HIST1H2AA
Histone H2A type 1-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HIST1H2AA gene.[3][4]
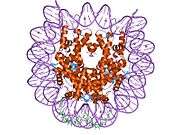
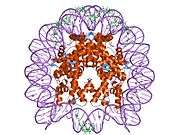
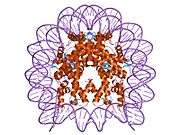
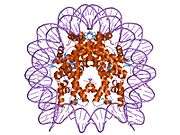
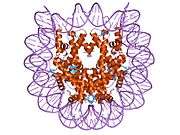
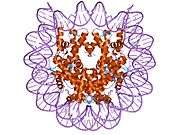
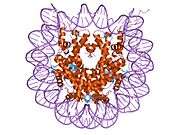
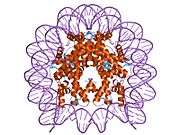
Histones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene is intronless and encodes a member of the histone H2A family. Transcripts from this gene contain a palindromic termination element.[4]
References
Further reading
- El Kharroubi A, Piras G, Zensen R, Martin MA (1998). "Transcriptional Activation of the Integrated Chromatin-Associated Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Promoter". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (5): 2535–44. doi:10.1128/mcb.18.5.2535. PMC 110633
 . PMID 9566873.
. PMID 9566873.
- Deng L, de la Fuente C, Fu P, et al. (2001). "Acetylation of HIV-1 Tat by CBP/P300 increases transcription of integrated HIV-1 genome and enhances binding to core histones". Virology. 277 (2): 278–95. doi:10.1006/viro.2000.0593. PMID 11080476.
- Deng L, Wang D, de la Fuente C, et al. (2001). "Enhancement of the p300 HAT activity by HIV-1 Tat on chromatin DNA". Virology. 289 (2): 312–26. doi:10.1006/viro.2001.1129. PMID 11689053.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241
 . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932.
- Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6". Nature. 425 (6960): 805–11. doi:10.1038/nature02055. PMID 14574404.
- Lusic M, Marcello A, Cereseto A, Giacca M (2004). "Regulation of HIV-1 gene expression by histone acetylation and factor recruitment at the LTR promoter". EMBO J. 22 (24): 6550–61. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg631. PMC 291826
 . PMID 14657027.
. PMID 14657027.
- Zhang Y, Griffin K, Mondal N, Parvin JD (2004). "Phosphorylation of histone H2A inhibits transcription on chromatin templates". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (21): 21866–72. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400099200. PMID 15010469.
- Aihara H, Nakagawa T, Yasui K, et al. (2004). "Nucleosomal histone kinase-1 phosphorylates H2A Thr 119 during mitosis in the early Drosophila embryo". Genes Dev. 18 (8): 877–88. doi:10.1101/gad.1184604. PMC 395847
 . PMID 15078818.
. PMID 15078818.
- Wang H, Wang L, Erdjument-Bromage H, et al. (2004). "Role of histone H2A ubiquitination in Polycomb silencing". Nature. 431 (7010): 873–8. doi:10.1038/nature02985. PMID 15386022.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928
 . PMID 15489334.
. PMID 15489334.
- Hagiwara T, Hidaka Y, Yamada M (2005). "Deimination of histone H2A and H4 at arginine 3 in HL-60 granulocytes". Biochemistry. 44 (15): 5827–34. doi:10.1021/bi047505c. PMID 15823041.
- Cao R, Tsukada Y, Zhang Y (2006). "Role of Bmi-1 and Ring1A in H2A ubiquitylation and Hox gene silencing". Mol. Cell. 20 (6): 845–54. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.12.002. PMID 16359901.
- Bergink S, Salomons FA, Hoogstraten D, et al. (2006). "DNA damage triggers nucleotide excision repair-dependent monoubiquitylation of histone H2A". Genes Dev. 20 (10): 1343–52. doi:10.1101/gad.373706. PMC 1472908
 . PMID 16702407.
. PMID 16702407.
PDB gallery |
|---|
|
| 1aoi: COMPLEX BETWEEN NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE (H3,H4,H2A,H2B) AND 146 BP LONG DNA FRAGMENT |
| 1eqz: X-RAY STRUCTURE OF THE NUCLEOSOME CORE PARTICLE AT 2.5 A RESOLUTION |
| 1hq3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HISTONE-CORE-OCTAMER IN KCL/PHOSPHATE |
| 1m18: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA |
| 1m19: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA |
| 1m1a: LIGAND BINDING ALTERS THE STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS OF NUCLEOSOMAL DNA |
| 1p34: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3a: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3b: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3f: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3g: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3i: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3k: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3l: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3m: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3o: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1p3p: Crystallographic Studies of Nucleosome Core Particles containing Histone 'Sin' Mutants |
| 1s32: Molecular Recognition of the Nucleosomal 'Supergroove' |
| 1tzy: Crystal Structure of the Core-Histone Octamer to 1.90 Angstrom Resolution |
| 1zbb: Structure of the 4_601_167 Tetranucleosome |
| 1zla: X-ray Structure of a Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus LANA peptide bound to the nucleosomal core |
| 2aro: Crystal Structure Of The Native Histone Octamer To 2.1 Angstrom Resolution, Crystalised In The Presence Of S-Nitrosoglutathione |
| 2cv5: Crystal structure of human nucleosome core particle |
| 2f8n: 2.9 Angstrom X-ray structure of hybrid macroH2A nucleosomes |
| 2fj7: Crystal structure of Nucleosome Core Particle Containing a Poly (dA.dT) Sequence Element |
| 2hio: HISTONE OCTAMER (CHICKEN), CHROMOSOMAL PROTEIN |
| 2nzd: Nucleosome core particle containing 145 bp of DNA |
|
|


 . PMID 9566873.
. PMID 9566873. . PMID 12477932.
. PMID 12477932. . PMID 14657027.
. PMID 14657027. . PMID 15078818.
. PMID 15078818. . PMID 15489334.
. PMID 15489334. . PMID 16702407.
. PMID 16702407.