HMS Pandora (N42)
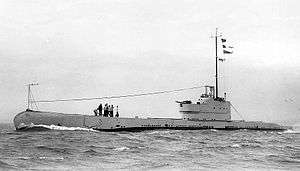 HMS Pandora | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | HMS Pandora |
| Namesake: | Pandora |
| Ordered: | 7 February 1928 |
| Builder: | Vickers-Armstrongs, Barrow in Furness |
| Laid down: | 9 July 1928 |
| Launched: | 22 August 1929 |
| Commissioned: | 30 June 1930 |
| Identification: | Pennant number: N42 |
| Fate: | Sunk by aircraft, 1 April 1942 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | Parthian-class submarine |
| Displacement: |
|
| Length: | 260 ft (79 m) |
| Beam: | 28 ft (8.5 m) |
| Draught: | 13 ft 8 in (4.17 m) |
| Propulsion: |
|
| Speed: |
|
| Range: | 8,500 nmi (15,700 km; 9,800 mi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Complement: | 59 |
| Armament: |
|
HMS Pandora was a British Parthian-class submarine commissioned in 1930 and lost in 1942 during the Second World War. This class was the first to be fitted with Mark VIII torpedoes. On 4 July 1940 she torpedoed and sank the French aviso Rigault de Genouilly off the Algerian coast. In an extension of the Lend-Lease program, Pandora, along with three other British and French submarines, was overhauled at Portsmouth Naval Shipyard in the United States.[1] She was sunk on 1 April 1942 by Italian aircraft at the Valletta dockyard, Malta.[2][3]
Design
The Parthian class was designed as an improvement of the earlier Odin class;[4] the new class was larger, built with a raked stem, and given a shield to cover the 4-inch gun.[3] The class had a design flaw in that the riveted external fuel tanks leaked, leaving an oil trail on the surface.[5]
All submarines of the Parthian class were fitted with eight 21-inch (533 mm) torpedo tubes, one QF 4-inch (102 mm) Mk XII deck gun, and two machine guns.[3][4] The class was the first to be outfitted with the Mark VIII torpedo.[6] Submarines of the Parthian class were designed for a complement of 53 officers and men.[4]
History
Pandora was ordered on 7 February 1928.[2] She was laid down on 9 July 1928 and built by Vickers-Armstrongs in the port of Barrow-in-Furness.[2][4] She was launched on 22 August 1929[4] before being commissioned on 30 June 1930.[2] Pandora was initially named Python; however, her name was changed in 1928 because of a distaste for serpent-named ships in the Royal Navy.[Note 1] The tenth ship to have this name, Pandora was named after the mythological first woman.[7]
In December 1930, Pandora cruised to China from Portsmouth. She arrived in Hong Kong in February 1931 and served in the China Station from 1931—1940.[7] In 1940, Pandora became part of the First Submarine Flotilla along with Parthian, Phoenix, Proteus, Grampus, Rorqual, Odin, Orpheus, Olympus, Otus, Otway, Osiris, and the depot ship Medway.[8]
Service in the Second World War
Pandora patrolled the Mediterranean from 1940 to 1942. She began her service in the Eastern Mediterranean in June 1940. In July, she was tasked with operations against the French Fleet near Oran off the coast of Algeria. On 4 July 1940, she sank the French ship, Rigault de Genouilly near Algiers. During August, Pandora delivered supplies to the blockaded island of Malta.[3][7]
The Italian torpedo boat Cosenz attacked Pandora with a depth charge in September, but Pandora survived the attack. In January 1941, she sank three vessels:[7] SS Palma south of Sardinia, SS Valdivagna, and one other ship near Cape Spartivento in Calabria.[3]
Sinking
Pandora arrived in Malta on 31 March 1942 to unload her stores. A bombing raid took place on 1 April 1942 while she was unloading, but the decision was made to continue the process to save time. Pandora took two direct bomb hits and was sunk. The survivors were on board the submarine Olympus when she was destroyed by a naval mine.[9] Of the 98 crew and passengers in Olympus, there were only 9 survivors.
Notes
References
- ↑ Watterson, Rodney (2011). 32 in '44: Building the Portsmouth Submarine Fleet in World War II. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. pp. 7–8. ISBN 978-1-59114-953-8. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 "HMS Pandora (N42) of the Royal Navy". uboat.net. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Parthian Class Early Patrol Submarines". BriTsuB. Retrieved 23 June 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Gardiner, Robert; Chesnau, Roger, eds. (1980). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships, 1922–1946. London: Conway Maritime Press. p. 48. Retrieved 2 August 2011.
- ↑ Brown, David K (2000). Nelson to Vanguard: Warship Design and Development, 1923–1945. London: Chatham Publishing. p. 109. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- ↑ Ward, John (2001). Submarines of World War II. St. Paul: Brown Partworks Limited. p. 35. ISBN 0-7603-1170-6. Retrieved 25 August 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Akermann, Paul (1 November 2002). Encyclopedia of British Submarines 1901–1955. Periscope Publishing. p. 299. ISBN 978-1-904381-05-1. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- ↑ McCartney, Innes (28 November 2006). British Submarines 1939–45. Osprey Publishing. p. 23. ISBN 978-1-84603-007-9. Retrieved 28 August 2012.
- ↑ Heden, Karl E. (15 October 2006). Sunken Ships, World War 2. Branden Books. pp. 235–. ISBN 978-0-8283-2118-1. Retrieved 22 August 2012.