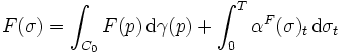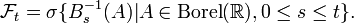Integral representation theorem for classical Wiener space
In mathematics, the integral representation theorem for classical Wiener space is a result in the fields of measure theory and stochastic analysis. Essentially, it shows how to decompose a function on classical Wiener space into the sum of its expected value and an Itō integral.
Statement of the theorem
Let ![C_{0} ([0, T]; \mathbb{R})](../I/m/5f9dc9eb9133c3e310f60c3474696add.png) (or simply
(or simply 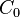 for short) be classical Wiener space with classical Wiener measure
for short) be classical Wiener space with classical Wiener measure 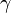 . If
. If 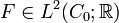 , then there exists a unique Itō integrable process
, then there exists a unique Itō integrable process ![\alpha^{F} : [0, T] \times C_{0} \to \mathbb{R}](../I/m/cc55ab4ef6e30ac3ad31a628d42f1470.png) (i.e. in
(i.e. in 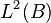 , where
, where 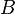 is canonical Brownian motion) such that
is canonical Brownian motion) such that
for 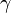 -almost all
-almost all 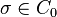 .
.
In the above,
-
![\int_{C_{0}} F(p) \, \mathrm{d} \gamma (p) = \mathbb{E} [F]](../I/m/3b73979a49f76c075e6a17d13f1a4c3d.png) is the expected value of
is the expected value of 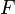 ; and
; and - the integral
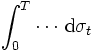 is an Itō integral.
is an Itō integral.
The proof of the integral representation theorem requires the Clark-Ocone theorem from the Malliavin calculus.
Corollary: integral representation for an arbitrary probability space
Let 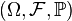 be a probability space. Let
be a probability space. Let ![B : [0, T] \times \Omega \to \mathbb{R}](../I/m/ab44a594d4f01873e2bfbcad7ea10e5c.png) be a Brownian motion (i.e. a stochastic process whose law is Wiener measure). Let
be a Brownian motion (i.e. a stochastic process whose law is Wiener measure). Let 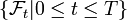 be the natural filtration of
be the natural filtration of 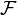 by the Brownian motion
by the Brownian motion 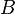 :
:
Suppose that 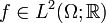 is
is 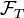 -measurable. Then there is a unique Itō integrable process
-measurable. Then there is a unique Itō integrable process 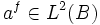 such that
such that
![f = \mathbb{E}[f] + \int_{0}^{T} a_{t}^{f} \, \mathrm{d} B_{t}](../I/m/60ff828143383f6bc6521fc2fb5c0a65.png)
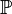 -almost surely.
-almost surely.
References
- Mao Xuerong. Stochastic differential equations and their applications. Chichester: Horwood. (1997)