Illinois State Police
| Illinois State Police | |
|---|---|
| Abbreviation | ISP |
|
Illinois State Police patch | |
|
Seal of the Illinois State Police | |
| Motto | Integrity, Service, Pride |
| Agency overview | |
| Formed | April 1, 1922 |
| Employees | 3,556 (as of 2004)[1] |
| Legal personality | Governmental: Government agency |
| Jurisdictional structure | |
| Operations jurisdiction* | State of Illinois, USA |
| Size | 57,918 sq mi (140,998 km²) |
| Population | 12,859,995 (2015 est.) |
| Legal jurisdiction |
|
| Governing body | Governor of Illinois |
| General nature | |
| Operational structure | |
| Overviewed by | Illinois State Police Merit Board |
| Headquarters |
801 South Seventh Street Springfield, Illinois |
| Troopers | 1,781 (as of Dec 2013) [1] |
| Civilians | 1,548 (as of 2004) [1] |
| Agency executive | Leo P. Schmitz, Director |
| Facilities | |
| Districts |
21
|
| Website | |
| www.isp.state.il.us | |
| Footnotes | |
| * Divisional agency: Division of the country, over which the agency has usual operational jurisdiction. | |
The Illinois State Police (ISP) is the state police force of Illinois. Officially established in 1922, the Illinois State Police have over 3,000 personnel[2] and 21 districts.[3] The main facilities of the Illinois State Police Academy, which were constructed in 1968, are located in Springfield. Prior to 1968, training was conducted at the Illinois State Fairgrounds.[4] ISP also maintains the Illinois sex offender registry,[5] administers the state's AMBER Alert program,[6] and issues Illinois Firearm Owner Identification Cards (FOID) and Concealed Carry Licenses.[7] The Illinois State Police is also responsible for driving and physically protecting the Governor of Illinois. In 2005, officers and duties of the Illinois Department of Central Management Services Police were merged into the Illinois State Police.
Organization
| Demographics comparison | ||
| ISP[8] | Illinois[9] | |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 91% | 49.0% |
| Female | 9% | 51.0% |
| White | 80% | 73.5% |
| African-American or Black | 13% | 15.1% |
| Hispanic | 6% | 12.3% |
| Asian | 1% | 3.4% |
As of 2006, the Illinois State Police is organized into several divisions:
- Governor of Illinois
- Director, State Police
- First Deputy Director
- Operations Division: performs all of the functions of highway safety and criminal investigation; traffic enforcement is one of the more visible aspects of the operations department.
- Regional Commands I - IV
- Operational Services Command
- Statewide Evidence Vault
- Special Operations Command
- Riverboat Gaming Command
- Intelligence Command
- Communication Services Bureau
- Forensic Services Division: provides the state with specialty crime scene services including DNA and fingerprint identification as well as computerized ballistics matching.
- Forensic Sciences Command
- Crime Scene Services Command
- Administration Division: includes facility administration, communication services and logistics functions that are vital to ISP.
- Support Services
- Administrative Services Bureau
- Bureau of Identification
- Logistics Bureau
- State Police Academy
- Technology Services
- Program Administration Bureau
- Information Services Bureau
- Firearms Services Bureau
- Support Services
- Internal Investigations Division: performs a similar function as other internal affairs divisions as well as investigation of wrongdoing in other agencies in the Illinois executive branch.[10]
- Northern Command
- Southern Command
- Administrative Services Command
- Identified Offender Program
- Operations Division: performs all of the functions of highway safety and criminal investigation; traffic enforcement is one of the more visible aspects of the operations department.
- First Deputy Director
- Director, State Police
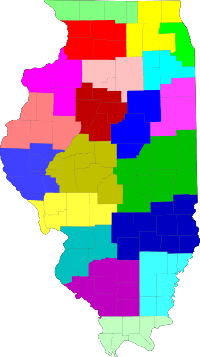
Illinois State Police districts
Traffic enforcement
Illinois State Police currently use various methods for speed limit enforcement on Illinois highways. Hand-held and moving RADAR, LIDAR, pacing, air speed utilizing the ISP fleet of aircraft, and time-distance measurement.[11] The IL State Police uses typical marked units (Crown Victorias, Impalas, and Chargers, Ford Police Interceptor) as well as unmarked units of vehicles ranging from Crown Victorias to Grand Prix GTPs to LS-1 powered Z28s to Mustang GTs. The Mustangs, Camaros, and other vehicles are for a program created to combat aggressive driving and speeding. Lightbars used on marked units are Code 3 X2100 LED units, Federal Signal Legend units and Code 3 MX7000 halogen/strobe units. Prior to that, it was a mixture of the Code 3 MX7000s and Federal Signal JetSonics and Federal Signal Vistas.
Currently, the Illinois State Police uses MPH Industries radar and Kustom Signals LIDAR.
