Finnish mythology
Finnish mythology is a commonly applied description of the folklore of Finnish paganism, of which a modern revival is practiced by a small percentage of the Finnish people. It has many features shared with fellow Finnic Estonian mythology and its non-Finnic neighbours, the Balts and the Scandinavians. Some of their myths are also distantly related to the myths of other Finno-Ugric speakers like the Samis.
Finnish mythology survived within an oral tradition of mythical poem-singing and folklore well into the 19th century.
Although the gradual influence of surrounding cultures raised the significance of the sky-god in a monolatristic manner, the father god "Ukko" (Old Man) was originally just a nature spirit like all the others. Of the animals, the most sacred was the bear, whose real name was never uttered out loud, lest his kind be unfavorable to the hunting. The bear ("karhu" in Finnish) was seen as the embodiment of the forefathers, and for this reason it was called by many circumlocutions: mesikämmen ("mead-paw"), otso ("browed one"), kontio ("dweller of the land"), metsän kultaomena ("the golden apple of the forest") but not a god.
Study of Finnish mythological and religious history
The first historical mention of Finnish folk religion was by the bishop and Lutheran reformer Mikael Agricola (1510–1555) in the preface to his 1551 Finnish translation of the Psalms.[1] Agricola supplied a list of purported deities of the Häme (in Swedish, Tavastia) and Karjala (Karelia), twelve deities in each region,[1][2] with their supposed functions briefly set out in verse form.[1][3] (Some commentators state that only eleven deities were listed for Häme,[4] not counting Agricola's mention of Piru, the Devil.) Due to the lists, Agricola is considered to be the father of the study of Finnish religious history and mythology.[1][5] Later scholars and students commonly quoted Agricola's lists as a historical source; only in the late eighteenth century did scholars begin to critically evaluate the "gods" in Agricola's lists and the information he presented about them,[6] determining with further research that most of the figures in his lists were not gods, but local guardian spirits, figures from folk mythology or explanatory legends, cultural heroes, Christian saints under alternative names, and, in one case, a harvest-time festival.[4]
Cristfried Ganander's Mythologia Fennica, published in 1789, was the first truly scholarly foray into Finnish mythology. In the 19th century, research into Finnish folklore intensified. Scholars like Elias Lönnrot, J.F. Cajan, M.A. Castrén, and D.E.D. Europaeus travelled around Finland writing down folk poetry sung by runo (poem) singers, many of whom were tietäjät (traditional ritual specialists). The genres they collected included material like the synnyt, which give mythical accounts of the origins of many natural phenomena. From this material Lönnrot edited the Kalevala as well as the Kanteletar. The wealth of folk poetry collected in the 19th century often deals with pre-Christian pagan themes, and has allowed scholars to study Finnish mythology in more detail.
The origins and the structure of the world
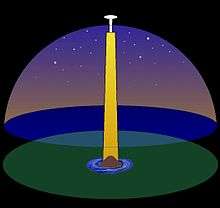
The world was believed to have been formed out of a pochard egg. The sky was believed to be the upper cover of the egg, alternately it was seen as a tent, which was supported by a column at the north pole, below the north star.
The movement of the stars was explained to be caused by the sky-dome's rotation around the North Star and itself. A great whirl was caused at the north pole by the rotation of column of sky. Through this whirl souls could go to the outside of the world to the land of dead, Tuonela.
Earth was believed to be flat. At the edges of Earth was Lintukoto, "the home of the birds", a warm region in which birds lived during the winter. The Milky Way is called Linnunrata, "the path of the birds", because the birds were believed to move along it to Lintukoto and back. In Modern Finnish usage, the word lintukoto means an imaginary happy, warm and peaceful paradise-like place.
Birds had also other significance. Birds brought a human's soul to him at the moment of birth, and took it away at the moment of death. In some areas, it was necessary to have a wooden bird-figure nearby to prevent the soul from escaping during sleep. This Sielulintu, "the soul-bird", protected the soul from being lost in the paths of dreams.
Waterfowl are very common in tales, and also in stone paintings and carvings, indicating their great significance in the beliefs of ancient Finns.
Tuonela, the land of the dead
Tuonela was the land of dead. It was an underground home or city for all the dead people, not only the good or the bad ones. It was a dark and lifeless place, where everybody slept forever. Still a brave shaman could travel to Tuonela in trance to ask for the forefathers' guidance. To travel to Tuonela, the soul had to cross the dark river of Tuonela. If he had a proper reason, then a boat would come to take him over. Many times a shaman's soul had to trick the guards of Tuonela into believing that he was actually dead.
