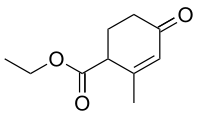
Hagemann's ester
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ethyl 2-methyl-4-oxocyclohex-2-enecarboxylate | |
| Other names
4-Carbethoxy-3-methyl-2-cyclohexen-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
| 487-51-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 71353 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.962 |
| PubChem | 79020 |
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C10H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 182.22 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.078 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 268 to 272 °C (514 to 522 °F; 541 to 545 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Hagemann's ester, or ethyl-2-methyl-4-oxo-2-cyclohexenecarboxylate, is an organic compound that was first prepared and described in 1893 by German chemist Carl Hagemann. The compound is used in organic chemistry as a reagent in the synthesis of many important natural products including sterols, trisporic acids, and terpenoids.
Preparation
Hagemann's approach
Methylene iodide and two equivalents of acetoacetic ester react in the presence of sodium methoxide to form the diethyl ester of 2,4-diacetyl pentane. This precursor is treated with base to induce cyclization. Finally, heat is applied to generate Hagemann's ester.
Knovenagel's approach
Soon after Hagemann, Knovenagel presented the following modified procedure. Formaldehyde and two equivalents of acetoacetic ester undergo condensation in the presence of catalytic piperidine to produce the diethyl ester of 2,4-diacetyl pentane. This precursor is treated with base to induce cyclization. Finally, heat is applied to generate Hagemann's ester.
Newman and Lloyd approach
2-Methoxy-1,3-butadiene and ethyl-2-butynoate undergo a Diels Alder reaction to generate a precursor. The precursor is hydrolyzed to obtain Hagemann's ester. By varying the substituents on the butynoate starting material, this approach allows for different C2 alkylated Hagemann's ester derivatives to be synthesized.
Mannich and Forneau approach
Original
Methyl vinyl ketone, acetoacetic ester, and diethyl-methyl-(3-oxo-butyl)-ammonium iodide react to form a cyclic aldol product. Sodium methoxide is added to generate Hagemann's ester.
Variations
Methyl vinyl ketone and acetoacetic ester undergo aldol cyclization in the presence of catalytic pyrrolidinum acetate or Triton B or sodium ethoxide to produce Hagemann's ester.
References
- Pollini, Gian Piero; Benetti, Simonetta; De Risi, Carmela; Zanirato, Vinicio (2010). "Hagemann's ester: a timeless building block for natural product synthesis". Tetrahedron. 66: 2775. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2010.01.078.
- White, James D.; Sung, Wing Lam (1974). "Alkylation of Hagemann's ester. Preparation of an intermediate for trisporic acid synthesis". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 39: 2323. doi:10.1021/jo00930a001.
- John A. Hogg (1948). "Synthetic Sterols. I. Model Experiments Employing Hagemann's Ester". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 70 (1): 161–164. doi:10.1021/ja01181a047. PMID 18918810.