Gold monoiodide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Iodogold | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Gold(1+) iodide | |
| Other names
Gold monoiodide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 10294-31-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 74478 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.584 |
| PubChem | 82526 |
| UNII | T1UDV7ES1A |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| AuI | |
| Molar mass | 323.871 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellowish to greenish-yellow powder |
| Density | 8.25 g/cm3[1] |
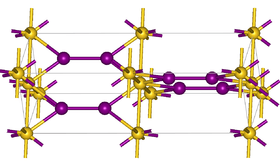
| Structure | |
| tetragonal, Pearson symbol tP8, Z = 4 | |
| P42/ncm (No. 138)[1] | |
| a = 0.435, b = 0.435, c = 1.373 nm | |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification (DSD) |
|
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26, S37/39 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Gold monoiodide (AuI) is a chemical compound of gold and iodine. This compound is commercially available. It can be synthesized by heating gold and iodine in a sealed tube at 120°C for about four months. It decomposes when treated with hot water.[2] But its related complexes are much more stable.[3]
References
- 1 2 Jagodzinski H. (1959). "Die Kristallstruktur des AuJ". Z. Kristallogr. 112: 80–87.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-08-037941-9.
- ↑ Tang, Zhongjia; Litvinchuk, A. P.; Lee, Hye-G.; Guloy, Arnold M. (1 September 1998). "Crystal Structure and Vibrational Spectra of a New Viologen Gold(I) Iodide". Inorganic Chemistry. 37 (19): 4752–4753. doi:10.1021/ic980141q.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/3/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.