Ukko, the God of sky and thunder
Ukko ("old man") was a god of the sky, weather, and the crops. He was also the most significant god in Finnish mythology and the Finnish word for thunder, "ukkonen" (little Ukko) or "ukonilma" (Ukko's weather), is derived from his name. In the Kalevala he is also called "ylijumala" (overgod, Supreme God), as he is the god of things of the sky. He makes all his appearances in myths solely by natural effects when invoked.
Ukko's origins are probably in Baltic Perkons and the older Finnish sky god Ilmarinen. Also Thor is related to Perkons. While Ukko took Ilmarinen's position as the Sky God, Ilmarinen's destiny was to turn into a smith-hero, or the god of the rock. In the epic poetry of the Kalevala, Ilmarinen is credited with forging the stars on the dome of the sky and the magic mill of plenty, the Sampo.
Ukko's weapon was a hammer, axe or sword, by which he struck lightning. While Ukko mated with his wife Akka ("old woman"), there was a thunderstorm. He created thunderstorms also by driving with his chariot in clouds. The original weapon of Ukko was probably the boat-shaped stone-axe of battle axe culture. Ukko's hammer, the Vasara (means merely "hammer"), probably meant originally the same thing as the boat-shaped stone axe. While stone tools were abandoned in the metal ages, the origins of stone-weapons became a mystery. They were believed to be weapons of Ukko, stone-heads of striking lightnings. Shamans collected and held stone-axes because they were believed to hold many powers to heal and to damage.
The viper with the saw-figure on its skin has been seen as a symbol of thunder.
Heroes, gods and spirits
- Ahti (or Ahto), god of the depths, giver of fish.
- Ajatar (sometimes Ajattara), an evil forest spirit.
- Akka ("old lady"), female spirit, feminine counterpart of "Ukko".[7]
- Äkräs, the god of fertility and the protector of plants, especially the turnip.
- Antero Vipunen, deceased giant, protector of deep knowledge and magic.
- Hiisi, demon, originally meaning a sacred grove, later a mean goblin.
- Iku-Turso, a malevolent sea monster; probably same as Tursas.
- Ilmarinen, the great smith, maker of heaven. Designed the Sampo mill of fortune. Originally a male spirit of air.
- Ilmatar, female spirit of air; the daughter of primeval substance of creative spirit. Mother of Väinämöinen in Kalevala.
- Jumala, a generic name for a major deity. Originally the name given by the Finns to the sky, the sky-god, and the supreme god. Later taivas and Ukko were used as the names for the sky and the sky-god. The word means god and was later used for the Christian God. The origin of the word is unknown – some possible explanations are derivation from Jomali, the supreme deity of the Permians and origination from the Estonian word jume.
- Kalevanpoika (son/man of Kaleva), a giant hero who can cut down forests and mow down huge meadows, identical with Estonian national epic hero Kalevipoeg.
- Kave, ancient god of sky, later the deity of the lunar cycle. Father of Väinämöinen. Also Kaleva.
- Kullervo, tragic antihero. Model for Túrin Turambar in Tolkien's Silmarillion.
- Kuu, goddess of the Moon.
- Lemminkäinen (Ahti Saarelainen, Kaukomieli), a brash hero.
- Lempo, originally a fertility spirit, became synonymous with demon in the Christian era.
- Lalli, Finn who slew Bishop Henry on the ice of Lake Köyliö, according to a legend.
- Louhi, the matriarch of Pohjola, hostess of the Underworld.
- Loviatar, the blind daughter of Tuoni and the mother of Nine diseases.
- Luonnotar, spirit of nature, feminine creator.
- Menninkäinen, a fairy spirit, gnome, leprechaun of some sort.
- Metsänväki, spirit of forest, forest creature.
- Mielikki, wife of Tapio, the goddess of the forest.
- Nyyrikki, the god of hunting, son of Tapio.
- Näkki, the fearsome spirit of pools, wells and bridges (A spiteful and beautiful womanlike creature with woman's body and fish's behind who flatters men into water in Estonian mythology). Same as Nix.
- Otso, the spirit of bear (one of many circumlocutory epithets).
