Isobutylidenediurea
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Isodur; Diureidoisobutane; Isobutylenediurea; Isobutylidene biurea; 1,1-Diureidisobutane; Isobutylidendiharnstoff;1,1'-Isobutylidenedi-urea; 1,1'-Isobutylidenebisurea; N,N-(isobutylidene)diurea; N,N-(Isobutylidene)bisurea | |
| Identifiers | |
| 6104-30-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 21083 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.025.505 |
| EC Number | 228-055-8 |
| MeSH | C014058 |
| PubChem | 22478 |
| UNII | 20K1225668 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 174.20 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Low | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
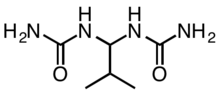
Isobutylidenediurea (abbreviated IBDU) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2CHCH{NHC(O)NH2}2. It is a derivative of urea (OC(NH2)2), which itself is highly soluble in water, but IBDU is not. It functions as a controlled-release fertiliser owing to its low solubility, which limits the rate of its hydrolysis to urea, which is a fast-acting fertiliser.[1]
It is produced by the condensation reaction of isobutyraldehyde and two equivalents of urea:
- (CH3)2CHCHO + 2 OC(NH2)2 → (CH3)2CHCH{NHC(O)NH2}2 + H2O
The controlled-release process is the reverse of the above reaction, which only occurs after the IBDU dissolves.
References
- ↑ C. Nitschke, G. Scherr (2005), "Urea Derivatives", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.o27_o04
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.