Gamma Ray Spectrometer
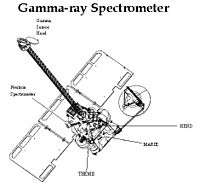
Gamma Ray Spectrometer (GRS) is a gamma-ray spectrometer on the 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft, a space probe orbiting the planet Mars since 2001. Part of the United States' NASA's Mars Surveyor Program, it returns geological data about Mars' surface such as identifying elements and the location of water. It is managed by the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory at the University of Arizona in the United States. This instrument mapped the distribution of water in the surface..[1]
GRS specifications
The Gamma-Ray Spectrometer weighs 30.5 kilograms (67.2 lb) and uses 32 watts of power. Along with its cooler, it measures 468 by 534 by 604 mm (18.4 by 21.0 by 23.8 in). The detector is a photodiode made of a 1.2 kg germanium crystal, reverse biased to about 3 kilovolts, mounted at the end of a six-meter boom to minimize interferences from the gamma radiation produced by the spacecraft itself. Its spatial resolution is about 300 km.[2][3]
The neutron spectrometer is 173 by 144 by 314 mm (6.8 by 5.7 by 12.4 in).
The high-energy neutron detector measures 303 by 248 by 242 mm (11.9 by 9.8 by 9.5 in). The instrument's central electronics box is 281 by 243 by 234 mm (11.1 by 9.6 by 9.2 in).
References
- ↑ http://grs.lpl.arizona.edu/latestresults.jsp
- ↑ W.V. Boynton, W.C. Feldman, I.G. Mitrofanov, L.G. Evans, R.C. Reedy, S.W. Squyres, R. Starr, J.I. Trombka, C. d'Uston, J.R. Arnold, P.A.J. Englert, A.E. Metzger, H. Wänke, J. Brückner, D.M. Drake, C. Shinohara, C. Fellows, D.K. Hamara, K. Harshman, K. Kerry, C. Turner, M. Ward1, H. Barthe, K.R. Fuller, S.A. Storms, G.W. Thornton, J.L. Longmire, M.L. Litvak, A.K. Ton'chev (2004). "The Mars Odyssey Gamma-Ray Spectrometer Instrument Suite". Space Science Reviews. 110 (1–2): 37. Bibcode:2004SSRv..110...37B. doi:10.1023/B:SPAC.0000021007.76126.15.
- ↑ http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/database/MasterCatalog?sc=2001-014A&ex=2