Since 1986, the Illinois State Police has patrolled Chicago Expressways (Districts 3 and 4 which merged to become District Chicago). Illinois also announced in February 2006, that photo radar mounted in vans would be used for speed enforcement in construction zones statewide. Recently, the program has been expanded for speed enforcement throughout the state. Though the vans are manned by State Police troopers, a private company, ACS State and Local Solutions, provides the vans for a fee and receives a bonus of $15 per ticket issued.[12]
A Motorcycle Enforcement Bureau (MEB) was created in 2006 consisting of 41 officers in six squads dispersed throughout the state.[13] 50 Harley-Davidson FLHTPI Electra Glide's were leased for this use by the MEB.[14] Due to cost-cutting measures in mid 2010, the Motorcycle Enforcement Bureau was disbanded, however some motorcycle officers remain in the larger Districts such as Chicago and East St. Louis.
As of late 2007, all ISP districts have moved their radio operations to the new STARCOM 21 (700/800Mhz Motorola Project 25) trunked radio system.[15]
Illinois State Police Merit Board
The Illinois State Police Merit Board administers the certification of the appointment and promotion of state police officers as well as their discipline, removal, demotion and suspension. The merit board consists of five civilian members who are appointed by the governor with the advice and consent of the state senate. Each member serves for a term of six years and no more than three members may be affiliated with the same political party.[16]
List of ISP Superintendents and Directors
Superintendents
- John T. Stack (1922–1929)
- Walter L. Moody (1929–1933)
- Lawrence M. Taylor (1933–1935)†
- Walter Williams (1935–1941)
- Jesse H. Grissom (1941)
- T.P. Sullivan (1941)
- Leo M. Carr (1941–1942)
- Harry Yde (1942–1945)
- Harry I. Curtis (1945–1950)
- Thomas J. O'Donnell (1950–1953)
- Philip M. Brown (1953–1956)
- William H. Morris (1956–1968)
- Albert S. Hinds (1968–1969)
- James T. McGuire (1969–1971)
- Dwight E. Pitman (1971–1977)
- Lynn E. Baird (1977–1979)
- Ronald J. Miller (1979–1983)
- Laimutis A. Nargelenas (1983–1987)
Directors
- Jeremy D. Margolis (1987–1991)
- Terrance W. Gainer (1991–1998)
- Sam W. Nolen (1998–2003)
- Larry G. Trent (2003–2009)
- Jonathon E. Monken (2009–2011)†
- Hiram Grau (2011–2015)
- Leo P. Schmitz (2015– )
Fallen officers
Since the establishment of the Illinois State Police, 61 troopers [17] have been killed in the line of duty, with a partial list that follows.
| Officer | Death date | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Albert J. Hasson | |
Struck by vehicle |
| Lory Lee Price | |
Gunfire |
| Paul E. Clendening | |
Automobile accident |
| George E. Wheeler | |
Motorcycle accidental |
| Robert L. Fisher | |
Motorcycle accident |
| Robert Jefferson McDonald | |
Vehicle pursuit |
| Frank M. Schwartz | |
Motorcycle accident |
| Kenneth L. Church | |
Motorcycle accident |
| James Grady Sutton | |
Gunfire |
| Richard Groja | |
Motorcycle accident |
| John L. McCabe | |
Motorcycle accident |
| Joseph Merritt Elliott | |
Automobile accident |
| Leo J. LaVelle | |
Motorcycle accident |
| Ray Embree | |
Automobile accident |
| Bernard D. Skeeters | |
Automobile accident |
| John H. Kugelman | |
Vehicular assault |
| Chong S. Lim | |
Vehicular assault |
| Stanley W. Talbot | |
Vehicular assault |
| Kyle W. Deatherage | |
Struck by vehicle |
| James M. Sauter | |
Automobile accident |
Uniform
The uniform of the Illinois State Police has certain qualities that separate it from its neighbors. Instead of a chocolate brown uniform (similar to the Iowa State Patrol), or a light blue on dark blue (similar to the Missouri State Highway Patrol), they wear light tan/khaki shirts, and dark green pants with black trim. Dress uniforms include a jacket that matches the pants. The cold weather gear incorporates a chocolate brown all weather jacket. Leather duty gear consists of black high gloss clarino holsters, belts and accessories. The hat that is worn by the state police is a dark brown campaign hat. The badge, instead of the traditional shield surmounted by an eagle design, is a six-pointed star that reads the rank of the trooper, and the words "Illinois State Police" in black, along with (beginning in 2002) the officer's badge number. (The badge's sequential inventory number is found stamped on the reverse side of the badge.) The badges are silver, or chrome plated steel for all ranks below Sergeant, and for Sergeant and above, the star is gold plated. Over recent time there have been uniform variations such as brown wooly-pully style sweaters for cold weather, brown leather bomber style jackets, variations for truck enforcement officers, etc.
