 2008-12-07.
- ↑ "Things you didn't know about... Palmers Green", Yellow Pages
- ↑ "Greek in Palmers Green", UKTV
- ↑ "Palmers Green", Trusted Places
- ↑ Philip Baker & John Eversley, Multilingual Capital, commissioned by City of London Corporation, published by Battlebridge 2000.
- ↑ Bowcott, Owen (2006-09-13). "''Six million Britons are entitled to Irish citizenship''". London: Guardian. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- ↑ "Irish in London". Merseyreporter.com. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- ↑ "Irish in London 2". BBC News. 2001-03-16. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- ↑ "Jamaica Mapping Exercise" (PDF). International Organization for Migration. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 11, 2011. Retrieved 2010-04-22.
- ↑ Sakai, Page unstated (PT67). "Although the Japanese have no precise geographical location for their community, they are connected with each other personally, and one of their geographical centres is the Japanese school in London, previously in North London and now in West Acton."
- 1 2 3 4 5 Fischer, Paul. "The Korean Republic of New Malden: How Surrey became home to the 70 year-old conflict." The Independent. Monday 23 February 2015. Retrieved on 2 November 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 Parrish, Charlie. "Why is New Malden home to more North Koreans than any other place in Europe?" The Telegraph. 6 October 2014. Retrieved on 2 November 2015.
- ↑ Moore, Fiona. "The German School in London, UK: Fostering the Next Generation of National Cosmopolitans?" (Chapter 4). In: Coles, Anne and Anne-Meike Fechter. Gender and Family Among Transnational Professionals (Routledge International Studies of Women and Place). Routledge, 6 August 2012. ISBN 1134156200, 9781134156207. CITED: Google Books PT90.
- ↑ Moore, Fiona. "The German School in London, UK: Fostering the Next Generation of National Cosmopolitans?" (Chapter 4). In: Coles, Anne and Anne-Meike Fechter. Gender and Family Among Transnational Professionals (Routledge International Studies of Women and Place). Routledge, 6 August 2012. ISBN 1134156200, 9781134156207. CITED: Google Books PT89-PT90.
- ↑ Nigerian London (2008-08-20). "Nigerian London". Bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- ↑ "http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/4182341.stm". BBC News. 2005-01-25. Retrieved 2010-01-03. External link in
|title=(help) - ↑ "UK statistics on Nigerian-born people in Britain". BBC News. 2005-09-07. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
- ↑ Neighbourhood Statistics. "Pecham Ethnicity, 2001". Neighbourhood.statistics.gov.uk. Retrieved 2010-01-03.
Further reading
- Cherti, Miriam. Paradoxes of Social Capital: A Multi-generational Study of Moroccans in London (IMISCOE dissertations Sussex theses ; S 6271). Amsterdam University Press, 2008. ISBN 9053560327, 9789053560327.
External links
- Ethnicity Profiles: London by the Commission for Racial Equality