Shire of Boonah
| Shire of Boonah Queensland | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Location within Queensland | |||||||||||||
| Population | 8,770 (2006 census)[1] | ||||||||||||
| • Density | 4.5639/km2 (11.820/sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Established | 1880 | ||||||||||||
| Area | 1,921.6 km2 (741.9 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Council seat | Boonah | ||||||||||||
| Region | South East Queensland | ||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| Website | Shire of Boonah | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
The Shire of Boonah was a local government area in South East Queensland, Australia, about 80 kilometres (50 mi) southwest of Brisbane. The shire covered an area of 1,921.6 square kilometres (741.9 sq mi), and existed from 1880 until its merger with parts of the Shire of Beaudesert and City of Ipswich to form the Scenic Rim Region on 15 March 2008.
The shire was part of the "Scenic Rim", a group of mountain ranges forming part of the Great Dividing Range, and contained four national parks—Main Range, Mount French, Moogerah Peaks and Mount Greville National Park which is now part of Moogerah Peaks National Park.
History
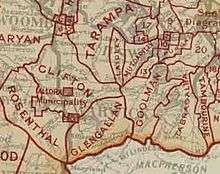
The Goolman Division was incorporated on 11 November 1879 under the Divisional Boards Act 1879 with a population of 1542.[2] It was centred on Boonah and its board consisting of six councillors. On 4 January 1884, there was an adjustment of boundaries between No. 2 subdivision of Mutdapilly Division and subdivision No. 2 of the Goolman Division.[3][4] Initially, the Goolman Division had its office in Flinders (27°46′59″S 152°42′59″E / 27.78306°S 152.71639°E). However, in 1887, the railway line from Ipswich was extended to Boonah, and the Goolman Division office moved to Boonah.[5]

On 25 October 1890, part of the northern section of Goolman Division became part of the new Normanby Division. With the passage of the Local Authorities Act 1902, Goolman Division became the Shire of Goolman on 31 March 1903. The Shire offices were in High Street, Boonah. The Goolman Shire War Memorial was unveiled in Boonah (then part of the Goolman Shire) on 19 May 1920 by General Birdwood and Councillor Alexander John Tait McKay. It is generally known as the Boonah War Memorial.[6] On 14 October 1937 was renamed Shire of Boonah,[7] which apparently means "bloodwood tree" in the local Aboriginal language.
Greater Ipswich Scheme of 1949
On 29 January 1949, a new Local Government Act was enacted to further amalgamate local government in the Ipswich area, abolishing the Shires of Normanby and Rosewood. The City of Ipswich was enlarged (from 12¼ square miles to 30 square miles) to include the more urban parts of the Shire of Moreton (formerly known as the Shire of Ipswich). The Shire of Moreton was then enlarged by the inclusion of the northern part of the Shire of Normanby and all the Shire of Rosewood. The southern part of the Shire of Normanby was transferred to an enlarged Shire of Boonah (a gain of 384 people and 109 km2 (42 sq mi)).[8][9][10][11]
The council for the enlarged Shire of Boonah was subdivided into three divisions, each electing three councillors.[12]
Amalgamations in 2000
In March 2000, Boonah added to its area part of the City of Ipswich, including Mount Walker, Warrill View and Rosevale, and the divisions were abolished, with a seven-member council representing the entire district.
Amalgamations of 2008
On 15 March 2008, under the Local Government (Reform Implementation) Act 2007 passed by the Parliament of Queensland on 10 August 2007, Boonah merged with the southern rural section of the Shire of Beaudesert and the Harrisville–Peak Crossing section of the City of Ipswich to form the Scenic Rim Region.
