Germany Must Perish!

Germany Must Perish! is a 104-page book written by Theodore Newman Kaufman, which he self-published in 1941 in the United States. The book advocated the genocide through sterilization of all Germans and the territorial dismemberment of Germany. Kaufman founded the Argyle Press in Newark, New Jersey, United States, in order to publish this book. He was the sole proprietor of the Argyle Press and it is not known to have published any other works.
The Nazi Party used the book, written by a Jewish author, to support their argument that Jews were plotting against their country.[1]
American reactions to the book
Though written and self-published by a non-notable author, the book received considerable attention. Time magazine published a review in its 24 March issue that compared the book to Jonathan Swift's 1792 satirical essay A Modest Proposal, which proposed reducing the population pressure in Ireland by the cannibalistic consumption of poor Irish children. However, the Time essay recognized that Kaufman's work was not satirical; it described the book as the "enshrinement of a single sensational idea." "Since Germans are the perennial disturbers of the world's peace, says the book, they must be dealt with like any homicidal criminals. But it is unnecessary to put the whole German nation to the sword. It is more humane to sterilize them."[2][3]
According to one study, reviews in the United States "reflected an odd combination of straight reporting and skepticism."[4] Kaufman's second and more moderate pamphlet, "No More German Wars" published in 1942, was ignored both in the U.S. and in Germany.[4]
An advertisement in The New York Times stated that the book was released to the public on March 1, 1941. Kaufman also promoted the book by mailing a miniature black cardboard coffin with a hinged lid to reviewers.[5] Inside the coffin was a card proclaiming, "Read GERMANY MUST PERISH! Tomorrow you will receive your copy."[2][6]
The book's dust jacket contained excerpts from reviews of the book. One blurb read: A Plan For Permanent Peace Among Civilized Nations! -- New York Times.[7]
Kaufman's advocacy of mass sterilization of Germans was echoed in a later book by another American Jew, Louis Nizer, who cited Kaufman.[8] In his 1944 book What To Do With Germany, Nizer accepted collective punishment of Germans and considered, but ultimately rejected, their mass "eugenic sterilization".[8]
In 1945, a Jewish journalist wrote an article claiming that the book was "little more than self-indulgence in dire vituperation by a man who sees Germany as the sole cause of the world's woes."[9]
Contents
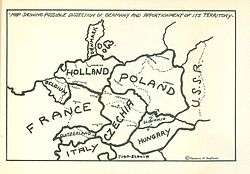
Kaufman advocated the mass extermination through forced sterilization of the German people and the territorial dismemberment of Germany after an Allied victory in World War II.[6]
Kaufman summarized Germany Must Perish! in advertisements in the New York Times and New York Post as: "A dynamic volume outlining a plan for the extinction of Germany and containing a map showing possible dissection and apportionment of its territory."[10] In an interview carried in the September 26, 1941, issue of The Canadian Jewish Chronicle, Kaufman defended his plan for the "sterilization of all Germans":[11]
I believe that the Jews have a mission in life. They must see to it that the nations of the world get together in one vast federation. "Union Now" is the beginning of this. Slowly but surely the world will develop into a paradise. We will have perpetual peace. And the Jews will do the most to bring about this confederation, because they have the most to gain. But how can you get peace if Germany exists? The only way to win an eternal peace is to make the punishment of waging war more horrible than war itself. Human beings are penalized for murder, aren't they? Well, Germany starts all the wars of magnitude. Let us sterilize all Germans and wars of world domination will come to an end!
The German reaction
The book has been widely quoted as evidence of a plan for genocide against the German people, and was also the first time the term "Final Solution" was used in the context of genocide. According to one analysis:[12]
Few Americans have ever heard of a prominent fellow-citizen named Kaufman ... In Germany every child has known of him for a long time. Germans are so well informed about Mr. Kaufman that the mere mention of his name recalls what he stands for. In one of his recent articles Dr. Goebbels wrote, 'Thanks to the Jew Kaufman, we Germans know only too well what to expect in case of defeat.'
Kaufman was a Manhattan-born Jew and his advocacy of genocide attracted great attention in Germany.[2] The book was denounced as an "orgy of Jewish hatred" and U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt's polemical anti-German agitation was seen as having inspired it.[13] American journalist Howard K. Smith was in Germany when Germany Must Perish! became known. He wrote:[14]
No man has ever done so irresponsible a disservice to the cause his nation is fighting and suffering for than Nathan Kaufman. His half-baked brochure provided the Nazis with one of the best light artillery pieces they have, for, used as the Nazis used it, it served to bolster up that terror which forces Germans who dislike the Nazis to support, fight and die to keep Nazism alive ...
In September 1941, Julius Streicher published an essay in Der Sturmer that called Kaufman's book "the crazy thinking of [an] insane Jewish brain". He quoted Kaufman at length and then commented: "By destroying the German people, the Jew wants to stop up the spring from which, since the beginning, the world has always found its creative blood, the source of all that is beautiful, good and noble."[15] Joseph Goebbels also gave a radio address from Berlin warning Germans of "plans 'for sterilization of our entire population under 60 years' of age."[6] These concerns were echoed by Adolf Hitler himself after the US entered WW II, he claimed mass sterilization of German male youth was a "primary" American goal.[6]
When the Jews of Hanover were evicted on September 8, 1941, the local authorities cited Kaufman's book as one of the reasons.[1] Kaufman responded:[16][17]
This is just a flimsy pretext for another of the innate cruelties of the German people ... I don't think it was my book that prompted this barbarity. They employed every possible German cruelty against the Jews long before my book was published.
