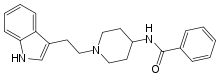
Indoramin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | C02CA02 (WHO) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
26844-12-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 33625 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 501 |
| DrugBank |
DB08950 |
| ChemSpider |
31014 |
| UNII |
0Z802HMY7H |
| KEGG |
D04531 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL279516 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.043.659 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H25N3O |
| Molar mass | 347.454 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Indoramin (trade names Baratol and Doralese) is a piperidine antiadrenergic agent.
It is an alpha-1 selective adrenoceptor antagonist[1] with direct myocardial depression action; therefore, it results in no reflex tachycardia. It is also used in benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).[2]
It is commonly synthesized from tryptophol.[3]
Dosage
Indoramin is commonly prescribed as 20 mg tablets when used in BPH.[4]
Side Effects
Drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth, nasal congestion, headache, fatigue, weight gain, hypotension, postural hypotension, depression, problems with ejaculation, diarrhoea, nausea, increased need to pass urine, and palpitations.[5]
Synthesis
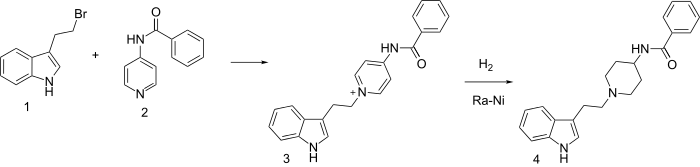
Tryptamine and serotonin are naturally occurring indole ethylamino compounds with pronounced pharmacological activities. They have served as the inspiration for synthesis of numerous analogues.
One such study involved alkylation of 4-benzamidopyridine (2) with 3-(2-Bromoethyl)-1H-indole (1) to give quaternary salt (3); this intermediate was in turn hydrogenated with a Raney nickel catalyst to give indoramine (4).
References
- ↑ Pierce V, Shepperson NB, Todd MH, Waterfall JF (February 1986). "Investigation into the cardioregulatory properties of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor blocker indoramin". Br. J. Pharmacol. 87 (2): 433–441. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10834.x. PMC 1916533
 . PMID 3955309.
. PMID 3955309. - ↑ "Indoramin 20mg tablets". Medicines.org.uk. April 20, 2011. Retrieved September 30, 2012.
- ↑ Ullman's encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Sixth Edition, 2002.
- ↑ "Indoramin hydrochloride". National Health Service (UK). Retrieved September 30, 2012.
- ↑ "Indoramin 20mg tablets". Medicines.org.uk. Retrieved September 30, 2012.
- ↑ J. L. Archibald, J. L. Jackson, ZA 6803204; eidem, U.S. Patent 3,527,761 (1969, 1970 both to Wyeth).
- ↑ Archibald, J. L.; Alps, B. J.; Cavalla, J. F.; Jackson, J. L. (1971). "Synthesis and hypotensive activity of benzamidopiperidylethylindoles". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 14 (11): 1054. doi:10.1021/jm00293a009. PMID 5115203.