Towns and localities
The Shire of Boonah included the following settlements:
- Boonah
- Aratula
- Charlwood
- Coulson
- Fassifern
- Harrisville1
- Kalbar
- Maroon
- Moogerah
- Mount Alford
- Mount Walker
- Roadview
- Rosevale
- Silverdale
- Tarome
- Templin
- Warrill View
1 - split with the City of Ipswich
Population
| Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1879 | 1,542 |
| 1933 | 6,430 |
| 1947 | 5,855 # |
| 1954 | 5,929 |
| 1961 | 5,852 |
| 1966 | 5,471 |
| 1971 | 5,466 |
| 1976 | 5,378 |
| 1986 | 5,991 |
| 1991 | 6,541 |
| 1996 | 6,879 |
| 2001 | 8,207 |
| 2006 | 8,770 |
# The estimated 1947 population of the post-1949 area was 6,239.[13]
Chairmen and mayors

- 1880: Charles William Hunt
- 1915: William Ramsden Bowman (the great-grandson of John Macarthur)[14]
- 1927: W. Farley[15]
- 1943-1947 Harold Richter[16]
- 1959–1961: Oliver Walter Hooper (the grandson of one of the original landowners of the area that is now the city of Boonah. Many of the streets of Boonah are named after his aunts & uncles). Oliver was a member of the Boonah Shire Council for 15 yrs, becoming chairman (mayor) and dying during his second term.
- 1994–2008: John Brent
See also
References
- ↑ Australian Bureau of Statistics (25 October 2007). "Boonah (S) (Local Government Area)". 2006 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 18 March 2008.
- ↑ "Proclamation [Goolman Division constituted]". Queensland Government Gazette. 11 November 1879. p. 25:991.
- ↑ "Proclamation [Mutdapilly Division amended]". Queensland Government Gazette. 5 January 1884. p. 34:20.
- ↑ "Proclamation [Goolman Division amended]". Queensland Government Gazette. 5 January 1884. p. 34:21.
- ↑ "Boonah". Queensland Places. Centre for the Government of Queensland, University of Queensland. Retrieved 28 April 2014.
- ↑ "Boonah War Memorial". Monument Australia. Retrieved 4 April 2014.
- ↑ "Order in Council". Queensland Government Gazette. 14 October 1937. p. 149:1078.
- ↑ "Agency ID1425, Moreton Shire Council". Queensland State Archives. Retrieved 12 September 2013.
- ↑ "Local Government Acts 1936–1948 – Order in Council". Queensland Government Gazette. 29 January 1949. p. 1949:343.
- ↑ "GREATER IPSWICH AREA BY MAY.". Queensland Times. Ipswich, Queensland: National Library of Australia. 28 January 1949. p. 1 Edition: DAILY. Retrieved 13 September 2013.
- ↑ "BIGGER SHIRES OPERATE SOON.". The Courier-Mail. Brisbane: National Library of Australia. 15 January 1949. p. 4. Retrieved 13 September 2013.
- ↑ "Order in Council". Queensland Government Gazette. 29 January 1949. p. 172:343.
- ↑ Queensland Year Book, No.11 (1950), p.46.
- ↑ Fox, Matthew Joseph (1923). "Boonah". History of Queensland: its People and its industries (PDF). Brisbane: States Publishing Company. Retrieved 5 April 2014.
- ↑ Pugh, Theophilus Parsons (1927). Pugh's Almanac for 1927. Retrieved 13 June 2014.
- ↑ Richter, Sir Harold — Parliament of Queensland. Retrieved 21 April 2016.
External links
- "Boonah Shire". Queensland Places. Centre for the Government of Queensland, University of Queensland.
- Fox, Matthew Joseph (1923). "Boonah". History of Queensland: its People and its industries (PDF). Brisbane: States Publishing Company.
Further reading
- Nash, E. R. (1980). Serving the Shire – History of Local Government in Boonah Shire from 1879. Boonah Shire Council. ISBN 0-9593939-0-0. (70 pages)
- Pfeffer, Collin (1991). The Fassifern story : a history of Boonah Shire and surroundings to 1989. Boonah Shire Council. ISBN 0-9593939-1-9. (349 pages)
- Collyer, Angela (ed.) (1988). Centenary stories : a collection of articles concerning the history of the Boonah Shire. (171 pages – mostly photocopied newspaper articles)
Coordinates: 27°59′50.41″S 152°40′55.98″E / 27.9973361°S 152.6822167°E