The book appeared in many pieces of National Socialist propaganda. The Parole der Woche's weekly wall newspaper included it as evidence that the Allies' war aims included the destruction of Germany.[18] The pamphlet "The War Goal of World Plutocracy" detailed the contents of the book, although with some omissions from the text that it quoted.[19] It was used in 1944 in a pamphlet, "Never!", which described Kaufman's importance:[20]
The Jewish president of the American Federation of Peace is no anonymous individual, no fanatic rejected by world Jewry, no mentally ill crackpot, but rather a leading and widely known Jewish personality in the United States. He belongs to the so-called Roosevelt Brain Trust, which provides intellectual and political education and advice to the American President. "It is therefore beyond question that his book and its demand that 'Germany must perish' corresponds to the official opinion of the leading circles of world plutocracy."
At his Nuremberg trial Julius Streicher cited Kaufman's book in his defense, claiming his anger at Jews was prompted by Germany Must Perish!.[6] The German philosopher and historian Ernst Nolte argues that the German reaction to Germany Must Perish! supports his contention that World War II was a genuine response to German fears of a worldwide Jewish plot.[21]
See also
- Germania est delenda
- Society for the Prevention of World War III
- Your Job in Germany
- Germany is Our Problem
- Morgenthau Plan
References
- 1 2 "Jews of Hanover Forced from Homes. Mayor Cites American Book, 'Germany Must Perish'". New York Times. September 9, 1941. Retrieved April 19, 2011.
- 1 2 3 "A Modest Proposal". Time magazine. March 24, 1941. Retrieved April 19, 2011.
- ↑ "A Modest Proposal (review from Time magazine)". The Nizkor Project. Retrieved September 27, 2014.
- 1 2 Berel Lang, Philosophical Witnessing: The Holocaust as Presence, University Press of New England: 2009), pp. 130–131, 135
- ↑ Anonymous. Advertisement for Germany Must Perish!. New York Times. March 1, 1941. p. 13
- 1 2 3 4 5 Lombardo, Paul A. (2010). Three Generations, No Imbeciles: Eugenics, the Supreme Court and Buck v. Bell (paperback ed.). Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins UP. pp. 228, 236. ISBN 978-0-8018-9824-2.
- ↑ "Latest Books Received." New York Times. March 16, 1941. p. BR29
- 1 2 Nizer, Louis (1944). What To Do With Germany. Chicago: Ziff-Davis Publishing Co. pp. 3–5, 205.
- ↑ Donald F. Lach, "What They Would Do about Germany", Journal of Modern History, Vol. 17, No. 3. (September 1945), pp. 227-243
- ↑ New York Post, Friday, February 28, 1941, p. 22
- ↑ Harold U. Ribalow (September 26, 1941). "Hitler Will Be Nothing But A Rosebud Says Author 'Germany Must Perish!'. One Man's Plan For Peace Forever". The Canadian Jewish Chronicle. p. 5. Retrieved December 4, 2011.
- ↑ Argus (1944). "Behind Enemy Lines" (PDF). The Nation. p. 510. Retrieved April 19, 2011.
- ↑ "Nazis Attack Roosevelt". New York Times. July 24, 1941. Retrieved September 27, 2014.
- ↑ Howard K. Smith, Last Train from Berlin (London: Phoenix Pr., 1942), p. 134
- ↑ Streicher, Julius. "The Battle with the Devil". German Propaganda Archive. Calvin College. Retrieved September 27, 2014.
- ↑ "Hanover Jews Victims of Latest Oppression". Associated Press. September 9, 1941. Retrieved April 20, 2011.
- ↑ "Unknown Title". New York Times. September 9, 1941. Retrieved September 27, 2014.
- ↑ Parole der Woche
- ↑ War Aims of World Plutocracy
- ↑ Goitsch, Heinrich. "Never!". German Propaganda Archive. Calvin College. Retrieved September 27, 2014. The use of quotation marks for the last sentence of this quotation is unexplained.
- ↑ Nolte, Ernst "Between Myth and Revisionism", pages 17-38 from Aspects of the Third Reich, edited by H.W. Koch (NY: St. Martin's Press, 1985), pp. 27-28
Further reading
- Randall Bytwerk, "The Argument for Genocide in Nazi Propaganda," Quarterly Journal of Speech, 91 (2005), pp. 37–62
- Jeffrey Herf, The Jewish Enemy: Nazi Propaganda During World War II and the Holocaust, Harvard University Press, 2006, pp. 110–115
External links
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- Text
- Germany must perish! Newark, N.J., Argyle Press 1941 (probable first edition)
- Germany must perish! Newark, N.J. : Argyle Press c1941 (apparently the second or later ed. published by Kaufman)
- Germany Must Perish! ed. published by the Institute for Historical Review, with an introduction by Mark Weber
- The full text of the book from wikisource
- Propaganda
- "The War Goal of World Plutocracy" A September 1941 pamphlet by Wolfgang Diewerge
- "When you see this symbol..." Cover illustration and excerpts from a November 1941 flyer