G5 howitzer
| G5 155 mm Howitzer | |
|---|---|
|
G5 on display | |
| Type | Howitzer |
| Place of origin | South Africa |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1983 – present[1] |
| Used by | Operators |
| Wars |
South African Border War Iran–Iraq War Gulf War |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Lyttelton Engineering Works |
| Designed | 1976 – 1983 |
| Manufacturer | Denel Land Systems |
| Produced | 1982 – present |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 13,750 kg (30,314 lbs)[1] |
| Length | 9.5 m (31 ft 2 in) |
| Barrel length | 6.975 m (22 ft 11 in) L/45 |
| Width | 3.3 m (10 ft 10 in) |
| Height | 2.1 m (6 ft 11 in) |
| Crew | 8 soldiers |
|
| |
| Shell | high explosive |
| Caliber | 155 mm (6.10 in) |
| Breech | Semi-automatic interrupted screw |
| Carriage | split trail |
| Elevation | -3° to +75° |
| Traverse |
Up to 15°: 82° Above 15°: 65° |
| Rate of fire | 3 rounds/minute |
| Muzzle velocity | 897 m/s (2,943 ft/s) |
| Maximum firing range |
Standard: 30 km (19 mi) Base bleed: 39 km (24 mi) VLAP: 50 km (31 mi)[2] |
| Feed system | Breech-loaded |
The G5 is a South African towed howitzer of 155 mm calibre designed and developed in South Africa by Denel Land Systems. The G5 design was based on the Canadian GC-45 155mm gun which was highly modified to suit southern African conditions.
Production history
During the Angolan Bush War, the South African Defence Force found itself at a disadvantage when facing opponents equipped with long-range Soviet Katyusha rocket launchers, which outranged South Africa's World War II-era 5.5-inch howitzers by a considerable margin.[3] This led to the issue of a staff requirement for a new artillery system as well as ammunition systems, gun tractor, fire control equipment and a fire control computer system.[4]
From 1963, South Africa had been placed under a United Nations sponsored anti-apartheid arms embargo that led to the creation of the indigenous Armscor military-industrial company to circumvent the arms embargo and to produce weapons systems uniquely tailored to South Africa's needs. Armscor responded to the staff requirement and commenced development in 1976. A number of existing designs were evaluated and examples procured in contravention of the arms embargo. As an interim weapon system to act as a stop-gap during the indigenous production process, a number of Soltam 155mm M-71 gun-howitzers were procured from Israel and entered service as the G4 howitzer.[4]
The Canadian GC-45 was selected as the baseline howitzer from which to commence indigenous development.[4] Armscor procured barrels, 30,000 rounds and design specifications for the GC-45 from Gerald Bull. One of the GC-45 test pieces was mounted on a U.S. 155mm M59 carriage - and a further six GC-45s had changes made to internal ballistics, barrel construction and carriage and cradle fixtures, to become the prototype models eventually leading to the G5. These GC-45s had been developed by SRC International of Belgium, a joint venture between Gerald Bull's Space Research Corporation of Canada and PRB of Belgium.[5] Further changes included the addition of a small APU to allow the gun to dig itself in and move short distances at up to 16 kilometres per hour (9.9 mph), as well as the addition of an advanced muzzle brake. The G5 became operational in 1983.[4]
Using the normal Extended Range, Full Bore (ERFB) ammunition the normal range is 30 kilometres (19 mi), which can be extended to about 39.6 kilometres (24.6 mi) using base bleed shells, or 50 kilometres (31 mi) using rocket assisted V-LAP rounds. In 2002 Denel produced the G5-2000 version, with much greater range and accuracy than the earlier 45-calibre version.
The G5 gun has been placed on an OMC 6×6 chassis to produce the fully self-propelled G6 howitzer, and won major export sales in this form from the United Arab Emirates and Oman. In response to a request from India it has also been tested on the back of a TATRA 8×8 wheeled truck, a combination known as the T5-2000. It has also been fitted into a turret, named the T6, that can be placed on any suitable vehicle; it has been fitted on the T-72 tank.
Operational history
The G5 howitzer saw action in Angola and Namibia in the South African Border War between 1982–1987, where it was in service with the South African Defence Force. The G5 also saw action in the Iran-Iraq War between 1980 and 1988, where it was used by both Iraq and Iran.
Variants
- G5 Mk I
- G5 Mk II
- G5 Mk III
- G5 Mk IIIA
- G5-2000: 52-calibre gun
Operators
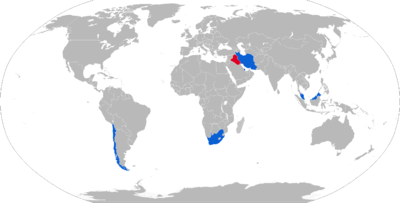

Current operators
 Chile: 25
Chile: 25 Iran: 30[6]
Iran: 30[6] Malaysia: 22[7][6]
Malaysia: 22[7][6] Qatar: 12 - to be replaced by PzH 2000[8][6]
Qatar: 12 - to be replaced by PzH 2000[8][6] South Africa: 6 in service. Up to 66 in storage.[9][6]
South Africa: 6 in service. Up to 66 in storage.[9][6]
Former operators
 Iraq: Saddam Hussein's army operated about 100 G5s, but these have probably all been destroyed or abandoned since the 2003 invasion of Iraq.[6]
Iraq: Saddam Hussein's army operated about 100 G5s, but these have probably all been destroyed or abandoned since the 2003 invasion of Iraq.[6]
See also
References
- 1 2 Kinard, Jeff. Artillery: An Illustrated History of Its Impact (2007 ed.). ABC-CLIO Publishers. pp. 301–476. ISBN 978-1-85109-561-2.
- ↑ "G5 155mm Towed Gun/Howitzer" (PDF) (Press release). Denel. 2004-09-03.
- ↑ The Encyclopedia of World Military Weapons 1988. ISBN 0-517-65341-9
- 1 2 3 4 Jane's Armour and Artillery 1996-97. Janes Information Group. 1996. p. 697. ISBN 9780710613745.
- ↑ Janes (1996), pg. 645
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Denel G5 155mm - Development and Operational History, Performance Specifications and Picture Gallery". Military Factory. Retrieved 6 July 2016.
- ↑ Malaysia buys artillery guns, rocket system
- ↑ Qatar Orders 24 PzH 2000 Self-Propelled Howitzers and 62 Leopard 2 A7+ Main Battle Tanks - Deagel.com, April 18, 2013
- ↑
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to G5 howitzer. |
- Denel G5 brochure
- G5 at Globalsecurity.org
- G5 is battle ready
- G5 at armyreco.ifrance.com
.jpg)