Genipin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
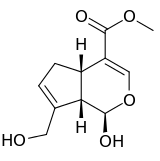
| IUPAC name
Methyl (1R,2R,6S)-2-hydroxy-9-(hydroxymethyl)-3-oxabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-4,8-diene-5-carboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 6902-77-8 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL459016 |
| ChemSpider | 390864 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.015 |
| KEGG | C09780 |
| PubChem | 442424 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H14O5 | |
| Molar mass | 226.226 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Genipin is a chemical compound found in gardenia fruit extract. It is an aglycone derived from an iridoid glycoside called geniposide present in fruit of Gardenia jasminoides.
Genipin is an excellent natural cross-linker for proteins, collagen, gelatin, and chitosan cross-linking.[1] It has a low acute toxicity, with LD50 i.v. 382 mg/kg in mice, therefore, much less toxic than glutaraldehyde and many other commonly used synthetic cross-linking reagents.[1] Furthermore, genipin can be used as a regulating agent for drug delivery, as the raw material for gardenia blue pigment preparation, and as the intermediate for alkaloid syntheses.[2]
In vitro experiments have shown that genipin blocks the action of the enzyme uncoupling protein 2.[3]
References
- 1 2 CBC Genipin
- ↑ Introduction of genipin
- ↑ Zhang, CY; Parton, LE; Ye, CP; Krauss, S; Shen, R; Lin, CT; Porco Jr, JA; Lowell, BB (2006). "Genipin inhibits UCP2-mediated proton leak and acutely reverses obesity- and high glucose-induced beta cell dysfunction in isolated pancreatic islets". Cell Metabolism. 3 (6): 417–27. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.04.010. PMID 16753577.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 2/13/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.