Rank Insignia
| Rank | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Director | |
| First Deputy Director | |
| Colonel | |
| Lieutenant Colonel | |
| Major | |
| Captain | |
| Lieutenant | |
| Master Sergeant | |
| Sergeant | |
| Master Trooper | |
| Trooper First Class | |
| Trooper |
ISP awards, commendations, citations and medals
- Medal for Valor
- Medal of Honor
- Achievement Medal
- Purple Heart
- Lifesaving Medal
- Meritorious Service Medal
- Officer of the Year
- Department Special Award
- Department Commendation
- Department Unit Citation
- Problem Solving Ribbon
- Department Service Ribbon
- Certificate of Recognition[18]
Duty weapons
The Illinois State Police was the first major law enforcement agency to carry a semi-automatic pistol, starting in 1968 with the Smith & Wesson Model 39, which it carried until 1981, transitioning then to the 2nd generation Smith & Wesson Model 439. The Model 439 was in service until 1988 when the ISP transitioned to the Smith & Wesson Model 459 for uniform use and the Smith & Wesson Model 469 for investigations and senior command officers. In 1993 ISP went to the 3rd generation Smith & Wesson Model 5904 for uniform use and the Smith & Wesson Model 6904 for investigations and senior command officers. During the ISP's long tenure with the 9mm cartridge, a special high velocity load designated "The Illinois State Police Load" was created at the request of the ISP. The load was a 115 grain round at +P+ velocities. The round earned a great reputation as a "street stopper" in the 9mm cartridge and was adopted by many agencies. The ISP carried this load until the transition to the .40 S&W round in 1999. In 1999 ISP transitioned to the .40 S&W caliber with the Glock 22 for uniform use and the Glock 23 for investigations and senior command officers. For patrol carbines, troopers are issued ArmaLite AR-15 rifles. Remington 870 12-gauge shotguns are issued as well. Less lethal options issued to troopers include OC pepper spray, Tasers and the expandable straight baton.
Aircraft
The Illinois State Police have six aircraft used for law enforcement throughout the state, one Cessna 421C and five Cessna 182. These aircraft are stationed at four airports, Abraham Lincoln Capital Airport, DuPage Airport, MidAmerica St. Louis Airport and Whiteside County Airport.[19] ISP has used aircraft for speed enforcement, using stop watch time measurement, since 1959.[11] According to the FAA, aircraft registered to ISP include, a Cessna 182R N291SP[20], a Cessna 182S N551SP[21], a Cessna 182S N661SP[22], a Cessna 182S N771SP[23], a Cessna 182S N881SP[24], a Cessna 421C N4131Q[25] and a 1953 Bell H13G N33615[26].
See also
Bibliography
- Clark, Harry F. (1972), Illinois State Police: A Division of the Department of Law Enforcement, 1922-1972, Springfield, Ill.: State Police Benevolent Group, ISBN 978-1-934729-22-9, OCLC 417833
- Illinois State Police (1997), Illinois State Police 75th, 1922-1997, Springfield, Ill.: Illinois State Police, ISBN 978-1-890105-00-6, OCLC 38965840
References
- 1 2 3 USDOJ Statistics Archived November 20, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Illinois State Police. History. Accessed June 3, 2006.
- ↑ Illinois State Police. Districts. Accessed June 3, 2006.
- ↑ Illinois State Police. Facilities. Accessed June 3, 2006.
- ↑ "Illinois Sex Offender Registration Information Website". Illinois State Police. Retrieved 14 June 2011.
The Illinois State Police provides an online listing of sex offenders required to register in the State of Illinois.
- ↑ "AMBER Alert Notification Plan". Illinois State Police. Retrieved 14 June 2011.
- ↑ http://www.isp.state.il.us/foid/foidinfo.cfm
- ↑ Law Enforcement Management and Administrative Statistics, 2000: Data for Individual State and Local Agencies with 100 or More Officers Archived September 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ 2000 US Census factfinder - Illinois Archived May 21, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Departmental organization. Accessed June 7, 2006.
- 1 2 Illinois State Police. Speed Limit Enforcement. Accessed June 3, 2006.
- ↑ Illinois Department of Transportation. IDOT, ISP & Tollway Unveil Photo Speed Enforcement Van At Chicago Auto Show. February 9, 2006. Accessed June 3, 2006.
- ↑ ISP. 2006 Annual Report.
- ↑ purchase.state.il.us 50 1 year leases for $1,920 each starting 05/01/06.
- ↑ http://www.radioreference.com/apps/db/?sid-2324
- ↑ Illinois Compiled Statutes 20 ILCS 2610/
- ↑ Illinois State Police Fallen Officers. Accessed June 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Annual Report" (PDF). Illinois State Police. 2014. Retrieved 12 August 2016.
- ↑ Illinois State Police. Air Operations. Accessed June 3, 2006.
- ↑ "FAA Registry". Federal Aviation Administration.
- ↑ "FAA Registry". Federal Aviation Administration.
- ↑ "FAA Registry". Federal Aviation Administration.
- ↑ "FAA Registry". Federal Aviation Administration.
- ↑ "FAA Registry". Federal Aviation Administration.
- ↑ "FAA Registry". Federal Aviation Administration.
- ↑ "FAA Registry". Federal Aviation Administration.
External links
- Illinois State Police
- Title 20, Chapter II: Department of State Police in the Illinois Administrative Code

