fdisk
For computer file systems, fdisk is a command-line utility that provides disk partitioning functions. In versions of the Windows NT operating system line from Windows 2000 onwards, fdisk is replaced by more advanced tool called diskpart. Similar utilities exist for Unix-like systems.
Implementations
DOS and Windows
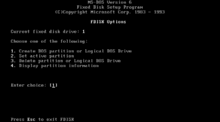
IBM introduced fdisk, Fixed Disk Setup Program version 1.00, with the March 1983 release of the IBM PC/XT, the first PC to store data on a hard disk, and the IBM Personal Computer DOS version 2.0. Version 1 could be used to create one FAT12 DOS partition, delete it, change the active partition or display partition data. fdisk writes the master boot record, which supported up to four partitions. The other three were intended for other operating systems such as CP/M-86 and Xenix, which were expected to have their own partitioning utilities as fdisk did not support them.
In August 1984, PC DOS 3.0 added FAT16 partitions to support larger hard disks more efficiently.
In April 1987, PC DOS/fdisk 3.30 added support for extended partitions, which could hold up to 23 "logical drives" or volumes.
Support for FAT16B was added with Compaq MS-DOS 3.31, and later became available with MS-DOS/PC DOS 4.0.
Most DOS fdisk programs, including the fdisk program that came with the original Windows 95, are only capable of creating FAT partitions of types FAT12, FAT16 and FAT16B.
A derivative of the MS-DOS fdisk was provided with Windows 95, Windows 98, and later Windows ME. Only those fdisk versions shipping with Windows 95B or later are able to manipulate FAT32 partitions.[1] Windows 2000 and later do not use fdisk, they have the Logical Disk Manager feature, as well as DiskPart.
Unlike the fdisk programs for other operating systems, the fdisk programs for DOS and Windows 9x/Me not only alter data in the partition table, but will also overwrite many sectors of data in the partition itself. (However, to create an extended partition any partition editor must put extended boot records before each logical drive on the disk.) Users must be sure the correct disk/partition has been chosen before using a DOS/Windows fdisk for partitioning. The fdisk /mbr switch is undocumented but well known for repairing the master boot record.
The fdisk supplied with Windows 98 does not report the correct size of a hard disk that is larger than 64 GB. An updated fdisk is available from Microsoft that corrects this.[2]
FreeDOS
The implementation of fdisk in FreeDOS is free software.
OS/2
OS/2 shipped with two partition table managers up until version 4.0. These were the text mode fdisk and the GUI-based fdiskpm. The two have identical functionality, and can manipulate both FAT partitions and the more advanced HPFS partitions.
OS/2 versions 4.5 and higher (including eComStation) can use the JFS filesystem as well as FAT and HPFS, and replace fdisk with the Logical Volume Manager (LVM).
PC DOS 7.10
IBM PC DOS 7.10 contained FDISK32 and FORMAT32 utilities.
See also
References
- ↑ "How to Use the Fdisk and Format Tools to Partition or Repartition a Hard Disk". Support (6.0 ed.). Microsoft. 28 June 2012.
- ↑ "Fdisk Does Not Recognize Full Size of Hard Disks Larger than 64 GB". Support (4.0 ed.). Microsoft. 24 August 2012.
External links
- Linux Partition HOWTO. Partitioning with fdisk
- Linux Programmer's Manual, fdisk(8)
- fdisk from utils-linux-ng
- blkid - command-line utility to locate/print block device attributes
- Using the blkid Command .
- FreeBSD System Manager's Manual, FDISK(8)