Half-harmonic generation
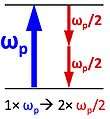
Half-harmonic generation (also called wavelength doubling or frequency halving) is a nonlinear optical process in which photons "split" to generate pairs of new photons with half the energy, therefore half the frequency and twice the wavelength of the initial photons. The half-harmonic generation process is the inverse of second-harmonic generation and can occur in optical parametric oscillators at degeneracy, and is a phase and frequency locked down-conversion process.
In the continuous wave regime, stable half-harmonic generation in an optical parametric oscillator was experimentally demonstrated in 1990,[1] and in the femtosecond regime, it was experimentally demonstrated in 2012.[2] Half-harmonic generation is used as a phase and frequency locked down conversion process for generation of mid-infrared frequency combs using near-infrared frequency combs, and a conversion efficiency of ~64% is experimentally demonstrated.[3]
References
- ↑ Nabors, C. D.; Yang, S. T.; Day, T.; Byer, R. L. (1990-05-01). "Coherence properties of a doubly resonant monolithic optical parametric oscillator". Journal of the Optical Society of America B. 7 (5). doi:10.1364/josab.7.000815. ISSN 1520-8540.
- ↑ Marandi, Alireza; Leindecker, Nick C.; Pervak, Vladimir; Byer, Robert L.; Vodopyanov, Konstantin L. (2012-03-26). "Coherence properties of a broadband femtosecond mid-IR optical parametric oscillator operating at degeneracy". Optics Express. 20 (7). doi:10.1364/oe.20.007255. ISSN 1094-4087.
- ↑ Marandi, Alireza; Ingold, Kirk A.; Jankowski, Marc; Byer, Robert L. (2016-03-20). "Cascaded half-harmonic generation of femtosecond frequency combs in the mid-infrared". Optica. 3 (3). doi:10.1364/optica.3.000324. ISSN 2334-2536.