Glutaurine
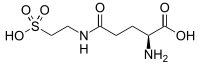 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-(2-Sulfoethyl)-L-glutamine | |
| Other names
γ-Glutamyltaurine; γ-L-Glutamyltaurine[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 56488-60-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL2106758 |
| ChemSpider | 62003 |
| PubChem | 68759 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H14N2O6S | |
| Molar mass | 173.1897 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Glutaurine is a chemical compound which is an amide formed from glutamic acid and taurine.
Biological role
Glutaurine, an endogenous compound (KEGG: C05844), has been noted as an antiepileptic, with antiamnesia properties. The dipeptide γ-glutamyltaurine (γ-GT; glutaurine, Litoralon) was discovered in the parathyroid in 1980, and later in the mammalian brain. This led to studies on intrinsic and synthetic taurine peptides, and the suggestion that γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT; γ-glutamyl-transpeptidase) in the brain is responsible for its in vivo formation.[2]
The versatile molecule mimicks the anxiolytic drug diazepam, and is implicated in phenomena from feline aggression to amphibian metamorphosis, radiation protection and the glutamatergic system in schizophrenic disorders.[2]
References
- ↑ "56488-60-9 CAS Manufactory". Chemicalbook.com. Retrieved 2012-04-21.
- 1 2 Bittner S et al (2005) γ-L-glutamyltaurine. Amino Acids, 28(4): 343-356