- Pekko (or Pellon Pekko), the god of crops, especially barley and brewing.
- Perkele, the Devil. Originally a god of thunder, Perkele was demonized with the introduction of the Christian religion. Related to Baltic Perkunas and Norse Thor.
- Pellervo (or Sampsa Pellervoinen), the god of harvest.
- Pihatonttu, tutelary of the yard.
- Piru, spirit, demon. Probably later loan word related to "spirit".
- Päivätär, the goddess of day.
- Raako, the Karelian god of time; Rahko tars the moon describes the phases of the moon.
- Surma, the personification of a violent death.
- Saunatonttu, tutelary of the sauna.
- Tapio, the god of the forest.
- Tellervo, the goddess of the forest, daughter of Tapio and Mielikki.
- Tonttu, generally benign tutelary. Originally, a patron of cultivated land, keeper of lot.
- Tuonetar, name referring to both the mistress and the daughter of Tuoni.
- Tuoni, the personification of Death.
- Tursas, the Tavastian god of war. May be the same as the Norse Tyr and the Germanic Tîwaz.
- Tuulikki, daughter of Tapio and Mielikki, goddess of animals.
- Ukko ("old man") the god of the sky and thunder, related to Thor (Estonian Taara).
- Vellamo, the wife of Ahti, goddess of the sea, lakes and storms. A current image of Vellamo can be seen on the coat of arms of Päijät-häme.
- Vedenemo ("mother of waters"), Karelian goddess of water.
- Väinämöinen, the old and wise man, who possessed a potent, magical voice. Also related to Estonian Vanemuine. The central character in Finnish folklore and he is the main character in the Kalevala.
Places
- Kyöpelinvuori (Raatikko); where women who die as virgins go, and later a place where witches meet at Easter.
- Tuonela; (also Manala, Pohjola) abode of the dead, Underworld.
- Kalevala
- Pohjola
- Aarnivalkea, an eternal flame marking the spot of buried treasure
- Lintukoto, a mythical place where migratory birds were believed to live in wintertime, the word is used as a metaphor for a happy place in Finnish.
Animals

- Brown bear; the bear was considered the most sacred of animals, only referred to by euphemisms (see taboo). The killing of a bear was followed by a great feast in honour of the bear (peijaiset), where a substantial part of the celebrations consisted of convincing the bear's spirit that it had died accidentally and hadn't been murdered. Afterwards, the bear's skull was hung high upon a pine tree so its spirit could re-enter the heavens. Kalevala on the bear.
- Swan of Tuonela; (Tuonelan joutsen).
- Elk of Hiisi; (Hiiden hirvi).
Artifacts
- The Sampo, a magical artifact that brought good fortune to its holder. According to Lönnrot's interpretation in the Kalevala, it was a mill that made flour, salt, and gold out of thin air.
- Väinämöinen's magic kantele which he made from the jaws of a huge pike and a young lady's hair.
- Väinämöinen's great sword, which shines like sun and is extraordinarily sharp.
See also
Notes
References
- Honko, Lauri, Senni Timonen, Michael Branch, and Keith Bosley. (1994). The Great Bear: A Thematic Anthology of Oral Poetry in the Finno-Ugrian Languages. New York: Oxford University Press. Originally published 1993 by the Finnish Literature Society.
- Holmberg, Uno. (1964). Finno-Ugric, Siberian. The Mythology of All Races, Vol. IV (ed. by John Arnott MacCullough). New York: Cooper Square Publishers, 1964. Originally published 1927 by Marshall Jones, Boston.
- Pentikäinen, Juha Y. (1999). Kalevala Mythology, expanded ed. Translated by Ritva Poom. Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
- Kuusi, Matti, Keith Bosley, and Michael Branch. (1997). Finnish Folk Poetry: Epic. Helsinki: Finnish Literature Society.
- Pentikäinen, Juha. (2002). "Kalevala: the Finnish national epic" ThisisFINLAND
- Talve, Ilmar. (1997). Finnish Folk Culture. Studia Fennica, Ethnologica 4. Translated by Susan Sinisalo. Helsinki: Finnish Literature Society.
- Virtanen, Leea and Dubois, Thomas. (2000). Finnish Folklore. Studia Fennica, Folklorista 9. Translated by Thomas Dubois. Helsinki: Finnish Literature Society in association with University of Washington Press, Seattle, WA.